

BioMed and BioSci Advances is a cutting-edge, peer-reviewed journal dedicated to advancing the frontiers of biomedical and biological sciences. Our mission is to provide a global platform for researchers, clinicians, and innovators to publish high-impact discoveries that drive progress in human health, disease mechanisms, and biotechnology. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we bridge the gap between fundamental research and clinical applications, accelerating the translation of scientific breakthroughs into real-world solutions. The journal publishes original research articles, authoritative reviews/perspectives, and concise communications spanning a broad spectrum of topics, including Molecular and Cellular Biology, Genetics and Genomics, Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Neuroscience and Neurodegeneration, Cancer Biology and Precision Oncology, Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Therapy, Pharmacology and Drug Development, Biomedical Engineering and Nanomedicine, Systems Biology and Bioinformatics, Public Health and Epidemiology, Structural Biology and Proteomics, and Translational Medicine. With a commitment to open science and innovation, BioMed and BioSci Advances highlights emerging technologies such as CRISPR and gene editing, AI-driven diagnostics, wearable biosensors, organ-on-a-chip systems, and next-generation therapeutics. We also emphasize One Health approaches, linking human, animal, and environmental health to address global challenges like antimicrobial resistance and pandemic preparedness. By uniting diverse perspectives—from bench scientists to clinical practitioners—we aim to catalyze breakthroughs that redefine medicine and improve lives. BioMed and BioSci Advances serves as a vital resource for the scientific community, policymakers, and industry leaders, empowering them with knowledge to shape a healthier, more sustainable future.
Volume 2, Issue 2 (June 2025)
Review
Carbohydrate-Isoxazole Hybrids: Design, Synthesis, and Therapeutic Applications in Drug Discovery
Pravin S. Bhale, Nikita N. Mali, Sadanand N. Shringare, Tukaram D. Jadhav, Dipak S. Bhandigare, Dnyaneshwar M. Sirsat
Summary: This review explores the design, synthesis, and therapeutic applications of carbohydrate-isoxazole hybrids in drug discovery. Focusing on their biological activities, structure-activity relationships, and mechanisms of action, it discusses their potential in treating diverse conditions such as cancer, inflammation, and infections. The study emphasizes the importance of rational design in optimizing these hybrids, while addressing challenges like metabolic stability and selective targeting, offering insights for future drug development strategies.
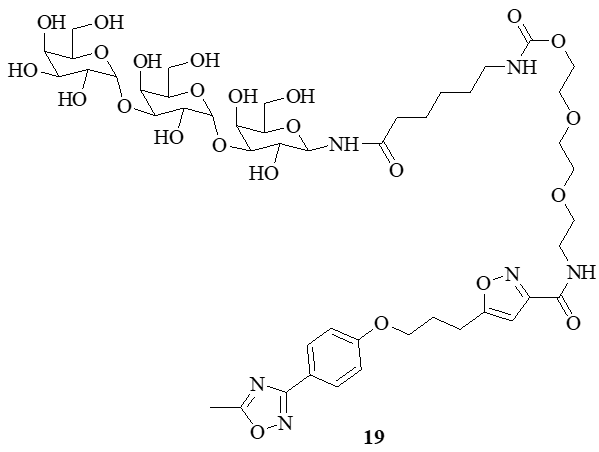
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 16 June 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(2), 63-73 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0063Advancing Insect Taxonomy and Biodiversity Research: A Comprehensive Review of DNA Barcoding and Non-Destructive DNA Extraction Techniques and Applications
Muzamil Liakat Mir, Nuzhat Parveen, Shahid Bin Zeya, Ramsha Ashraf, Amreen Fatima, Suhaima Safdar, Sana Jameel, Faiqua Haque, G.G.H.A. Shadab
Summary: This review explores the application of DNA barcoding in insect taxonomy, focusing on its role in species identification, biodiversity assessment, and ecological research. It examines advancements in non-destructive DNA extraction methods and the integration of next-generation sequencing, portable technologies, and AI. The study also addresses challenges such as database limitations and numts, offering insights into how these issues can be overcome to improve the reliability and effectiveness of DNA barcoding in entomology and conservation.
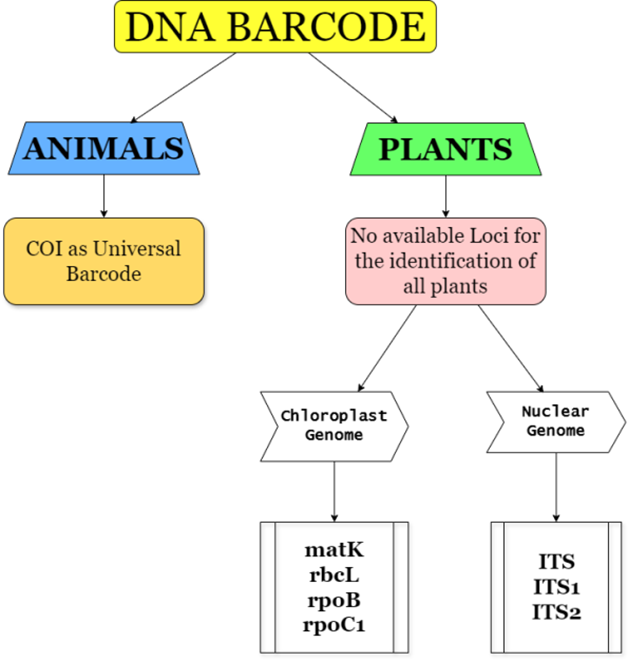
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 27 April 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(2), 74-95 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0074Research Articles
Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Butterfly Fauna in Chikhli, Buldhana District, Maharashtra, India
Roshana K. Hushare, R. B. Gade, M. T. Nikam
Summary: The study investigated the diversity and seasonal abundance of butterflies in Chikhli, Buldhana District, from June to September 2022. Seventeen species across five families were recorded, with the Nymphalidae family dominating. Highest diversity was found in grasslands, scrub jungles, and agricultural peripheries, peaking during the monsoon. Seasonal variations in butterfly populations were linked to host plant availability and climatic conditions. The study emphasizes the need for habitat conservation to protect butterfly populations and floral diversity.
