

Welcome to MatSci Express (MSE), a premier multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal committed to the rapid dissemination of groundbreaking research in the dynamic field of materials science. Our mission is to provide a robust platform for scientists, scholars, and researchers to showcase their cutting-edge discoveries and advancements. MatSci Express (MSE) stands at the forefront of interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together experts from various fields including science, engineering, and medicine. We publish original research articles, comprehensive reviews, and insightful communications, fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange across diverse disciplines. By uniting the expertise of materials scientists, physicists, engineers, ceramicists, chemists, metallurgists, theoreticians, biologists, medical scientists, and technocrats, we aim to foster collaboration and innovation across diverse disciplines. With a focus on both fundamental principles and practical applications, MSE explores the latest frontiers of advanced materials, driving innovation and progress in the field.
Volume 2, Issue 2 (June 2025)
Research Articles
Synthesis and Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Co/MnO@C Composite Derived from Rod–like CoMn MOF–74
Shuo Zhang, Shuaiqi Ren, Mingyu Han, Xiangyu Chen, Jiahang Qiu, Mu Zhang
Summary: Co/MnO@C composites were synthesized via a MOF-74 precursor route and subjected to high-temperature reduction to enhance microwave absorption properties. The study demonstrated that a Co:Mn ratio of 0.6 provided the best impedance matching and attenuation efficiency, achieving a strong reflection loss and broad absorption bandwidth. The results emphasize the role of synergistic dielectric and magnetic losses in optimizing absorption performance, paving the way for the design of next-generation electromagnetic shielding materials.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 07 February 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 132-141 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0132Comparative Adsorption Study of Methylene Blue Dye Using Green and Chemically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles
Teenu Jasrotia, Neha Garg, Ganga Ram Chaudhary, Savita Chaudhary, Rajeev Kumar, Abhijit Dan
Summary: This study reinforces the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using both green and chemical method. Then characterization and toxicological studies were carried out to determine the behaviour of the NPs. A comparative analysis for the adsorptive removal of MB dye was done to compare the efficiency of both NPs. The results were found to be better with green synthesized NPs showing higher efficiency with good reusability and regenerability ability. This study fosters the innovation of green methods for sustainable wastewater methodologies.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 11 February 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 142-160 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0142Importance of Metal–Ligand Bond Stretching Frequency in Cancer Drug Activity of Ru and Os Metal Clusters
Moumita Dinda, Arijit Bag
Summary: This study investigates the anticancer potential of tri-ruthenium (0) carbonyl clusters and their osmium analogs, focusing on metal-ligand bond stretching frequency and CO bond vibrational characteristics. Computational and in-silico analyses reveal that osmium derivatives exhibit enhanced drug activity due to optimized electronic interactions. By applying a property-based drug design (PBDD) framework, the study predicts key pharmacological parameters, offering insights into the rational design of transition metal-based chemotherapeutics for improved efficacy and stability in cancer treatment.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 13 February 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 161-171 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0161First-Principles Investigation of Vibrational Modes in Calcium Monochalcogenide Nanoparticles: Size, Morphology, and Composition Effects
