Aiswarya M., P. Predeep
1 Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology Calicut, Kozhikode, India
2 School of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam 686560, Kerala, India
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
aiswaryasan2@gmail.com (Aiswarya M.)
ABSTRACT
Organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites have emerged as promising materials for high-performance optoelectronic devices due to their superior properties. Crystal quality plays a pivotal role in optimizing their performance. This study investigates the incorporation of Capsaicin (C18H27NO3), a natural organic compound, as a dopant in methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) single crystals, synthesized through the inverse temperature crystallization method. Vibrational spectroscopic analyses were performed to understand the structural and functional impact of Capsaicin on crystal growth, nucleation, and quality. Raman spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) reveal significant enhancements in the structural stability and purity of MAPbI3 crystals upon doping with Capsaicin. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the improved phase purity, with impurity peaks observed in pristine MAPbI3 eliminated in the doped crystals. The addition of Capsaicin was found to modulate the nucleation rate and enhance the growth rate, leading to larger, and high-quality crystals with improved stability. Vibrational spectroscopic studies further highlighted reduced water absorption and enhanced molecular interactions within the doped crystals. This work underscores the potential of Capsaicin as an effective organic ligand to regulate the crystallographic properties of hybrid perovskites. The findings pave the way for utilizing Capsaicin and similar organic additives in engineering optoelectronic materials with enhanced stability and efficiency. Future studies could explore the broader applications of Capsaicin-doped perovskites, particularly in photovoltaics and photodetectors, further advancing the field of hybrid perovskite research.
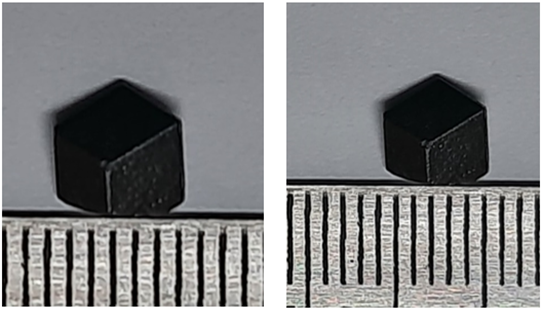
Significance of the Study:
This study demonstrates the transformative potential of Capsaicin, a natural organic molecule, as a dopant to enhance the structural integrity, phase stability, and crystallographic quality of hybrid perovskite single crystals. These advancements open new pathways for improving perovskite-based optoelectronic devices, such as solar cells and photodetectors.
Summary of the Study:
Capsaicin-doped MAPbI₃ single crystals were synthesized using inverse temperature crystallization. Vibrational spectroscopy and XRD confirmed enhanced phase purity, reduced defects, and improved structural stability. Capsaicin modulated nucleation rates, promoting larger, high-quality crystals with reduced water absorption and enhanced molecular interactions. These findings highlight the promise of Capsaicin and similar organic dopants for advanced optoelectronic applications.