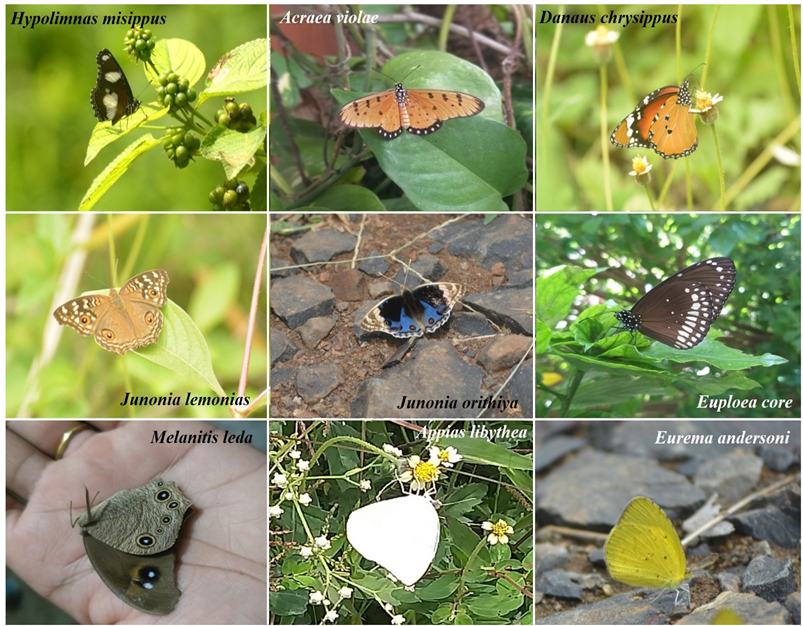

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 May 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(2), 96-104 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0096Biocontrol Potential of Native Trichoderma Isolates Against Phytophthora infestans in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): Isolation, Characterization, and Antagonistic Efficacy
Mat Both Dol, Delelegn Woyessa, Shiferaw Demissie, M. Sadre Alam Fakhri
Summary: This research isolated and characterized native Trichoderma strains from tomato rhizospheres in Ethiopia to evaluate their antagonistic effects against P. infestans. Ten isolates were obtained, and four strains exhibited substantial growth inhibition of the pathogen, with Ju-TGDb-2 showing the highest efficacy (61.4%). These findings suggest that native Trichoderma isolates can be used as effective biocontrol agents, offering a promising solution for managing late blight in tomatoes.
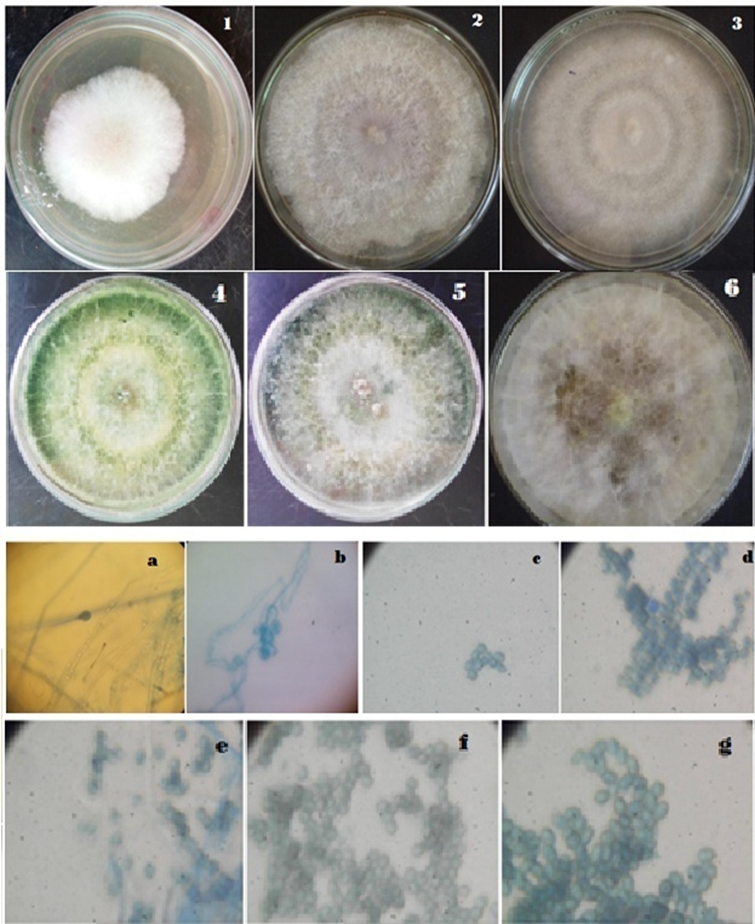
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 May 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(2), 105-113 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0105.Volume 2, Issue 1 (March 2025)
Review
Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanisms, Implications, and Future Perspectives for Human and Environmental Health
Muzamil Liakat Mir, Nuzhat Parveen, Amreen Fatima, Suhaima Safdar, Faiqua Haque, G.G.H.A. Shadab
Summary: This review consolidates research on AgNP-induced genotoxicity, emphasizing DNA damage, chromosomal aberrations, and epigenetic modifications. It explores synthesis methods, characterization techniques, and toxicity mechanisms, including ROS generation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Comparative analysis of in vitro and in vivo studies reveals dose- and size-dependent effects, urging standardized testing protocols. The study advocates for balanced risk-benefit assessments, proposing safer AgNP alternatives and regulatory measures to mitigate risks while harnessing their antimicrobial and industrial potential for sustainable advancements.