Nikos Aravantinos-Zafiris, Fotios I. Michos, Mihail M. Sigalas
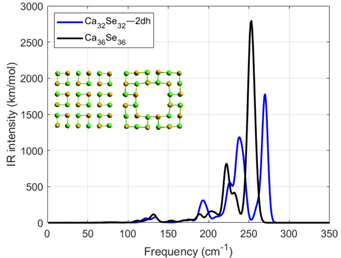
Summary: Density functional theory (DFT) was employed to investigate the vibrational spectra of CaₓYₓ (Y=S, Se, Te) nanoparticles (x=4–36). Results showed size-dependent phonon modes, with 1D structures exhibiting the strongest IR activity. Sulfur-based NPs displayed the highest frequencies, while tellurium analogs showed the lowest. Larger NPs (x=32,36) revealed complex spectra with defect-induced modes, highlighting their tunability for nanoscale applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 February 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 172-180 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0172Simulation–Based Optimization of Graphene Oxide Interfacial Layers in Heterojunction Germanium Solar Cells Using PC1D
Deb Kumar Shah, Houcine Naim, Abed Bouadi, Ahmad Umar, Sotirios Baskoutas, M. Shaheer Akhtar
Summary: This study utilized PC1D simulations to optimize the performance of heterojunction-based germanium (Ge) solar cells by engineering interfacial layers. The impact of emitter/base thickness, doping concentrations, and interfacial materials (ZnO, GO, and GO/ZnO bilayer) on photovoltaic parameters was systematically analyzed. Results demonstrated that a 10 nm GO/40 nm ZnO bilayer significantly enhances efficiency (21.15%) by reducing recombination and improving charge transport. The study provides design guidelines for high-efficiency Ge solar cells applicable in space and terrestrial photovoltaics.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 26 February 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 181-191 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0181Enhanced Acetone Sensing Performance of Silver–Doped Tin Oxide (Sn₁₋ₓAgₓO) Thick Films Synthesized via Hydrothermal Method
Laxman P. Chikhale, Nitin A. Tupsaminar
Summary: Pure and Ag-doped SnO₂ nanostructures were synthesized hydrothermally and fabricated into thick-film gas sensors. The 1 mol% Ag-doped SnO₂ (S2) exhibited optimal acetone sensing performance, with 94% response at 275°C, minimal interference from ethanol/LPG, and long-term stability (60 days). The improved performance stems from controlled crystallite size, catalytic Ag doping, and efficient surface reactions. This work presents a viable approach for developing high-performance, cost-effective acetone sensors for industrial and medical applications, particularly diabetes breath analysis.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 23 March 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 192-198 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0192Eco–Friendly Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Tinospora cordifolia Stem Extract: Characterization and Enhanced Antifungal Efficacy
Pankaj Chopra, Gautam Madhok, Anshula Chauhan, Dhriti Bragta, Muskanpreet Kaur, Manpreet Kaur Dhaliwal, Pushplata Jannagal, Sanjay Panwar, Savita Chaudhary, Rajeev Kumar
Summary: ZnO NPs were successfully synthesized using Tinospora cordifolia stem extract and characterized via UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM, and EDX. The NPs showed a spherical morphology (40 nm) and significant antifungal activity, with 88.24% inhibition at 1000 ppm. The study confirms the effectiveness of plant-mediated green synthesis in producing stable, bioactive nanoparticles, suggesting their potential in antifungal formulations, crop protection, and medical applications while promoting sustainable nanotechnology practices.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 April 2025
MatSci Express 2(2), 199-206 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0199Volume 2, Issue 1 (March 2025)
Review
Emerging Materials for Next Generation Supercapacitors: Exploring the Latest Trends and Innovations
