Sonika Sharma, Shubham Sharma, Meena Kumari
1 Department of Chemistry, MLSM College, Sunder Nagar, Himachal Pradesh, India
2 Department of Chemistry, Himachal Pradesh University, Summer Hill, Shimla-171005, India.
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
drmeenakchandel@gmail.com (Meena Kumari)
ABSTRACT
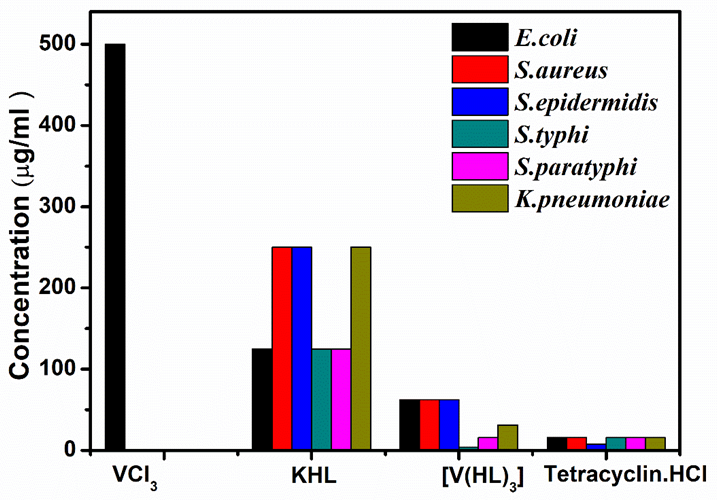
A new vanadium (III) hydroxamate complex of composition V(4- NO2C6H4CH=CHCONHO)3 has been synthesized by reaction of VCl3 with potassium salt of 4-nitrocinnamohydroxamate (4-NO2C6H4CH=CHCONHO) in 1:3 molar ratio in dry methanol solvent. The newly synthesized complex is characterized by elemental analysis, molar conductivity, magnetic moment measurements and IR, UV-Vis spectral studies and mass spectrometry. DFT calculations were carried out by using Orca 4.2.1 program and the negative values of the energies of EHOMO and ELUMO for the V(III) complex confirm its stability. A distorted-octahedral geometry around vanadium center has been suggested for complex based upon physicochemical, spectroscopic and DFT studies, involving bonding through hydroxylamine and carbonyl oxygens (O O coordination). The cyclic voltammogram of the complex shows single anodic and cathodic peak. The TGA/DTA curve indicates the single step decomposion of complex. The biological potential of the ligand and complex have been tested by in vitro antimicrobial studies and cytotoxicity assay. Antimicrobial activity of complex has been found increased as compare to precursor and ligand. The results of cytotoxicity reveal the complex less toxic as compared to standard drug simvastatin.
Significance of the study:
This paper introduces a novel vanadium (III) hydroxamate complex with notable stability and biological activity. The complex’s enhanced antimicrobial properties and lower cytotoxicity compared to standard drugs highlight its potential for medical applications. The study’s comprehensive spectroscopic and DFT analyses provide insights into the complex’s structure and stability, emphasizing its relevance in the development of new therapeutic agents.
Summary of the study:
The synthesis and characterization of a new vanadium (III) hydroxamate complex are detailed in this study. Elemental analysis, spectroscopic techniques, and DFT calculations confirmed the complex’s stability and distorted-octahedral geometry. The complex exhibits significant antimicrobial activity and lower cytotoxicity compared to simvastatin. These findings underscore the complex’s potential for biological applications, particularly as an antimicrobial agent.