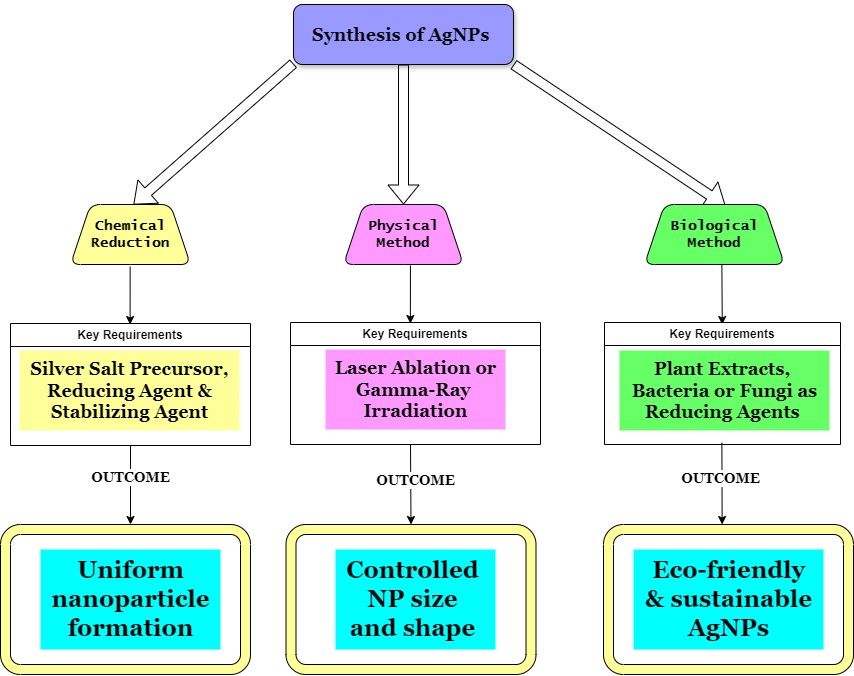
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 12 February 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(1), 01-22 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0001Neurotoxic Effects of Pyrethroid Insecticides: Mechanisms, Health Risks, and Future Perspectives
Mohd Zaid Khan, Faiqua Haque
Summary: Histopathological analysis revealed that pyrethroid exposure induces significant liver necrosis, cardiac atrophy, and renal tubular damage in animal models. Mosquito coil smoke caused the most severe toxicity, while antioxidant treatments showed partial protection. The study confirms pyrethroids’ multi-organ toxicity through oxidative stress and metabolic dysfunction, emphasizing the need for stricter exposure guidelines and alternative pest control strategies to mitigate long-term health risks in humans and wildlife.
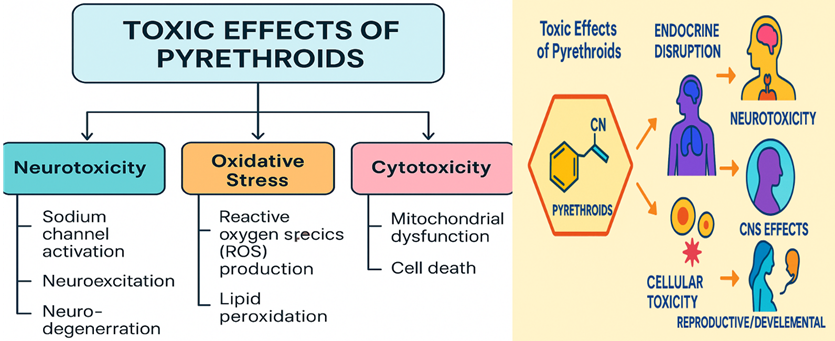
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 February 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(1), 23-38 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0023Research Articles
Isolation, Characterization, and Optimization of Glucoamylase – Producing Bacteria from Fruit Waste Soil for Industrial Applications
Darshan Hosmath, Jaysing Patil
Summary: The study isolated and characterized glucoamylase-producing bacteria from fruit waste soil in Tasawade MIDC, Karad. Among four isolates, T5 showed the highest activity (176.45 U/ml/min) and specific activity (309.56 U/mg). Optimal conditions were pH 6, 25°C, 0.2 mg/ml salt, and 2.5 mg/ml substrate, with MgCl₂ enhancing activity. T5, a Gram-positive coccus, demonstrated robust enzyme stability. The findings suggest its industrial potential in starch processing and biofuels, emphasizing sustainable microbial enzyme production from organic waste for eco-friendly biotechnological applications.