Nikita A. Wadodkar, Rahul S. Salunke, Sarla K. Pawar, Amardeep M. Patil, Ahmad Umar, D. J. Shirale
Summary: This review focuses on advanced materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, metal oxides, and conductive polymers, all of which have shown remarkable potential in improving supercapacitor performance, particularly in terms of electrochemical stability, energy density, and long-term cycling. It also covers the broad applications of supercapacitors across industries like electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics, positioning them as next-generation energy storage solutions.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 September 2024
MatSci Express 2(1), 01-28 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0001Exploring the Potential of Carbon Based Materials in Air Purification
Neha Garg, Armaandeep Kaur, Abhijit Dan, Savita Chaudhary
Summary: This review explores the potential of carbon-based nanomaterials (CBNs) synthesized from atmospheric particulates for air purification. It covers various synthesis methods, adsorption mechanisms, and photocatalytic processes used for air pollutants like VOCs and toxic gases. Additionally, the synergistic effects of CBNs with other materials, such as TiO₂ and graphene, are discussed. By converting harmful pollutants into useful materials, this study presents new opportunities for environmental remediation, addressing air pollution challenges while enhancing air purification technologies.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 September 2024
MatSci Express 2(1), 29-57 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0029Enhanced Functionalities of Co–Doped Sr–Eu Lanthanum Nickel Manganese Oxide (La2NiMnO6): A Review of Properties and Applications
Salman Firdous, Inder K. Pandey, Gul Faroz A. Malik
Summary: This review explores the unique functionalities of La₂NiMnO₆ (LNMO) when co-doped with strontium and europium, emphasizing its properties and applications across multiple fields. It assesses LNMO’s half-metallicity, Curie temperature, and responsiveness to magnetic and dielectric stimuli, which make it ideal for energy storage, optoelectronic, and spintronic applications. The article consolidates recent research findings on LNMO’s structural, electronic, and catalytic behaviors, underscoring its versatility and potential for sustainable, efficient technologies in fields like solar energy, hydrogen generation, and lead-free electronic devices.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 18 October 2024
MatSci Express 2(1), 58-76 (2025)
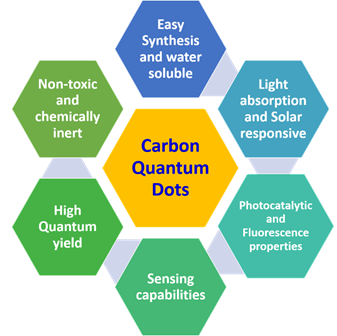
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0058Advancements in Gadolinium–doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Dual–Modal Bioimaging: Synthesis and Applications
Zobia Asghar, Fawad Ahmad, Muhammad Imran Khan, Abdallah Shanableh, Mushtaq Hussain Lashari
Summary: This study reviews the synthesis and applications of gadolinium-doped carbon quantum dots (Gd-CQDs) for dual-modal bioimaging. Gd-CQDs combine MRI and fluorescence imaging, offering high biocompatibility, tunable optical properties, and reduced toxicity. The one-pot synthesis method is emphasized for its scalability and superior particle properties. Future directions include enhancing stability, minimizing cytotoxicity, and exploring multi-functional uses like targeted drug delivery. Gd-CQDs hold promise for advancing personalized medicine, multi-modal imaging platforms, and safer diagnostic tools in clinical and biomedical applications.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 11 November 2024
MatSci Express 2(1), 77-92 (2025)
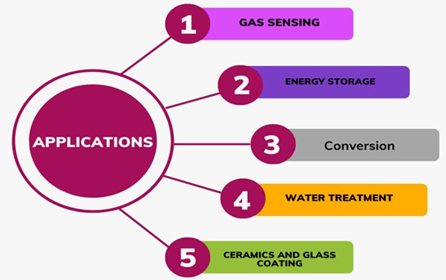
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0077An Insight into SnO2 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications
Nikki Bharadwaj, Ishita Kapil, Pinky Yadav, Ayana Bhaduri
