V. A. Sadafale
Department of Chemistry, Adarsha Science, J. B. Arts & Birla Commerce Mahavidyalaya, Dhamangaon Rly, Amravati, India.
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
vasadafale1980@gmail.com (V. A. Sadafale)
ABSTRACT
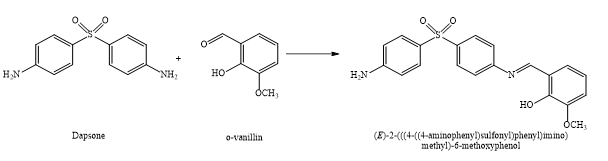
This study presents the synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and thermal analysis of novel Co(II), Fe(III), and Mn(III) complexes derived from a heterocyclic Schiff base ligand. The ligand, 2-(((4-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-6-methoxyphenol, was synthesized via the condensation of o-vanillin and dapsone in ethanolic medium under reflux conditions. The resulting Schiff base ligand was subsequently complexed with Co(II), Fe(III), and Mn(III) salts to form the corresponding metal complexes. These compounds were thoroughly characterized using elemental analysis, molar conductance measurements, and various spectroscopic techniques, including infrared (IR), ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis), mass spectrometry, and ¹H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The IR spectra confirmed the bidentate coordination of the ligand to the metal centers through the phenolic oxygen and azomethine nitrogen atoms. Electronic spectral data suggested a square planar geometry for the Co(II) complex and octahedral geometries for the Fe(III) and Mn(III) complexes. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was employed to investigate the thermal stability and decomposition patterns of the complexes under a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 10°C min⁻¹. The thermodynamic parameters, including activation energy (Eₐ), entropy change (ΔS), and free energy change (ΔF), were calculated using the Freeman-Carroll and Sharp-Wentworth methods. The results indicated that the Co(II) complex exhibited the highest thermal stability, followed by Mn(III) and Fe(III). The findings contribute to the understanding of Schiff base metal complexes and their potential applications in coordination chemistry, catalysis, and material science.
Significance of the Study:
This study demonstrates the successful synthesis and characterization of novel Schiff base metal complexes with potential applications in catalysis and materials science. The detailed spectroscopic and thermal analyses provide crucial insights into coordination behavior and stability, contributing to the development of tailored metal-organic compounds. The findings establish structure-property relationships that could guide the design of functional materials for industrial and pharmaceutical applications, while the synthetic methodology offers a reproducible route for preparing similar coordination complexes.
Summary of the Study:
A Schiff base ligand was synthesized from o-vanillin and dapsone, then complexed with Co(II), Fe(III), and Mn(III) ions. The compounds were characterized using elemental analysis, IR, NMR, mass spectrometry, and thermal techniques. Spectroscopic data confirmed bidentate coordination via phenolic oxygen and azomethine nitrogen. Thermal studies revealed high stability (Co > Mn > Fe), with decomposition pathways analyzed through kinetic parameters. The work provides a comprehensive understanding of these complexes’ structural and thermal properties.