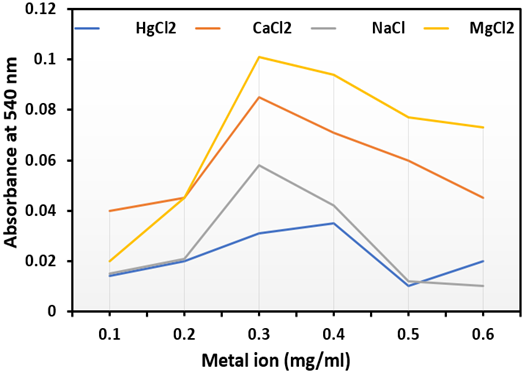
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 20 February 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(1), 39-45 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0039Dietary Supplementation of Black Pepper (Piper nigrum) Enhances Growth Performance and Hematological Parameters in Fingerling Spotted Snakehead (Channa punctatus)
Alvia Farheen , Mukhtar Ahmad Khan, Noorin Zafar
Summary: The study evaluated black pepper’s effects on Channa punctatus fingerlings, finding that 0.4% dietary inclusion significantly improved weight gain, growth rate, protein retention, and feed efficiency while reducing FCR. Higher doses reduced palatability and growth. Hematological parameters (hemoglobin, RBC, hematocrit) peaked at 0.4%, indicating better oxygen transport and metabolism. Black pepper enhanced protein deposition without altering fat or ash content. The results suggest its viability as a natural growth enhancer in sustainable aquaculture.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 20 February 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(1), 46-54 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0046Antibacterial Efficacy of Crude Extracts from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) Leaves Against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae: An In vitro Study
Gatluak Goanar, Geremew Tafesse, Workineh Mengesha, M. Sadre Alam Fakhri
Summary: The study evaluated the antibacterial efficacy of acetone and ethanol extracts from Tamarindus indica leaves against S. aureus and K. pneumoniae using disk diffusion and MIC assays. Both extracts showed significant antibacterial activity, with K. pneumoniae being more sensitive. The acetone extract exhibited lower MIC values (9.375 mg/mL) than ethanol (18.75 mg/mL). Results suggest that tamarind leaves contain bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential, supporting their traditional use. Further research is needed to isolate active constituents and assess mechanisms of action.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 24 February 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(1), 55-62 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0055Volume 1, Issue 1 (December 2024)
Review
Nanoparticles for Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Innovations, Applications, and Future Perspectives in Nanomedicine
Sadik Tyagi, Mohd Aarim, Salman Khan, Bushra Ahmad, Muzammil Liyakat Mir, Faiqua Haque, Suhaima Safdar, Amreen Fatima, Nuzhat Parveen, G.G.H.A. Shadab
Summary: Nanoparticles (NPs) enable breakthroughs in drug delivery through targeted, stimuli-responsive systems like liposomes and dendrimers, improving therapeutic outcomes in oncology and neurology. Innovations in green synthesis and DNA nanotechnology enhance sustainability and precision. Challenges include regulatory standardization, toxicity assessment, and scalable production. Future prospects involve AI-optimized designs, gene-editing carriers, and personalized nanomedicine. Interdisciplinary collaboration and ethical frameworks are vital for translating lab advancements into clinical practice, ensuring NPs redefine 21st-century medicine safely and equitably.

Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 24 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 03-25 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0003Bisphenol A and Breast Cancer: Mechanisms of Carcinogenicity, Tumor Microenvironment Modulation, and Nutritional Interventions
Sabahat Ariba, Monisha Banerjee
Summary: This comprehensive review analyzes BPA’s carcinogenic mechanisms in breast cancer, including receptor-mediated signaling, stromal reprogramming, and subtype-specific effects. It demonstrates how dietary components can exacerbate or counteract BPA’s toxicity through metabolic interactions. The study integrates molecular, epidemiological and clinical evidence to propose a multidisciplinary approach combining regulatory measures, public awareness and nutritional strategies to address BPA-associated breast cancer risks, emphasizing prevention through environmental and lifestyle modifications.

Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 28 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 26-39 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0026Biosynthesis of Essential Oil in Aromatic Plant Species: A review
Bushra Ahmad, Sadik Tyagi, Mohd. Aarim, Mohd. Sajid Khan, Ahamad Faiz Khan
Summary: The study systematically examines three key enzymes (MCT, CMK, MDS) in the DXP pathway, detailing their roles in converting metabolic intermediates to terpenoid precursors. Through structural and kinetic analyses, it highlights their plastid localization, catalytic mechanisms, and regulatory features. The research bridges gaps in plant isoprenoid biosynthesis, offering insights for biotechnological manipulation of terpenoid production. These discoveries pave the way for sustainable applications in agriculture, medicine, and industry by optimizing natural product synthesis.

Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 28 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 40-63 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0040Research Articles
In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Potential of Crude Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) Seed Extracts Against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia
Gatluak Goanar, Geremew Tafesse, M. Sadre Alam Fakhri
Summary: This study evaluated Tamarindus indica seed extracts (acetone/ethanol, 100-300 mg/mL) against S. aureus and K. pneumoniae using disk diffusion. No inhibition was observed, with no significant difference from the negative control (P = 1.00). Results suggest tamarind seeds lack antibacterial activity under tested conditions but warrant further study with varied methods, solvents, or synergistic combinations to confirm their potential as antimicrobial agents.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 28 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 64-70 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0064Dietary Curcumin Attenuates Arsenic-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neurobehavioral Impairments in Drosophila melanogaster: Mechanistic Insights from In Vivo and In Silico Analyses
Anjali Ranjan, Shruti Verma, Gajendra Kumar Azad, Shahla Yasmin
Summary: Arsenic trioxide (0.5–0.75 mM) caused dose-dependent lethality, oxidative stress, and motor deficits in Drosophila. Curcumin (1 mM) co-administration improved survival, reduced lipid peroxidation, and restored catalase activity and climbing ability. Bioinformatics revealed curcumin’s interactions with detoxification proteins like cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferases. Results suggest curcumin mitigates arsenic toxicity via antioxidant pathways, advocating its use as a neuroprotective supplement. Further studies in mammalian models are warranted.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 27 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 71-81 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0071Editorial
Pioneering Advances in Biomedical and Bioscience Research
Dianbao Zhang
Editorial | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 28 November 2024
BioMed and BioSci Advances 1(1), 01-02 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2024.0001Aims and Scope
Welcome to BioMed and BioSci Advances, a cutting-edge, peer-reviewed journal published by Ariston Publications, dedicated to accelerating breakthroughs in biomedical and biological sciences. Our mission is to provide a dynamic platform for researchers, clinicians, and biotechnologists to share pioneering discoveries that advance human health, decode disease mechanisms, and drive innovation in life sciences. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we bridge the gap between fundamental research and clinical translation, ensuring that scientific knowledge translates into real-world impact.