Summary: This study explores the synthesis and applications of SnO₂ nanoparticles, a key class of transition metal oxide semiconductors. With a band gap of 3.6-4.0 eV, SnO₂ nanoparticles exhibit high sensitivity, excellent thermal and chemical stability, rapid electron mobility, and superior electrical conductivity. These properties make them highly suitable for applications in transparent conductors, transistors, gas sensors, batteries, electrochromic devices, and photocatalysis. The review highlights various synthesis processes and their impact on material performance, particularly in energy and environmental sustainability.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 11 January 2024
MatSci Express 2(1), 93-112 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0093Research Articles
Comparative Analysis of Green and Chemical Synthesis Approaches for Lead Ion Detection Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Teenu Jasrotia, Neha Garg, Ganga Ram Chaudhary, Savita Chaudhary, Rajeev Kumar, Abhijit Dan
Summary: This research involves the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles via two different approaches (green and chemical) with better characteristics. The prepared NPs acquired high specificity and sensitivity towards toxic Pb²⁺ ion detection. FePE-NPs exhibited more efficiency with lower LOD value as compared to FeCH-NPs. Also, high recovery efficiency (94-98%) of NPs in real water samples reinforced its potential application in environmental remediation. This study encourages young researchers towards formation of various NPs using green method to contribute towards safeguarding the environment.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 13 January 2025
MatSci Express 2(1), 113-123 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0113Optimization of Polymerization Parameters for Enhanced Paracetamol Selectivity of Poly(1,4-diaminobenzene) Membrane Electrodes
Gamze Erdoğdu
Summary: The electrochemical polymerization of 1,4-diaminobenzene at 0.600 V led to the formation of a selective PDB membrane on a gold electrode. The optimized film, with a thickness of 7 mC, demonstrated high selectivity for paracetamol while effectively blocking ascorbic acid. Monomer and electrolyte concentrations were fine-tuned to achieve the best response. The study highlights the membrane’s potential as a cost-effective and reliable sensing platform for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications, ensuring precise, interference-free paracetamol detection.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 26 January 2025
MatSci Express 2(1), 124-131 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2025.0124Volume 1, Issue 4 (December 2024)
Review
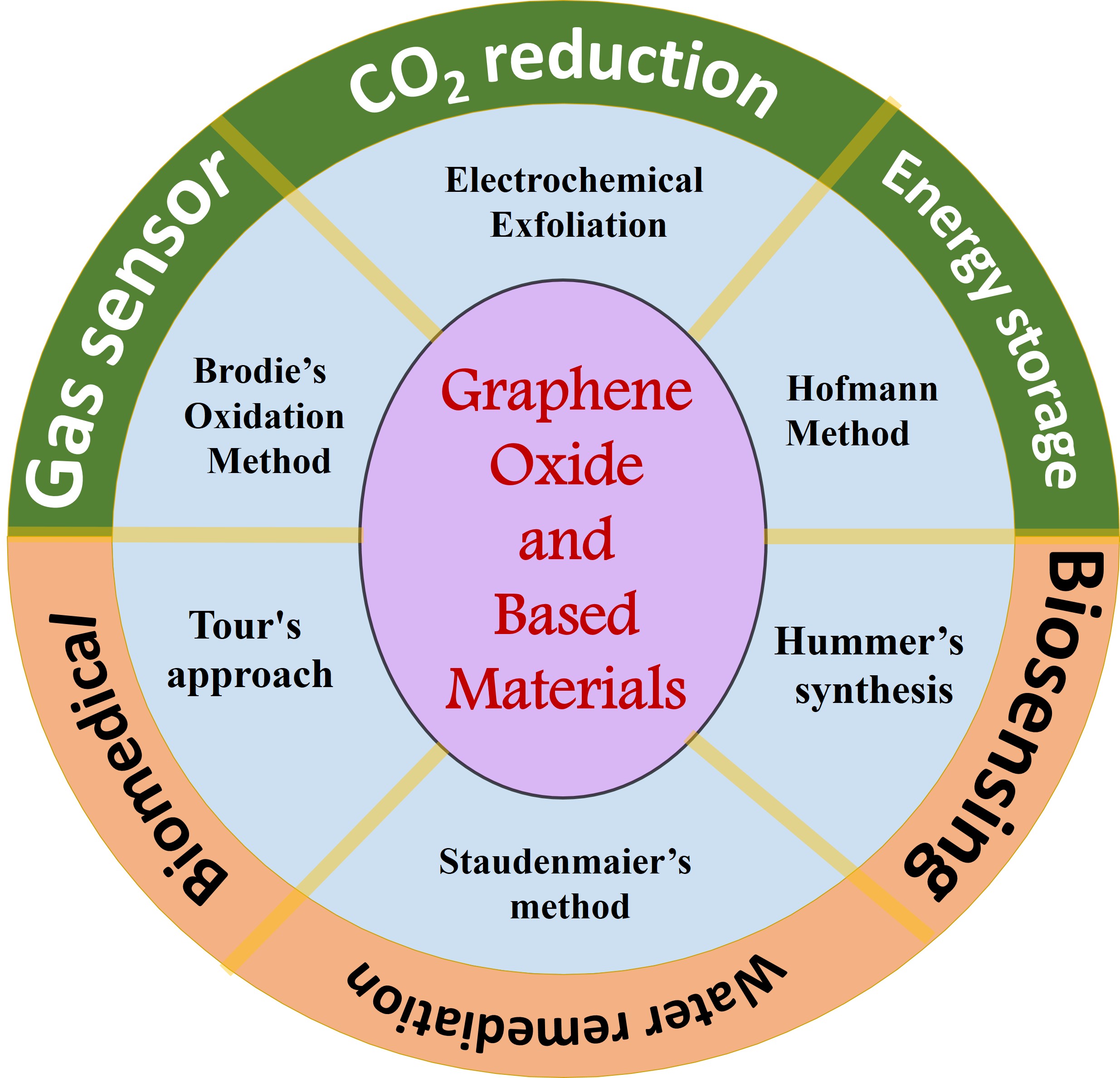
Graphene Oxide and Based Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications – A Comprehensive Review
Nosheen Farooq, Zohaib ur Rehman, Ayesha Hareem, Romaisa Masood, Rashida Ashfaq, Iqra Fatimah, Shahid Hussain, Sajid Ali Ansari, Nazish Parveen
Summary: This review explores the synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide (GO) and related materials. It examines recent advancements, including improved Hummer’s techniques, and highlights the role of GO in energy storage, environmental remediation, sensors, electronics, and so on. The review also addresses current challenges and future research directions, providing a comprehensive resource for the development of GO-based technologies.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 185-231 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0185Research Articles
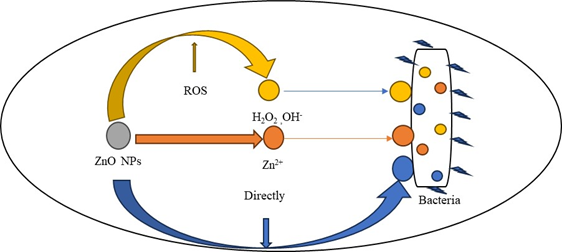
Plant Mediated Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Butea monosperma Plant Extract and Their Antibacterial Applications
Tanika Thakur, Manish Kumar, Abhishek Walia, Deepika Kaushal
