Anija Mol T Philip, Mayur V Khedkar, Shoeb R Khan, Shibin Chacko
Department of Chemistry, Hislop College, Maharashtra, 440001, India.
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
shibinchacko@gmail.com (Shibin Chacko)
ABSTRACT
Ferrocene, known for its aromaticity, lipophilicity, and stable redox properties, has emerged as a cornerstone in the design of functional molecules due to its unique chemical characteristics. Despite its classification as an organometallic compound, ferrocene and its derivatives exhibit remarkable stability under aqueous and aerobic conditions. Industrially, ferrocene finds applications in diverse sectors including petroleum, plastics, textiles, metallurgy, and catalysis. Medicinally, its derivatives are recognized for their cytotoxic, antitumor, antimalarial, and antianemic properties, which position ferrocene-conjugated biomolecules as promising candidates for therapeutic exploration. One strategy to enhance the water solubility and biocompatibility of ferrocene involves covalent conjugation with biomolecules such as amino acids, carbohydrates, cholesterol, and nucleic acids. These conjugates display unique structural, electrochemical, and biological properties that underpin their potential applications in medicinal and material sciences. However, limited synthetic methodologies have been reported for such conjugates. This review delves into recent advancements in the synthesis of ferrocene-conjugated carbohydrates, amino acids, cholesterol, and nucleobases, with an emphasis on strategies such as thioalkylation, click chemistry, and amide bond formation. Overall, the versatility of ferrocene derivatives, both in terms of chemical reactivity and biological activity, underscores their potential to drive innovations in therapeutic development and material science. Future research promises to uncover novel applications and expand the synthetic repertoire of ferrocene-based biomolecular conjugates.
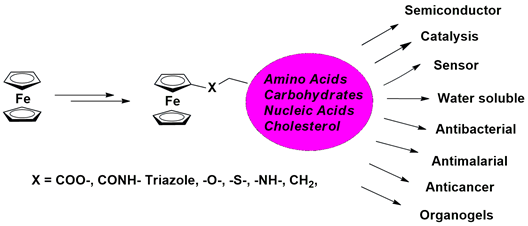
Significance of the Study:
Ferrocene-conjugated biomolecules offer immense potential in medicinal and material sciences due to their unique chemical properties, including redox stability, lipophilicity, and bioactivity. The ability to modify ferrocene through covalent conjugation with biomolecules such as amino acids, carbohydrates, cholesterol, and nucleobases enhances its solubility and biocompatibility. This research is crucial in advancing drug development, particularly for antibacterial, anticancer, and antimalarial therapies. By exploring innovative synthetic methodologies, this study contributes to expanding the applicability of ferrocene derivatives in pharmaceuticals, catalysis, and functional materials, paving the way for future breakthroughs in organometallic chemistry.
Summary of the Study:
This review highlights recent advancements in the synthesis of ferrocene-conjugated amino acids, carbohydrates, cholesterol, and nucleobases, emphasizing key strategies such as thioalkylation, click chemistry, and amide bond formation. It explores the industrial and medicinal significance of ferrocene derivatives, particularly their applications in drug development for antitumor, antianemic, and antimalarial treatments. The study also discusses the structural, electrochemical, and biological properties of these conjugates, underscoring their potential in biomedical research. Future directions focus on expanding synthetic methodologies to enhance the versatility and therapeutic efficacy of ferrocene-based biomolecules.