BioMed and BioSci Advances embraces the complexity of modern biomedical research, covering a wide spectrum of disciplines—from molecular biology and genetics to translational medicine and public health. We prioritize cutting-edge studies that push scientific boundaries, whether through novel therapeutics, AI-driven diagnostics, or sustainable biomedical technologies. Our rigorous peer-review process ensures that only high-quality, impactful research is published, while our open-access model promotes global knowledge sharing and inclusivity.
We invite researchers, clinicians, and industry experts worldwide to contribute their groundbreaking work to BioMed and BioSci Advances. Together, we can shape the future of medicine, improve global health outcomes, and foster a deeper understanding of life sciences.
Aims
BioMed and BioSci Advances aims to:
- Serve as a leading platform for disseminating high-impact research in biomedical and biological sciences.
- Foster interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and biotechnologists to accelerate scientific discovery.
- Advance understanding of disease mechanisms, therapeutic interventions, and biomedical innovations.
- Promote translational research that bridges laboratory findings with clinical applications.
- Support global health initiatives by publishing studies on emerging diseases, public health strategies, and medical technologies.
- Encourage open science and equitable access to cutting-edge research for scientists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals worldwide.
Scope
BioMed and BioSci Advances covers a broad range of topics in biomedical and biological research, including but not limited to:
Molecular and Cellular Biology
- Genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics
- Epigenetics and gene regulation
- Signal transduction and cellular communication
- Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine
Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutics
- Cancer biology and precision oncology
- Neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders
- Cardiovascular, metabolic, and infectious diseases
- Immunology, autoimmunity, and immunotherapy
Biomedical Technologies and Innovations
- CRISPR, gene editing, and synthetic biology
- Nanomedicine and drug delivery systems
- Wearable biosensors and AI-driven diagnostics
- Organ-on-a-chip and 3D bioprinting
Public Health and Epidemiology
- Emerging infectious diseases and pandemic preparedness
- Antimicrobial resistance and One Health approaches
- Global health equity and precision public health
- Environmental health and disease prevention
Translational and Clinical Research
- Biomarker discovery and personalized medicine
- Clinical trials and therapeutic developments
- Digital health and telemedicine
- Ethical, legal, and social implications (ELSI) of biomedical advances
Computational and Systems Biology
- Bioinformatics and multi-omics integration
- Machine learning in biomedicine
- Network biology and disease modeling
- Biomedical imaging and data science
Sustainability in Biomedicine
- Green biotechnology and sustainable drug development
- Biomedical waste management and eco-friendly lab practices
- Climate change and its impact on health
Objectives
- To publish rigorous, innovative research that advances biomedical and bioscientific knowledge.
- To facilitate interdisciplinary dialogue between biologists, clinicians, engineers, and data scientists.
- To accelerate translational research by connecting laboratory discoveries with clinical applications.
- To promote global health solutions through studies on infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, and public health strategies.
- To encourage ethical, sustainable, and equitable advancements in biomedicine.
Subject Covered(but not limited to):
BioMed and BioSci Advances provides comprehensive coverage of cutting-edge research across all areas of biomedical and biological sciences, with a strong emphasis on interdisciplinary innovation. We welcome original research, reviews, and clinical studies spanning experimental, theoretical, computational, and translational approaches. Topics include, but are not limited to:
Molecular & Cellular Biology
- Genomics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics
- Epigenetics and Gene Regulation
- Signal Transduction and Cell Communication
- Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine
- CRISPR, Gene Editing, and Synthetic Biology
Disease Mechanisms & Therapeutics
- Cancer Biology and Precision Oncology
- Neurodegenerative & Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Autoimmune Diseases
- Infectious Diseases & Antimicrobial Resistance
- Immunology, Immunotherapy, and Vaccine Development
Biomedical Technologies & Innovations
- Nanomedicine and Targeted Drug Delivery
- AI-Driven Diagnostics and Digital Pathology
- Wearable Biosensors and Point-of-Care Devices
- Organ-on-a-Chip and 3D Bioprinting
- Biomedical Imaging and Theranostics
Public Health & Epidemiology
- Emerging Infectious Diseases & Pandemic Preparedness
- One Health Approaches (Human-Animal-Environment Interface)
- Global Health Equity and Precision Public Health
- Environmental Health & Disease Prevention
- Antimicrobial Stewardship and Resistance Surveillance
Translational & Clinical Research
- Biomarker Discovery and Personalized Medicine
- Clinical Trials and Therapeutic Development
- Digital Health and Telemedicine
- Medical Ethics and Health Policy
Computational & Systems Biology
- Bioinformatics and Multi-Omics Integration
- Machine Learning in Disease Prediction & Drug Discovery
- Network Biology and Computational Modeling
- Biomedical Big Data Analytics
Sustainable Biomedicine
- Green Biotechnology & Eco-Friendly Therapeutics
- Biomedical Waste Management
- Climate Change and Human Health
Emerging Interdisciplinary Fields
- Neuroengineering and Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Microbiome Research and Gut-Brain Axis
- Aging Biology and Longevity Science
- Space Medicine and Extreme Environment Biology
Case Studies & Clinical Applications
- Real-World Implementation of Precision Medicine
- Innovative Healthcare Delivery Models
- Rare Disease Research and Patient Advocacy
Why Submit to BioMed and BioSci Advances?
Broad Impact: Covering fundamental to applied research with global relevance.
Interdisciplinary Focus: Bridging biology, medicine, engineering, and data science.
Rapid Dissemination: Fast-track review and open-access availability.
We invite researchers to contribute their groundbreaking work to advance the frontiers of biomedicine and bioscience!
Readership
BioMed and BioSci Advances engages a global, multidisciplinary audience at the forefront of biomedical and life sciences research. Our readership spans academia, clinical practice, industry, and policy-making, reflecting the journal’s commitment to bridging discovery with real-world impact.