Summary: This research demonstrates the plant-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Butea monosperma extract. The synthesized nanoparticles, confirmed by various analytical techniques, show effective antibacterial properties against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. This eco-friendly approach provides a viable method for producing potent antibacterial agents for biomedical and environmental applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 232-242 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0232First principle investigation of Sr and Eu doped La2NiMnO6: Structural, Electronic, Optical, Magnetic, and Spintronics properties
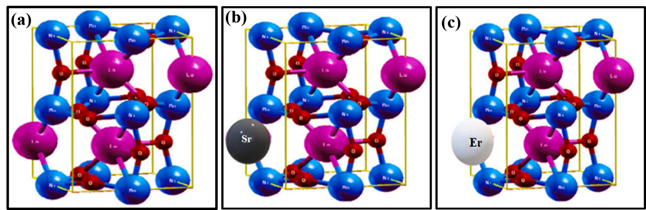
S. Firdous, G. F. A. Malik, N. Parveen, F. A. Khanday, I. K. Pandey
Summary: The research uses Density Functional Theory (DFT) and LDA + U to analyze Sr and Eu-doped La₂NiMnO₆ (LNMO). The study finds that doping with Sr and Eu enhances the dielectric constant, optical conductivity, and magnetic properties of LNMO. These improvements make the doped material suitable for applications in energy storage, optoelectronics, and spintronics, highlighting its potential for technological advancements in these fields.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 243-252 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0243Development and Modelling of a Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensor for Detecting Harmful Chemicals in Polycarbonate Plastics
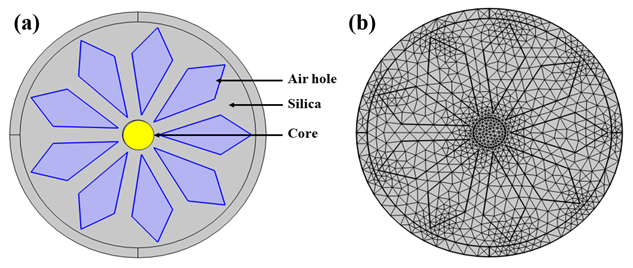
Pratishtha Pandey, Sapana Yadav, D. K. Dwivedi, Pooja Lohia
Summary: A photonic crystal fiber (PCF) sensor with a wheel-shaped, floral-patterned cladding was developed to detect harmful chemicals in polycarbonate plastics. The sensor showed high sensitivities of 90.716% for BPS and 84.688% for BPA. It exhibited low confinement loss and high nonlinearity, making it suitable for chemical detection and other applications. The sensor’s design allows real-time, label-free detection, enhancing its utility in various sensing and photonic device applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 22 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 253-261 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0253Magnetoexciton in the Ellipsoidal Quantum Dots
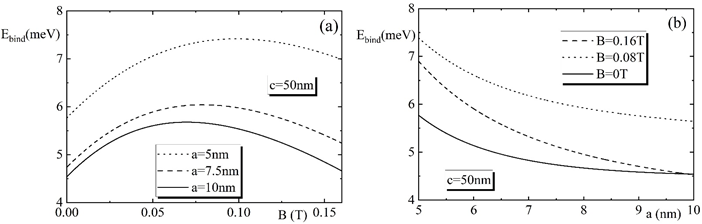
Y.Y. Bleyan, S. Baskoutas, D.B. Hayrapetyan
Summary: This study theoretically investigates exciton states in strongly prolate GaAs ellipsoidal quantum dots under an external magnetic field using the variational method. It examines the effects of the magnetic field and quantum dot geometry on exciton energy, binding energies, and magnetization. The research also estimates the radiative lifetime of magnetoexcitons, revealing critical insights into how these factors influence excitonic behavior. The findings offer valuable guidance for optimizing quantum dot-based technologies in various applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 29 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 262-268 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0262Experimental Analysis of Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Mortar Incorporating Agricultural Waste Materials
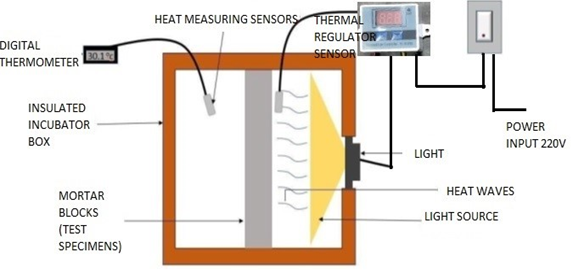
Md Ehsanullah, Satyam Singh, Rohit Kumar
Summary: The study investigates the thermal and mechanical properties of mortar incorporating Rice Husk Ash (RHA) and Bagasse Ash (BA) as sustainable alternatives. Results show significant reductions in thermal conductivity and shrinkage, with improved mechanical strength in both conventional and geopolymer mortars. RHA and BA-based mortars demonstrated superior thermal performance, particularly at 15% sand replacement levels. The findings underscore the benefits of agro-waste in creating efficient, sustainable construction materials.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 August 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 269-277 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0269Modelling the Optical Properties of Gold Nanoparticles using COMSOL Multiphysics: Influence of Geometry, Environment, and Temperature
Tigran A. Sargsian, Maksim Ya. Vinnichenko, David B. Hayrapetyan
