Aasim Rashid Khanday, Showket Ahmad Bhat, Faheem Ahmad Dar, Mohd. Ikram
1 Solid State Laboratory, Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology (NIT), Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir 190006, India
2 Solid State Research Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Kashmir, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir 190006, India.
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
showketbht7@gmail.com (Showket Ahmad Bhat)
ABSTRACT
This study investigates the impact of Gd3+ doping on the structural and optical characteristics of LiBaPO4. In this study, the solid-state reaction route was utilized to synthesized LiBa1-xGdxPO4 compounds with varying compositions (x = 0, 0.04, and 0.08). In this study, the phase of the samples was determined through Rietveld refinement analysis using Foolproof software. This analysis allowed us to obtain refined parameters such as lattice constants, volume of the unit cell, and goodness of fit (ꭕ2). The samples were observed to exhibit crystallization in the trigonal phase, characterized by the space group P31c. In this study, the surface morphology of the sample was analyzed using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The obtained FESEM images were further processed using ImageJ software to calculate the grain size. In this study, the optical band gap was determined through the application of the tauc plot method. The results revealed a decreasing trend in the band gap values (ranging from 3.06 eV to 2.14 eV) as the dopant concentration was increased. This study investigates the photoluminescence properties of brilliant red luminescent phosphor spheres and their potential application in red luminescent optical devices. The results indicate that these phosphor spheres exhibit strong red luminescence, indicating their suitability for use in such devices.
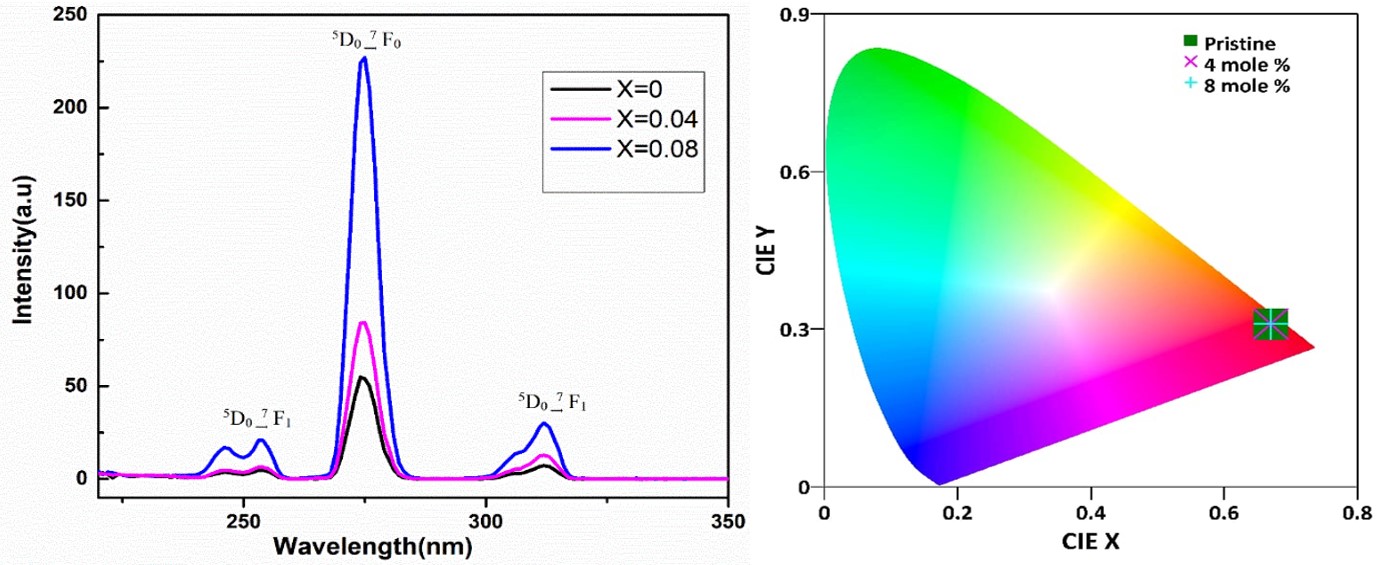
Significance of the study:
This paper explores the potential of Gd3+ doping in LiBaPO4 phosphors for enhancing white lighting applications. The study’s findings on structural and optical property modifications due to doping highlight the material’s suitability for red luminescent optical devices, offering insights into improving lighting technology.
Summary of the study:
The research examines Gd3+ doping in LiBaPO4, synthesized via the solid-state reaction method. Rietveld refinement confirms trigonal phase crystallization, while FESEM analysis reveals increased grain size with higher doping levels. Optical band gap analysis shows a decreasing trend, correlating with increased dopant concentration. The strong red luminescence of the doped phosphors suggests their applicability in red luminescent optical devices.
