S. Stephen Rajkumar Inbanathan, Poornima Jeyasekaran, S. Irfana Parveen, S. Shri Tharani Priya, K. Sneka
Post Graduate and Research Department of Physics, The American College, Madurai, 625002 Tamil Nadu, India
*Authors to whom correspondence should be addressed: ssrinbanathan@gmail.com (S. Stephen Rajkumar Inbanathan)
ABSTRACT
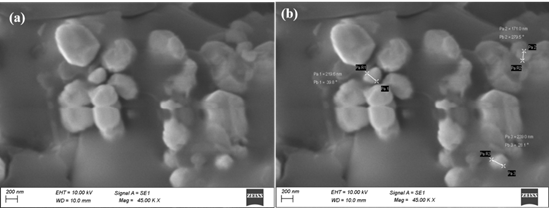
This study investigates the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Cardiospermum halicacabum leaf extract, which acts as both a reducing and stabilizing agent. The biosynthesis approach is eco-friendly and leverages the phytochemical constituents of Cardiospermum halicacabum. Characterization of the synthesized AgNPs was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), confirming the formation of nanoparticles with desired properties. SEM analysis revealed the morphology and size distribution of the AgNPs, while XRD provided insights into their crystalline nature, and FTIR identified functional groups involved in the reduction and stabilization processes. Despite the successful synthesis of AgNPs, antimicrobial assays indicated that these nanoparticles did not exhibit significant antibacterial activity against tested microorganisms such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The results suggest that the synthesized AgNPs require further optimization to enhance their antimicrobial efficacy. This study underscores the potential of Cardiospermum halicacabum in green nanoparticle synthesis and highlights the need for continued research to understand the factors influencing the antimicrobial properties of biosynthesized AgNPs, aiming to improve their effectiveness for clinical and industrial applications.
Significance of the study:
This study highlights the eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cardiospermum halicacabum leaf extract, demonstrating the potential of phytochemicals in nanoparticle production. The research emphasizes the importance of optimizing these biosynthesized nanoparticles for enhanced antimicrobial efficacy, paving the way for their application in clinical and industrial settings.
Summary of the study:
The study investigates silver nanoparticles synthesized using Cardiospermum halicacabum leaf extract. Characterization techniques confirmed the successful formation of nanoparticles. Initial antimicrobial tests against E. coli and S. aureus showed limited efficacy, suggesting the need for optimization. The research underscores the potential of these green-synthesized nanoparticles in various applications.
