Anu Malhotra, Suchitra Manjhu, Harish Kumar Meena, Karishma Jain, Sonia Srivastava, Anju Lavania, S.K. Jain, Rama S Lokhande, Balram Tripathi
1 Department of Chemistry, Jaipur National University, Jaipur-302018, India
2 Department of Physics, S S Jain Subodh PG College, Jaipur- 302004, India
3 Department of Physics, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004, India
4 Department of Physics, Manipal University Jaipur, Jaipur-302017, India
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
balramtripathi1181@gmail.com (Balram Tripathi)
ABSTRACT
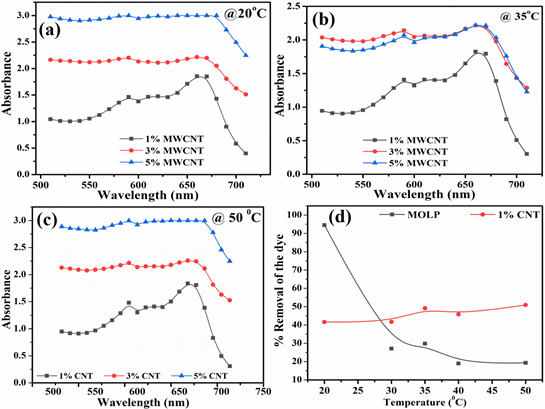
This study investigates the adsorption potential of methylene blue (MB) dye using a novel bio-composite prepared by intercalating carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with Moringa oleifera leaf powder (MOLP). Adsorption capacity optimization was performed under varying experimental conditions, including pH (4–9), initial MB concentration (0.05–1 ppm), adsorbent dosage, temperature (20–50°C), and contact time (0–60 minutes). The biosorbent’s surface properties and functional groups were characterized through Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, revealing the synergistic role of CNT intercalation in enhancing adsorption efficiency. SEM analysis confirmed a heterogeneous, porous morphology of MOLP, ideal for dye entrapment. FT-IR spectra indicated the presence of carboxylic, carbonyl, and phenolic groups, which significantly contributed to the binding of MB dye molecules through hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. The results demonstrate that functionalized MOLP exhibits superior adsorption performance compared to pristine MOLP, owing to the remarkable surface area and tunable chemistry of CNTs. This study highlights the potential of CNT-MOLP as a cost-effective, sustainable adsorbent for wastewater treatment, offering an efficient alternative to conventional methods for dye removal.
Significance of the Study:
This study underscores the efficacy of CNT-intercalated Moringa oleifera leaf powder (MOLP) as a sustainable and cost-effective adsorbent for wastewater treatment. By demonstrating superior adsorption of methylene blue dye, it provides an eco-friendly alternative to conventional adsorbents like activated carbon. The synergistic role of CNTs in enhancing surface properties and functional group interactions positions this bio-composite as a viable solution for addressing dye pollution, particularly in resource-limited settings, contributing significantly to environmental sustainability.
Summary of the Study:
The study evaluates the adsorption capacity of methylene blue (MB) dye using a bio-composite of CNT-functionalized Moringa oleifera leaf powder (MOLP). Systematic optimization of adsorption parameters, including pH, dye concentration, temperature, and contact time, revealed the superior efficiency of CNT-MOLP compared to pristine MOLP. Characterization via SEM and FT-IR confirmed enhanced porosity and functional groups essential for dye binding. This work establishes CNT-MOLP as a sustainable, cost-effective adsorbent for industrial wastewater treatment applications.