Key Audiences Include:
Researchers & Academics
- Molecular biologists, geneticists, and biochemists
- Translational scientists and pharmacologists
- Computational biologists and bioinformaticians
Clinicians & Healthcare Professionals
- Physicians, surgeons, and specialists in oncology, neurology, immunology, etc.
- Clinical trial investigators and medical innovators
- Public health experts and epidemiologists
Industry & Biotechnology Leaders
- Pharmaceutical and biotech R&D teams
- Medical device and diagnostic developers
- AI-driven healthcare startups
Policy Makers & Regulatory Experts
- Government health agencies and regulatory bodies
- Bioethics committees and health policy advisors
Educators & Students
- University faculty and postgraduate researchers
- Medical and life sciences students
Why Readers Choose BioMed and BioSci Advances?
- Cutting-Edge Insights: Stay updated on breakthroughs from bench to bedside.
- Interdisciplinary Relevance: Content spans basic science to clinical applications.
- Actionable Knowledge: Research directly applicable to healthcare, industry, and policy.
- Global Perspective: Diverse contributions addressing worldwide health challenges.
Editorial Board
Editors-in-Chief
Prof. Dianbao Zhang
Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine
China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Email: dbzhang@cmu.edu.cn
Editors
Prof. Lili Jin
School of Life Sciences
Liaoning University, Shenyang, China
Dr. K. K. Sharma
Professor, Zoology (Retd.) & Former Vice Chancellor
Department of Zoology
Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati University, Ajmer, India
Dr. B. Kumaran
Endocrinology & Toxicology
Indira Gandhi College of Arts and Science
Pondicherry University, Puducherry, India
Prof. Tao Liu
Department of Natural Products Chemistry
China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Prof. Monisha Banerjee
Molecular & Human Genetics Laboratory
Department of Zoology
University of Lucknow, UP, India
Dr. Yiming Yang
College of Basic Medical Sciences
Jilin University, Changchun, China
Dr. Reena Mathur
Professor (Retd.), Department of Zoology
Rajasthan University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Dr. A. Subramanyam
Professor (Retd.), Department of Zoology
Annamalai University, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India
Prof. Huazhe Yang
School of Intelligent Medicine
China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Dr. Syed Musthapa Meeran
Senior Principal Scientist & Professor AcSIR
Department of Biochemistry
CSIR-Central Food Technological Research Institute (CFTRI)
Mysore, Karnataka, India
Prof. Md. Equbal Ahmad
Department of Zoology
M. Bhagalpur University, Bhagalpur, Bihar, India
Editorial Board Members
Dr. Chuyuan Wang
Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism
The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Dr. Ruchi Jain
Department of Chemistry, SBSS College, Lalit Narayan Mithila University, Darbhanga, Bihar, India
Dr. Sudhir Kumar
Department of Zoology, B. R. D. Post Graduate College,
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gorakhpur University
Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh, India
Dr. Jiayu Chen
Department of Gastroenterology
Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
Dr. Tingting Liu
School of Pharmacy
Liaoning Agricultural Vocational and Technical College, Yingkou, China
Dr. Sam A. Masih
Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences (SHUATS), Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India
Dr. Yi Xin
School of Management
Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
Dr. Roli Mathur
Head , ICMR-Bioethics Unit, Bengaluru, India
Prof. Yogesh Rawal
Department of Zoology
Punjab University, Chandigarh, India
Dr. Shahla Yasmeen
Professor & Head, Department of Zoology
Patna University, Patna, Bihar, India
Dr. Ying Li
Medical Research Center
Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining, China
Dr. Boni Amin Laskar
Scientist-E, ZSI-HARC, Solan, Himachal Pradesh, India
Dr. Syed Mohi Alam Rizvi
Department of Zoology
Lalit Narayan Mithila University, Darbhanga, Bihar, India
Dr. Shamsun Nehar
Department of Zoology
Ranchi University, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
Guide for Reviewers and Editors
Guide to Reviewers: BioMed and BioSci Advances
Welcome to the Instructions for Reviewers for BioMed and BioSci Advances. As a valued reviewer, your expertise and insights play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and integrity of the journal’s publications. Your thorough evaluation and constructive feedback are instrumental in shaping the direction of scientific discourse in the field of Biomedical, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology. Below are guidelines to assist you in conducting a comprehensive review of manuscripts submitted to BioMed and BioSci Advances.
- Confidentiality: As a reviewer for BioMed and BioSci Advances, it is crucial to maintain the confidentiality of the manuscripts you are assigned to review. This means refraining from discussing the content of the manuscripts with anyone other than the editorial office. By upholding confidentiality, you contribute to the integrity of the peer review process.
- Timeliness: Time is of the essence in the peer review process. Reviewers are expected to evaluate manuscripts promptly and submit their reports within the specified deadline. If circumstances arise that prevent you from meeting the deadline, it is important to communicate with the editorial office and request an extension in advance.
- Constructive Feedback: Reviewers play a pivotal role in providing constructive feedback to authors. When assessing manuscripts, focus on identifying both strengths and weaknesses. Your comments should be specific, objective, and aimed at helping authors improve their work. Point out areas where the manuscript excels and areas where it could be enhanced.
- Originality and Ethical Standards: Evaluate the originality of the research presented in the manuscript and ensure that it meets ethical standards. Verify that proper citations are provided for previously published work and assess whether the research has been conducted in accordance with ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Content Evaluation: Dive deep into the content of the manuscript and evaluate its significance, novelty, and scientific rigor. Scrutinize the methodology used, the interpretation of results, and the contribution the research makes to the field. Your evaluation should be thorough and objective, focusing on the scientific merit of the work.
- Clarity and Presentation: Assess the clarity and organization of the manuscript. Consider factors such as the writing style, structure, and coherence of the presentation. Provide feedback on how the manuscript could be improved to enhance clarity and readability for readers.
