Manmeet Kour, Rajeev Kumar, Savita Chaudhary
1Department of Chemistry, Panjab University, Chandigarh 160014, India.
2Department of Environmental Studies, Panjab University, Chandigarh 160014, India.
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
schaudhary@pu.ac.in (S. Chaudhary)
ABSTRACT
The depletion of fossil fuel resources and their associated effects, such as greenhouse gas emissions, global warming, and environmental pollution, have prompted researchers to explore the bioeconomy in innovative ways. The concepts of sustainability and the circular economy have shifted the focus of research from mere development to development that also prioritizes environmental protection, known as sustainable development. Conventional plastics, derived from petroleum, can take hundreds of years to degrade naturally, thus harming the local environment. Bioplastics, which are biopolymers sourced from biological materials, offer the advantage of biodegradability in natural environments and are considered a virtuous replacement for conventional plastics. Starch, an abundant and low-cost biopolymer, is a promising material for bioplastics. However, starch-based bioplastics often fall short in practical applications due to limited mechanical and barrier properties. Effective solutions include copolymerization, the addition of fillers, plasticization, and chemical modification. This review focuses on starch-based bioplastics, enhanced with cellulose, polylactic acid, and polyhydroxyalkanoates, and their applications in food packaging, medical, and electronic sectors.
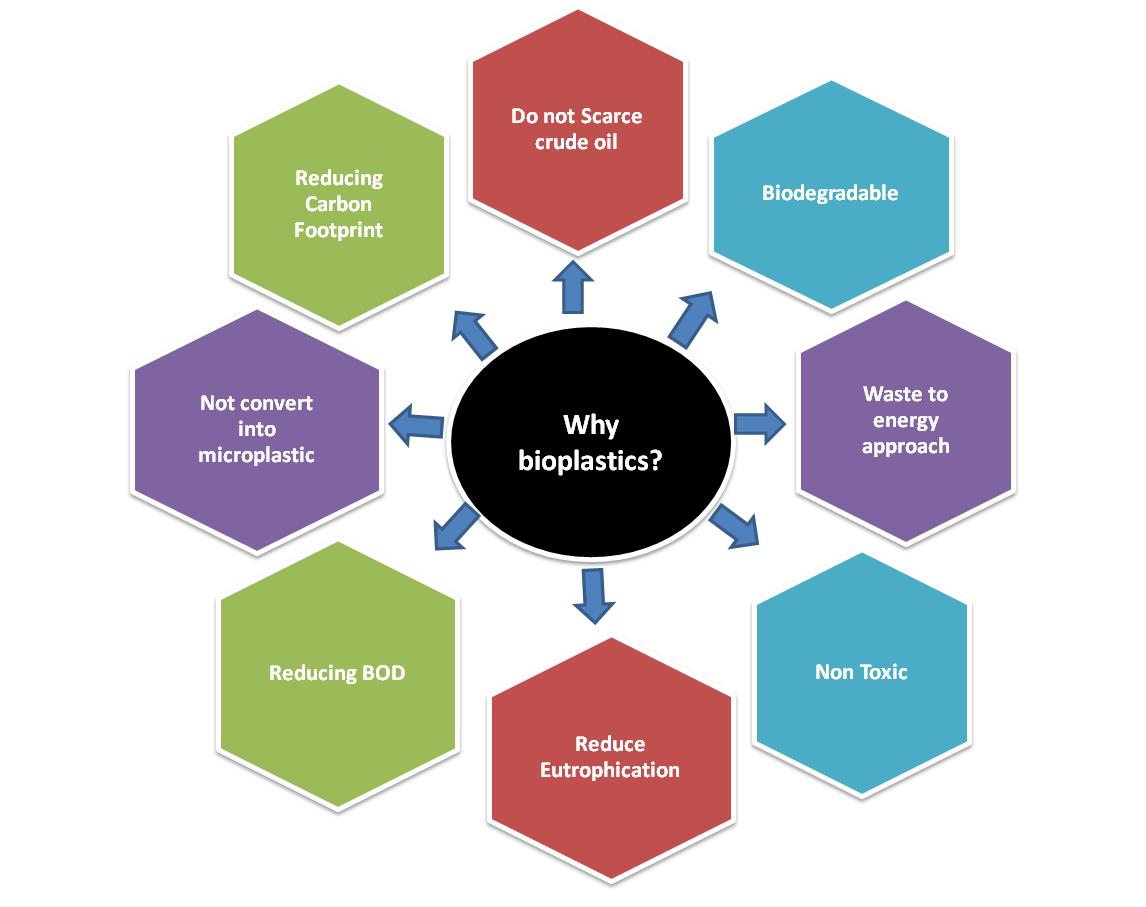
Significance of the study:
This study emphasizes starch-based bioplastics as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. By overcoming the limitations of starch bioplastics through copolymerization, plasticization, and fillers, the research highlights their improved mechanical and barrier properties. Focusing on applications in food packaging, medical, and electronics, it underscores their practical relevance, promoting sustainability and advancing the circular economy.
Summary of the study:
This review examines the progress in starch-based bioplastics, highlighting their biodegradability and potential to replace traditional plastics. It discusses enhancement techniques like copolymerization, plasticization, and blending with cellulose, PLA, and PHA to improve mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and barrier properties. The paper also explores their applications in food packaging, medical, and electronics, demonstrating their versatility and environmental benefits.
