Ravi Kumar, Naveen Thakur, Saurabh Sharma, Kuldeep Kumar
1Department of Chemistry, Career Point University, Hamirpur-176041, Himachal Preadesh, India
2Department of Physics, Career Point University, Hamirpur-176041, Himachal Pradesh, India
3Centre for Nano-Science and Technology, Career Point University, Hamirpur-176041, Himachal Pradesh, India
4Thakur PG College of Education, Dhaliara, Kangra-177103, Himachal Pradesh, India
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
kuldeep.sharma.753@gmail.com (Kuldeep Kumar)
ABSTRACT
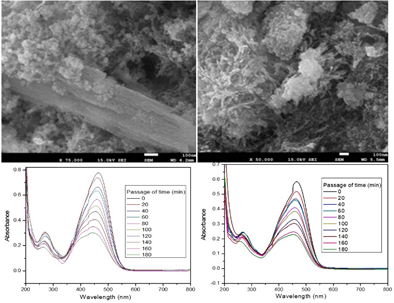
This study explores the green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using the leaf extract of Ocimum tenuiflorum as a reducing agent. Characterization of the synthesized ZnO NPs was performed using UV-visible spectroscopy, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The UV-visible absorption spectrum revealed maximum absorption peaks at 342 and 365 nm for ZnO NPs synthesized with 0.5 and 1.5 mmol.kg-1 zinc nitrate concentrations, yielding bandgap energies (Eg) of 3.62 and 3.39 eV, respectively. XRD analysis confirmed the crystalline nature of the ZnO NPs, exhibiting dominant peaks corresponding to the hexagonal wurtzite structure. The average crystalline sizes, were found to be 15.04 and 22.16 nm for the 0.5 and 1.5 mmol∙kg⁻1 concentrations of zinc nitrate, respectively. The SEM/TEM micrographs revealed that the nanoparticles have a roughly spherical-like morphology with an average size of 40-50 nm. The synthesized materials were examined for their photocatalytic activity towards the degradation of methyl orange (MO) dye. These findings demonstrate an eco-friendly method for synthesizing ZnO NPs with controlled properties suitable for various applications. Thus, the ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by using such type of eco-friendly method can be used for carrying out pharmaceutical research and therapeutic application in the future.
Significance of the study:
This study showcases the eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract, emphasizing a green, cost-effective method that leverages natural resources. The synthesized ZnO NPs exhibit promising photocatalytic properties for environmental remediation and potential applications in electronics, photonics, and biomedical engineering.
Summary of the study:
The research demonstrates the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract. Characterization techniques, including UV-visible spectroscopy, SEM, TEM, and XRD, confirmed the crystalline nature and spherical morphology of the nanoparticles. The synthesized ZnO NPs showed effective photocatalytic activity in degrading methyl orange dye, highlighting their environmental applications. This eco-friendly method offers a sustainable approach for producing ZnO NPs with controlled properties suitable for various advanced applications.
