Nazir Ahmad Teli, Showkat Hassan Mir
Department of Physics, University of Kashmir, Hazratbal. Srinagar, 190006 Jammu and Kashmir, India.
* Authors to whom correspondence should be addressed:
nazir.na465@gmail.com (Nazir. A. Teli)
mirshowkat07@gmail.com (Showkat H. Mir)
ABSTRACT
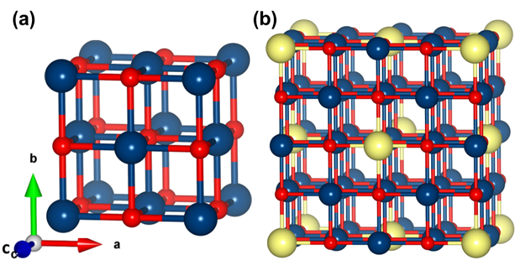
In this study, we employed the DFT+U method to systematically explore the electronic, and magnetic properties of nickel oxide doped with alkali metal atoms (Li, Na, K). The Hubbard potential-U was judiciously applied to all doped compound resulting from alkali doping, and were found to exhibited half-metallic properties. A noteworthy observation was the half-metallic band gap in the spin-down channel, which exhibited a linear variation with the increasing value of the Hubbard potential. Furthermore, the total magnetic moment was discernible in the supercells, with all supercells demonstrating 100% spin polarization at the Fermi level. Consequently, the findings from this study hold significant potential for applications in spintronics, thereby paving the way for future research in this domain.
Significance of the study:
This study investigates the electronic and magnetic properties of alkali-doped nickel oxide (NiO) using the DFT+U method, revealing significant half-metallic characteristics and 100% spin polarization. These findings are crucial for spintronics applications, offering insights that could drive future research and development in the field of magnetic and electronic materials.
Summary of the study:
Using the DFT+U method, this study explores the effects of alkali metal doping (Li, Na, K) on nickel oxide (NiO). The doped compounds exhibit half-metallic properties, with a spin-down band gap varying linearly with the Hubbard potential. The total magnetic moment in supercells demonstrates 100% spin polarization at the Fermi level, indicating potential applications in spintronics and advanced electronic devices.
