M. Beaula Ruby Kamalam, K. J. Sam Daniel, K. Hariramakrishnan, L. Ganesh, S. S. R. Inbanathan
Department of Physics, The American College, Madurai-625002, India
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
bealthambu10@gmail.com (M. Beaula Ruby Kamalam)
ABSTRACT
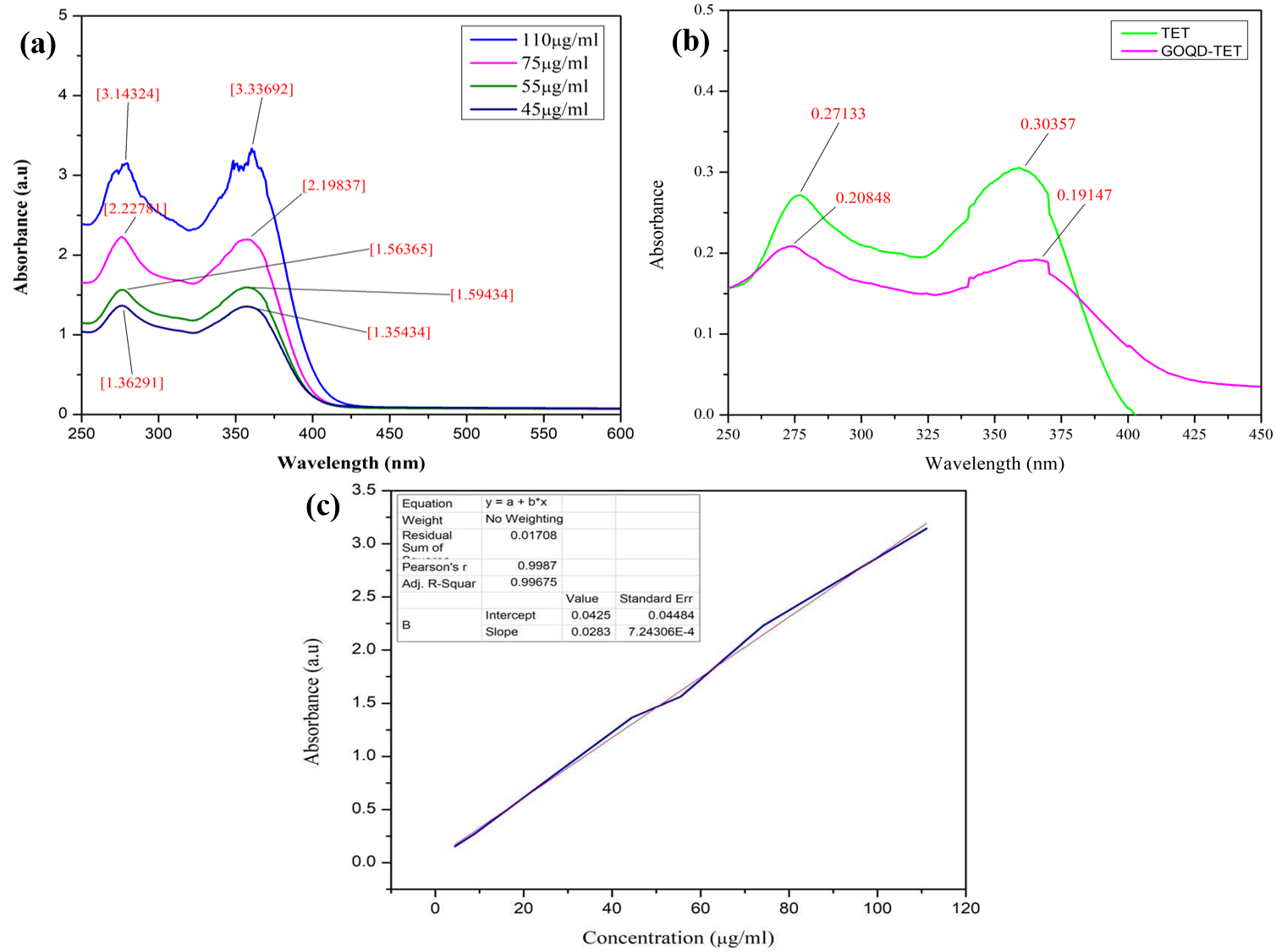
This study presents the synthesis and comprehensive characterization of graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) for applications in environmental remediation and biomedical drug delivery. Graphite oxide was initially synthesized using the modified Hummers method, followed by exfoliation via ultrasonication to obtain graphene oxide (GO). The GO was subsequently converted into GOQDs through hydrothermal treatment, yielding nanoparticles with enhanced optical and catalytic properties. The structural, chemical, and optical characteristics of GOQDs were systematically analyzed using UV-Vis spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The results confirmed the successful formation of GOQDs with distinct absorption and emission properties, making them suitable for photocatalytic applications. In environmental remediation, GOQDs demonstrated high efficiency in the degradation of methylene blue dye, achieving a degradation rate of 94.51% under UV irradiation, highlighting their potential for wastewater treatment. For biomedical applications, GOQDs were functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG) to enhance their biocompatibility and stability. Hemolytic assays and MTT cytotoxicity tests confirmed their low toxicity and suitability for drug delivery systems. Furthermore, drug loading studies using tetracycline revealed a high drug loading efficiency (DLE) of 95.8% and a drug loading content (DLC) of 1.23%, underscoring their potential as nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery. This research underscores the versatility of GOQDs, demonstrating their dual functionality in environmental catalysis and biomedical applications. The findings provide a foundation for future studies on optimizing GOQD-based systems for industrial and therapeutic uses.
Significance of the Study
This study highlights the dual functionality of graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) in environmental remediation and biomedical drug delivery. Their high photocatalytic efficiency (94.51% methylene blue degradation) offers a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment, while PEG-functionalized GOQDs demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and high drug-loading capacity (95.8% efficiency), making them promising for targeted nanomedicine. The research bridges material science and applied technology, providing a foundation for scalable GOQD synthesis and multifunctional applications in pollution control and healthcare, addressing critical environmental and biomedical challenges.
Summary of the Study
This study synthesized graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) via hydrothermal treatment, confirming their structural and optical properties through UV-Vis, FTIR, XRD, and PL analysis. GOQDs exhibited 94.51% photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue, proving effective for environmental cleanup. In biomedicine, PEGylated GOQDs showed low toxicity and high tetracycline loading (95.8% efficiency), indicating potential for drug delivery. The findings demonstrate GOQDs’ versatility in both pollution control and nanomedicine, paving the way for future industrial and therapeutic optimizations.