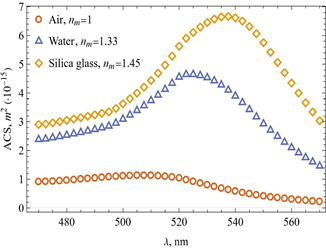
Summary: The study investigates the optical properties of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) using COMSOL Multiphysics simulations, exploring the effects of geometry, environment, and temperature. Various shapes, including nanospheres, nanorods, and core/shell structures, were analyzed in different media, and the dielectric function was modeled as a function of size and temperature. Results showed that larger particle sizes and higher temperatures cause a red-shift in localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR), offering insights for tailoring Au NP properties for applications like imaging and drug delivery.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 11 August 2024
MatSci Express 1(4), 278-290 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0278Volume 1, Issue 3 (September 2024)
Research Articles
Density Functional Theory (DFT) Based Local Density Approximation (LDA) Study on Tailoring Electronic and Optical Properties of SnO and In-Doped SnO
Mohammad Mahafuzur Rahaman, Md. Abdul Momin, Abhijit Majumdar, Mohammad Jellur Rahman
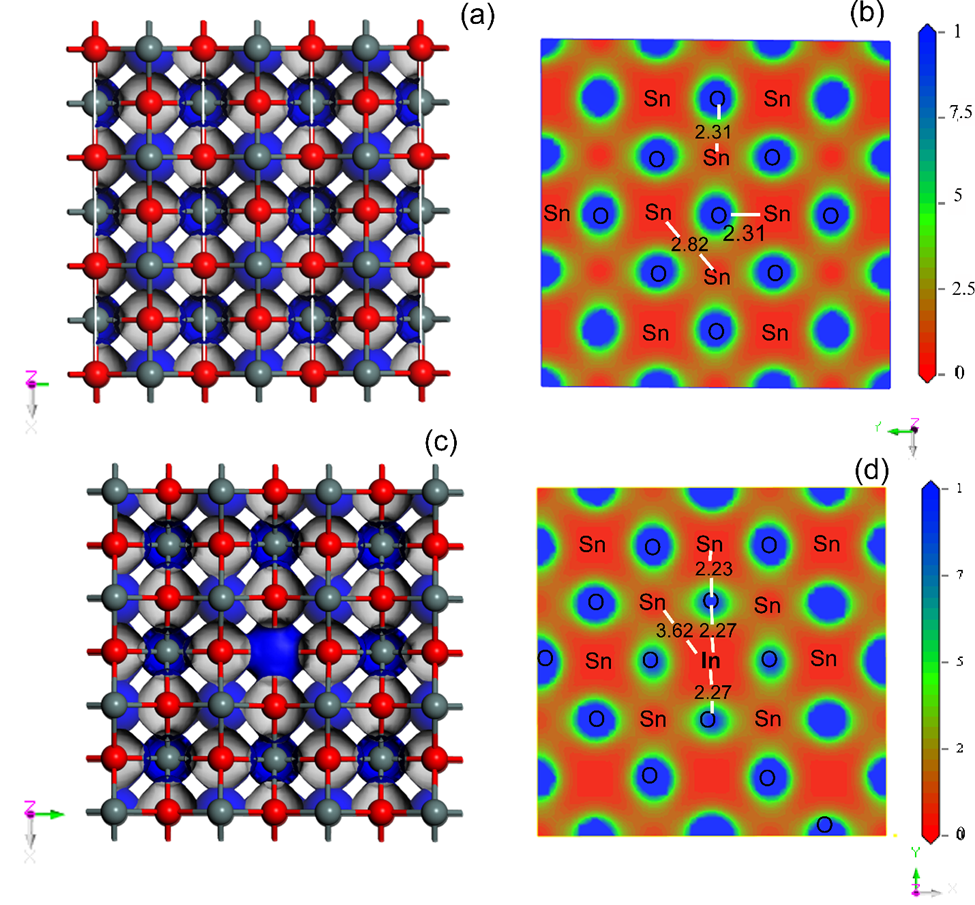
Summary: Using DFT and LDA, this study examines the structural, electronic, and optical properties of SnO and In-doped SnO. The results show that In doping reduces the band gap from 2.61 eV to 2.00 eV and decreases the refractive index and dielectric function. These changes suggest enhanced properties for electronic and optoelectronic applications, making In-doped SnO a promising candidate for future device development.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 125-134 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0125Synthesis and Characterization of CdS and Sr-Doped CdS Quantum Dots: Impedance Analysis for Nano-Tuned Electronic Applications
G. N. Dar, A. Firdous, S. Irfan, A. H. Pandith, I. Nazir, K. A. Shah, N. Ali, S. Showket, M. Q. Lone
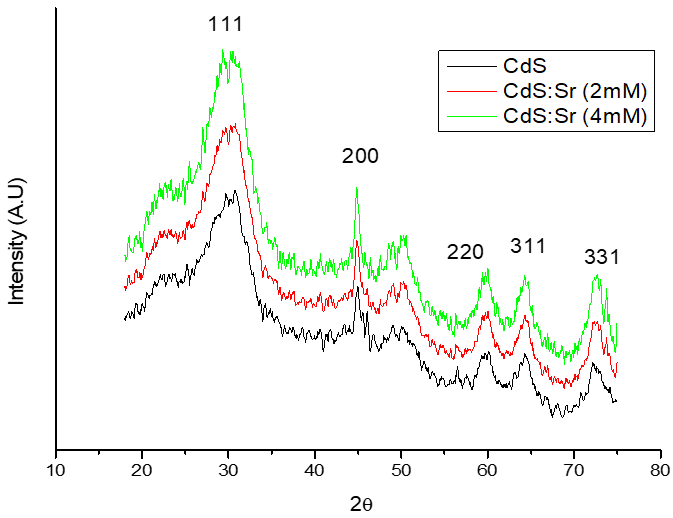
Summary: Pure and Sr-doped CdS quantum dots were synthesized via chemical precipitation and characterized using several techniques. The doping process was validated, and the nanomaterials exhibited hexagonal wurtzite structures with sizes within the quantum confinement regime. Impedance spectroscopy revealed frequency-dependent electrical properties, highlighting their capacitive nature and potential for use in nano-tuned electronic devices, such as tunable capacitors and high-frequency oscillators.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 08 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 135-141 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0135Deciphering the evolution of electronic and magnetic properties in alkali doped nickel oxide: An In-silico approach
Nazir Ahmad Teli, Showkat Hassan Mir
Summary: Using the DFT+U method, this study explores the effects of alkali metal doping (Li, Na, K) on nickel oxide (NiO). The doped compounds exhibit half-metallic properties, with a spin-down band gap varying linearly with the Hubbard potential. The total magnetic moment in supercells demonstrates 100% spin polarization at the Fermi level, indicating potential applications in spintronics and advanced electronic devices.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 09 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 142-150 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0142First Principle Study of Tunnel Magnetoresistance of Various Oxide Materials
Sharif Saleem, Gul Faroz Ahmad Malik, Amir Farooq, Farooq Ahmad Khanday
Summary: The paper presents a first-principle study on tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) across more than 30 oxide materials, categorized by their bandgaps. Results show that materials with lower bandgaps yield higher TMR ratios, with Cu2O achieving the maximum TMR. The study concludes that oxide materials with bandgaps under 3 eV are optimal for device-level fabrication, providing 100% TMR up to 3 nm thickness.
