Praveenkumar Babu, M. Thangamani, Chandra Sekar P.
1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Ramapuram, Chennai-600089, India.
2 Department of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Muthayammal Engineering College (Autonomous), Kakkaveri, Rasipuram-637408, Tamil Nadu, India.
3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Siddartha Institute of Science and Technology, Puttur-517583, Andhra Pradesh, India.
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
chandrushiva2013@gmail.com (Chandra Sekar P.)
ABSTRACT
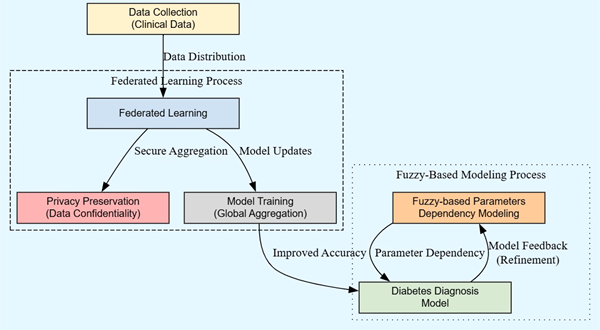
Diabetic is one of the deadliest diseases in the world. Most of the diabetic patients are from low and middle-income groups and if proper early detection system is been implemented, the majority of the patients can be prevented from diabetic. This research work aims to build a federated based fuzzy KNN approach that alerts the patients at an early stage. Despite many advancements in the research field in the area of diabetes, there are few drawbacks such as data privacy, performance issues, and so on. This research includes both internal parameters and external parameters. Internal parameters are those which are present inside the human body, examples of this kind include BMI, blood pressure, age, and so on. External parameters are very difficult to find the exact correlation towards diabetic because most of the external parameters such as agriculture output, climate change is dependent on time. All these parameters are closely monitored and a proper alert system is sent to the patients recommending them to be cautious. As per the medical domain, the existence of a connection between a parameter and the diabetic output is purely based on several combinations such that any one parameter may increase/decrease the effect of another parameter towards the diabetic output, hence, the fuzzy-based KNN algorithm is used for finding out the possibility of a parameter depending on another or not. The fuzzification process allows the proposed system to find the dependency between parameters and determine the alert process more accurately. The proposed model got the accuracy of 86% which is 23% higher than the traditional machine learning model.
Significance of the Study:
This study addresses the critical challenge of early diabetes detection, particularly for low- and middle-income groups, by introducing a federated learning framework integrated with fuzzy-based KNN modeling. By combining internal and external parameters, the model ensures accurate dependency analysis, overcoming data privacy and performance limitations of traditional methods. With an accuracy improvement of 23% over conventional models, the research provides a scalable and privacy-preserving solution that can significantly reduce diabetes-related complications through timely alerts and interventions.
Summary of the Study:
This research proposes a federated fuzzy KNN approach for early diabetes detection, incorporating internal parameters (e.g., BMI, blood pressure) and external factors (e.g., climate, agriculture output). The fuzzy-based method models interdependencies between parameters, enhancing accuracy and patient alerts. Integrating privacy-preserving mechanisms ensures secure data handling in distributed systems. The model achieved 86% accuracy, surpassing traditional machine learning methods by 23%, highlighting its potential for healthcare applications and better outcomes in real-world diabetes management.