- Recommendation: Based on your evaluation, make a recommendation regarding the manuscript’s fate—whether it should be accepted, revised, or rejected. Justify your recommendation with specific comments and suggestions for improvement. Your recommendation will be instrumental in guiding the editorial decision-making process.
- Conflicts of Interest: Be transparent about any potential conflicts of interest that may influence your review. If you have personal or professional connections to the authors or their research, disclose them to the editorial office. If you feel that a conflict of interest may compromise your impartiality, notify the editorial office immediately.
- Respectful Communication: Maintain professionalism and respect in all communications related to the peer review process. Avoid personal or derogatory remarks and focus solely on the scientific content of the manuscript. Your goal is to provide feedback that is helpful and constructive, regardless of your recommendation.
- Final Decision: Your review will be considered alongside those of other reviewers by the editorial team to make a final decision on the manuscript. Your feedback is invaluable in ensuring the quality and integrity of the research published in BioMed and BioSci Advances. Thank you for your dedication to the peer review process.
Guide to Editors: BioMed and BioSci Advances
Welcome to the comprehensive Guide to Editors for BioMed and BioSci Advances. As an editor for our esteemed journal, your pivotal role revolves around ensuring the quality, integrity, and timely dissemination of groundbreaking research within the realm of Biomedical, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology. This detailed guide is designed to equip you with the necessary instructions and best practices to navigate the editorial process with proficiency and efficacy. Your dedication and commitment as an editor are invaluable to the success and reputation of BioMed and BioSci Advances.
Editorial Workflow:
- Your initial task involves the meticulous assignment of suitable reviewers, drawing upon their expertise and availability to ensure thorough and insightful assessments.
- Efficiently manage the peer review process by overseeing the timely completion of reviews and judiciously evaluating reviewer comments to make informed editorial decisions.
- Maintain proactive communication with authors throughout the review process, providing updates, guidance, and constructive feedback as required.
- Thoughtfully evaluate the feedback provided by reviewers and exercise sound judgment in determining manuscript acceptance, revision, or rejection, upholding the journal’s standards of excellence.
Manuscript Handling:
- Uphold the journal’s submission guidelines rigorously, ensuring that submitted manuscripts adhere to formatting requirements and ethical standards.
- Conduct a comprehensive initial assessment of manuscripts to ascertain their suitability for peer review, considering factors such as novelty, relevance, and scientific rigor.
- Effectively manage revisions and resubmissions, facilitating productive interactions between authors and reviewers to address queries, concerns, or suggestions for improvement.
- Strive for consistency and rigor in the editorial process, upholding the journal’s reputation for scholarly excellence and integrity.
Ethical Considerations:
- Familiarize yourself thoroughly with the journal’s policies on plagiarism, authorship, conflicts of interest, and ethical conduct, ensuring strict adherence to established guidelines.
- Promptly address any instances of ethical misconduct or concerns, conducting impartial investigations and implementing appropriate measures in accordance with established procedures.
- Maintain the utmost confidentiality throughout the editorial process, safeguarding the anonymity of reviewers and respecting the privacy of authors to uphold the integrity of the peer review process.
Collaboration and Communication:
- Foster a collaborative and supportive environment conducive to constructive dialogue and scholarly exchange among authors, reviewers, and editorial board members.
- Encourage open communication and facilitate constructive feedback to foster continuous improvement in manuscript quality and scientific rigor.
- Serve as a liaison between authors and reviewers, facilitating effective communication and resolution of any conflicts or misunderstandings that may arise during the editorial process.
Continuous Improvement:
- Stay abreast of the latest developments and advancements in the field of Biomedical, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology and scholarly publishing, adapting editorial practices to reflect evolving standards and expectations.
- Solicit feedback from authors, reviewers, and colleagues to identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of the editorial process.
- Strive for continuous improvement in all aspects of editorial management, contributing to the enhancement of the journal’s reputation and impact within the scientific community.
Publication Ethics
Publication Ethics for BioMed and BioSci Advances
At BioMed and BioSci Advances, published by Ariston Publications, we uphold the highest ethical standards in scientific publishing to ensure the integrity, credibility, and trustworthiness of the research we disseminate. Our commitment to ethical practices extends across all stages of the publication process, from manuscript submission to post-publication dissemination. Our publication ethics policies are designed to guide authors, reviewers, editors, and all stakeholders involved in the publishing process. Adherence to these ethical principles is paramount to maintain transparency, fairness, and trust in scholarly communication.
- Authorship and Author Responsibilities: Authors are expected to adhere to the following ethical principles:
Authorship Criteria:
- Authorship eligibility hinges upon significant contributions to conceiving, designing, executing, or interpreting the research study.
- All contributors with substantial involvement in the work merit authorship recognition, while those offering support or assistance without meeting authorship criteria should be acknowledged accordingly.
- Authors are required to reveal any potential conflicts of interest that could impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
Originality and Plagiarism:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the originality of their work and confirming that it has not been previously published or is under consideration elsewhere for publication.
- Any form of plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, is unacceptable and will lead to immediate rejection or retraction.
- Any form of plagiarism, whether it involves directly copying text, ideas, or data without appropriate acknowledgment, is strictly forbidden.
- Editors utilize plagiarism detection software to screen submitted manuscripts and address any suspected cases of plagiarism promptly.
Conflict of Interest:
- Authors must reveal any potential conflicts of interest that might impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
- This includes financial interests, employment affiliations, consulting arrangements, or personal relationships.
Data Integrity:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the accuracy and integrity of their data, presenting research findings with honesty and transparency.
- Studies involving human subjects, animals, or sensitive data must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain the requisite approvals and permissions.
- Fabrication, falsification, or manipulation of data is considered unethical and constitutes scientific misconduct.