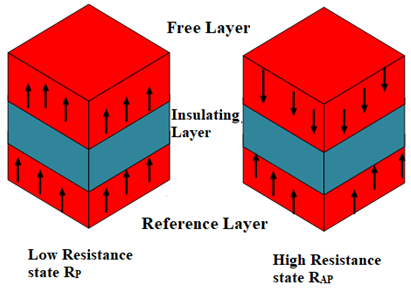
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 11 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 151-161 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0151Ceramic/Polymer Nanodielectrics: Towards a Multifunctional or Smart Performance
Georgios C. Psarras
Summary: This study explores ceramic nanoparticles/polymer composite nanodielectrics, emphasizing their tunable mechanical, thermal, electrical, and magnetic properties. By incorporating polar oxides or piezo/ferroelectric materials, the composites gain additional functionalities, paving the way for the development of smart materials. These multifunctional composites show promise for diverse engineering applications due to their enhanced performance and processability.
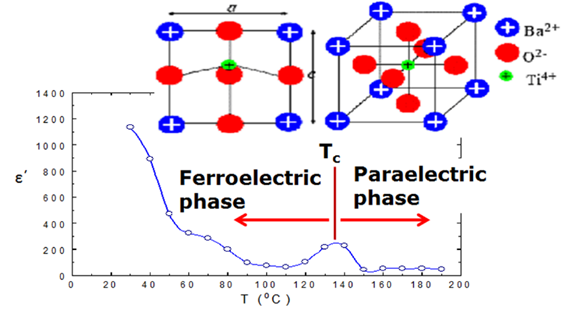
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 12 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 162-169 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0162Eco-Friendly Electrochemical Sensor for Accurate Soil Nitrate Detection using ZnOx/PANI Nanocomposite on Nickel Foam Electrode
S. K. Pawar, N. A. Wadodkar, R. S. Salunke, A. M. Patil, D. J. Shirale
Summary: An innovative electrochemical sensor for soil nitrate detection was developed using a ZnOx/PANI nanocomposite on a Nickel foam electrode. Characterized by different techniques, the sensor showed high sensitivity (4.53 µA/µM) and a low detection limit (0.40 µM). Optimized for various parameters, this sensor provides accurate nitrate measurements, offering significant benefits for agriculture, water quality monitoring, and environmental sustainability.
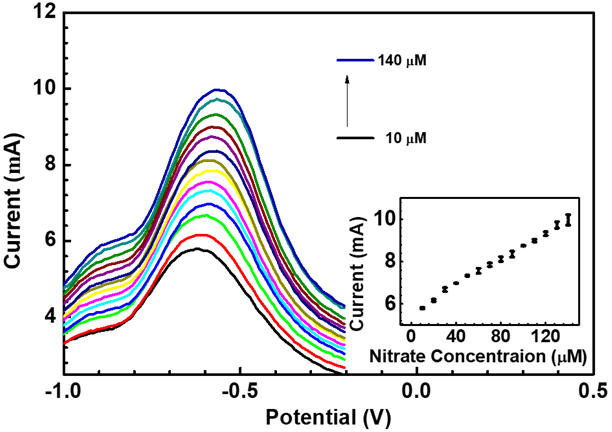
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 13 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 170-178 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0170Selective Determination of Acetaminophen in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Poly (p-Methoxyphenol) Electrode
Gamze Erdoğdu
Summary: The research details the modification of a gold electrode with poly(p-methoxyphenol) for acetaminophen detection amidst ascorbic acid interference using differential pulse voltammetry. Optimal polymerization conditions led to distinct peak potentials for acetaminophen and ascorbic acid, with a detection limit of 0.2 nM for acetaminophen. This modified electrode demonstrates high selectivity and sensitivity, offering significant potential for precise pharmaceutical analysis.
