Mukesh S. Kadam, Sharif A.Kazi, Sandip A. Nirwan, Bhimrao C. Khade
1 Department of Chemistry, Loknete Gopinathji Munde Arts, Commerce & Science College, University of Mumbai, Mandangad, Ratnagiri-415203, Maharastra, India.
2 Departments of Chemistry, Dnyanopasak Arts, Commerce and Science College, Parbhani-431401, Maharastra, India.
*Author to whom correspondence should be addressed:
mukeshkadam21@gmail.com (M. S. Kadam)
ABSTRACT
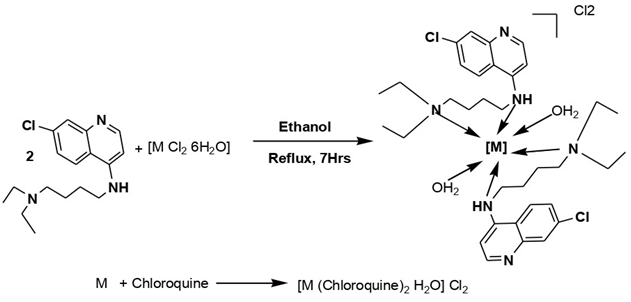
The present study reports the synthesis, structural characterization, and antifungal evaluation of novel Ru(III) and Rh(III) coordination complexes with Chloroquine. X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) analysis revealed that both complexes crystallize in a triclinic system, with distinct unit cell parameters. The intense diffraction bands observed in the spectrograms indicate a closely packed atomic arrangement, confirming high crystallinity. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) demonstrated the thermal stability of the complexes, with decomposition pathways involving the loss of coordinated water molecules, chloride ions, and organic moieties, ultimately forming stable metal oxides above 800°C. Elemental analysis and molar conductance measurements supported the proposed stoichiometry and ionic nature of the complexes. Antifungal screening against Aspergillus niger and Candida albicans revealed that both Ru(III) and Rh(III) complexes exhibit enhanced inhibitory activity compared to free Chloroquine. Notably, the Rh(III) complex displayed superior efficacy against A. niger, while the Ru(III) complex showed higher potency against C. albicans. The observed bioactivity correlates with the structural features and metal-ligand interactions elucidated through X-ray diffraction and thermal studies. These findings highlight the potential of transition metal-Chloroquine complexes as promising antifungal agents, warranting further pharmacological exploration.
Significance of the Study:
The work demonstrates how metal coordination can improve chloroquine’s physicochemical properties and bioactivity, offering potential for developing novel antifungal agents. The enhanced efficacy against resistant fungal strains highlights their therapeutic promise, contributing to metallodrug research for infectious diseases.
Summary of the Study:
This study synthesized and characterized Ru(III) and Rh(III) complexes with chloroquine, confirming their structures through elemental analysis, XRD, and TGA. Both complexes exhibited enhanced thermal stability and crystallized in a triclinic system. Antifungal assays revealed superior activity compared to free chloroquine, with Rh(III) showing greater efficacy against Aspergillus niger and Ru(III) against Candida albicans.