- Peer Review Process:
- Reviewers must uphold the confidentiality of the peer review process and refrain from sharing any details about the manuscript or their assessment with unauthorized individuals without permission from the journal.
- Peer review is conducted with fairness.
- Reviewers are expected to conduct their evaluations impartially and offer constructive feedback aimed at enhancing the manuscript’s quality.
- Reviewers should declare any potential conflicts of interest and evaluate manuscripts objectively, focusing solely on their scientific quality.
- Editors oversee the peer review process to ensure its integrity and rigor, avoiding bias or favoritism.
- Editorial Responsibilities:
Editorial Integrity:
- Editors uphold the integrity and quality of the editorial process, maintaining objectivity and impartiality in decision-making.
- Manuscripts are evaluated based on their scientific quality, significance, originality, and methodological rigor, without discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, religion, region, or institutional affiliation.
Conflict of Interest:
Editors are responsible for managing conflicts of interest transparently and impartially, ensuring that they do not compromise the integrity of the editorial process.
Transparency:
Editors should ensure transparency in the publication process by clearly communicating the editorial policies, peer review process, and any conflicts of interest.
- Post-Publication Concerns:
Corrections and Retractions:
- Authors, editors, and publishers are responsible for promptly addressing errors or inaccuracies in published articles, issuing corrections, clarifications, or retractions as necessary.
- Corrections are published promptly to rectify errors and maintain the integrity of the scientific record.
Ethical Concerns:
Any concerns about ethical issues, such as research misconduct or violations of publication ethics, will be thoroughly investigated by the journal and appropriate actions will be taken.
- Compliance with Policies and Guidelines:
All stakeholders are expected to comply with the journal’s policies, guidelines, and ethical standards, as well as relevant regulatory requirements and best practices in scholarly publishing.
Indexing and Abstracting
BioMed and BioSci Advances is committed to achieving high visibility and widespread dissemination of the research it publishes. While the journal is currently not indexed, we are actively working towards being indexed in prominent databases and directories relevant to Biomedicine, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology. Our goal is to ensure that the valuable and impactful research published in BioMed and BioSci Advances reaches a broad audience of scholars, researchers, and practitioners in the field.
We are in the process of applying for indexing in key databases and directories, such as Scopus, Web of Science, MEDLINE/PubMed and others, to enhance the visibility and discoverability of articles published in the journal. As we progress in our efforts to expand the journal’s indexing coverage, we aim to increase its impact and ensure that the research published in BioMed and BioSci Advances contributes to the advancement of knowledge and practical solutions in Biomedicine, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology. Stay tuned for updates as we work towards achieving these goals and further elevating the journal’s reach within the global scientific community.
Article Processing Charges
At present, there are no article processing charges (APCs) associated with publishing in BioMed and BioSci Advances. As an open-access journal, all articles are published free of cost to authors. The publisher covers the expenses incurred in the publication process, allowing authors to disseminate their research without any financial burden. There are no fees for submission, processing, or publication of articles in BioMed and BioSci Advances. This approach ensures equitable access to scientific knowledge and supports the dissemination of research findings across the global scientific community.
Special Issues
BioMed and BioSci Advances welcomes proposals for special issues that align with the journal’s aims, scope and objectives. Special issues provide an opportunity to delve into specific topics or emerging areas within Biomedicine, Bioscience, Bioengineering, Biotechnology and related fields, offering a focused platform for in-depth exploration and discussion.
If you have a proposal for a special issue, please submit it to the editorial office for consideration. Your proposal should include a brief outline of the proposed topic, its significance and relevance to the field, potential contributors, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Once your proposal is received, it will undergo careful evaluation by the editorial team to assess its suitability for publication in BioMed and BioSci Advances. If approved, you will be invited to serve as a guest editor or co-editor for the special issue, working closely with the editorial team to oversee the review and publication process.
We look forward to receiving your proposals and collaborating with you to bring forth exciting and impactful special issues for our readership.
Please submit the special issue proposal at: info@aristonpubs.com
Conferences
BioMed and BioSci Advances welcomes the opportunity to collaborate with organizers of conferences, symposiums, and workshops to publish special issues or proceedings featuring research articles presented at these events.
If you are organizing a conference or similar academic gathering and wish to publish selected research papers in BioMed and BioSci Advances, we encourage you to reach out to our editorial office with your proposal. Your proposal should include details such as the theme and scope of the conference, the number of anticipated submissions, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Upon receiving your proposal, our editorial team will review it carefully to assess its alignment with the journal’s scope and objectives. If approved, we will work closely with you to facilitate the submission and review process for the conference papers, ensuring timely publication in a dedicated special issue or proceeding.
By publishing conference-related research in BioMed and BioSci Advances, authors can benefit from the journal’s wide readership and open access model, maximizing the visibility and impact of their work within the Biomedical, Bioscience, Bioengineering, and Biotechnology community. We look forward to the opportunity to collaborate with you on showcasing cutting-edge research from your conference in our journal.
Article in Press
Current Issue
Biocontrol Potential of Native Trichoderma Isolates Against Phytophthora infestans in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): Isolation, Characterization, and Antagonistic Efficacy
Mat Both Dol, Delelegn Woyessa, Shiferaw Demissie, M. Sadre Alam Fakhri
Summary: This research isolated and characterized native Trichoderma strains from tomato rhizospheres in Ethiopia to evaluate their antagonistic effects against P. infestans. Ten isolates were obtained, and four strains exhibited substantial growth inhibition of the pathogen, with Ju-TGDb-2 showing the highest efficacy (61.4%). These findings suggest that native Trichoderma isolates can be used as effective biocontrol agents, offering a promising solution for managing late blight in tomatoes.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 May 2025
BioMed and BioSci Advances 2(2), 105-113 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/bba.2025.0105.