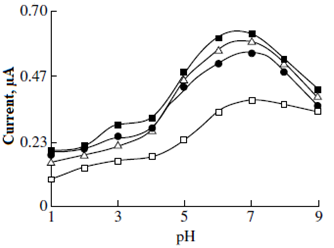
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 July 2024
MatSci Express 1(3), 179-184 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0179Volume 1, Issue 2 (June 2024)
Review
Bimetallic Oxide Nanocomposites for Better Photocatalytic Activity: A Review
Ravi Kumar, Kuldeep Kumar, Naveen Thakur
Summary: This review explores the superior photocatalytic capabilities of bimetallic oxide nanocomposites for degrading pollutants in industrial wastewater. The study finds that factors such as particle size, crystallinity, and surface area significantly impact their efficiency. Bimetallic nanocomposites demonstrate better performance compared to monometallic counterparts, suggesting a promising, cost-effective approach to water purification.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 49-68 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0049Research Articles
Selective Recognition of Lead and Cadmium in Potable Water Using Single Polypyrrole Nanowire Decorated with Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles Electrode
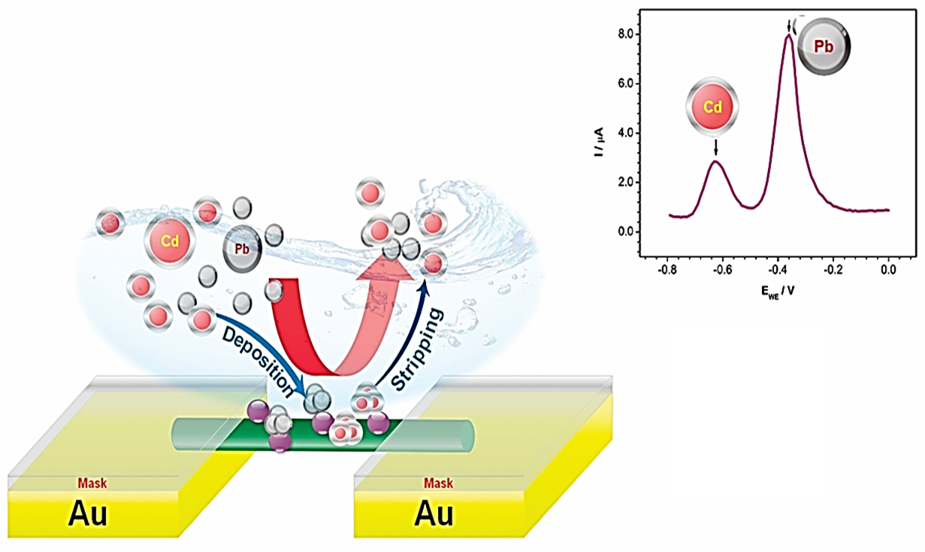
Rahul S. Salunke, Yogesh Nakate, Ahmad Umar, Amardip M. Patil, Umesh Nakate, Sotirios Baskoutas, Dhammanand J. Shirale
Summary: The paper presents the development and characterization of a sensor based on a polypyrrole nanowire decorated with cobalt oxide nanoparticles for lead and cadmium detection in water. Utilizing square wave anodic stripping voltammetry, the sensor achieved excellent sensitivity and selectivity, with detection limits of 0.22 μM for cadmium and 0.013 μM for lead, making it a promising tool for water quality monitoring.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 69-80 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0069Synthesis, Spectroscopic, and DFT Studies of Vanadium (III) Hydroxamate Complex with Potential Biological Applications
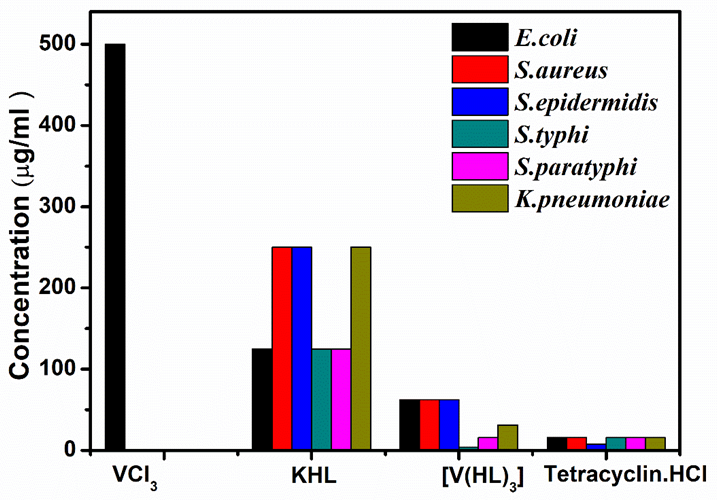
Sonika Sharma, Shubham Sharma, Meena Kumari
Summary: The synthesis and characterization of a new vanadium (III) hydroxamate complex are detailed in this study. Elemental analysis, spectroscopic techniques, and DFT calculations confirmed the complex’s stability and distorted-octahedral geometry. The complex exhibits significant antimicrobial activity and lower cytotoxicity compared to simvastatin. These findings underscore the complex’s potential for biological applications, particularly as an antimicrobial agent.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 81-95 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0081Catalytic Activity of CuO-bentonite Bead for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Fenton like Process
R. R. Chavan, K. C. Rathod, V. R. More, N.V. Pawar, J. P. Jadhav, R. B. Patil, A. D. Chougale
Summary: The research details the synthesis and characterization of CuO-bentonite beads, confirmed through XRD, FESEM, and EDS analyses. These beads demonstrated a 94.08% methylene blue dye removal efficiency in 20 minutes via a Fenton-like process. The beads maintained an 89.03% removal rate over five reuse cycles, indicating their robustness and potential for sustainable wastewater treatment applications.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 96-104 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0096Investigating the Potential of Gd3+ doped LiBPO4 Phosphors in Improving White Lighting Applications: Synthesis, Characterization, and Analysis of Their Optical Properties
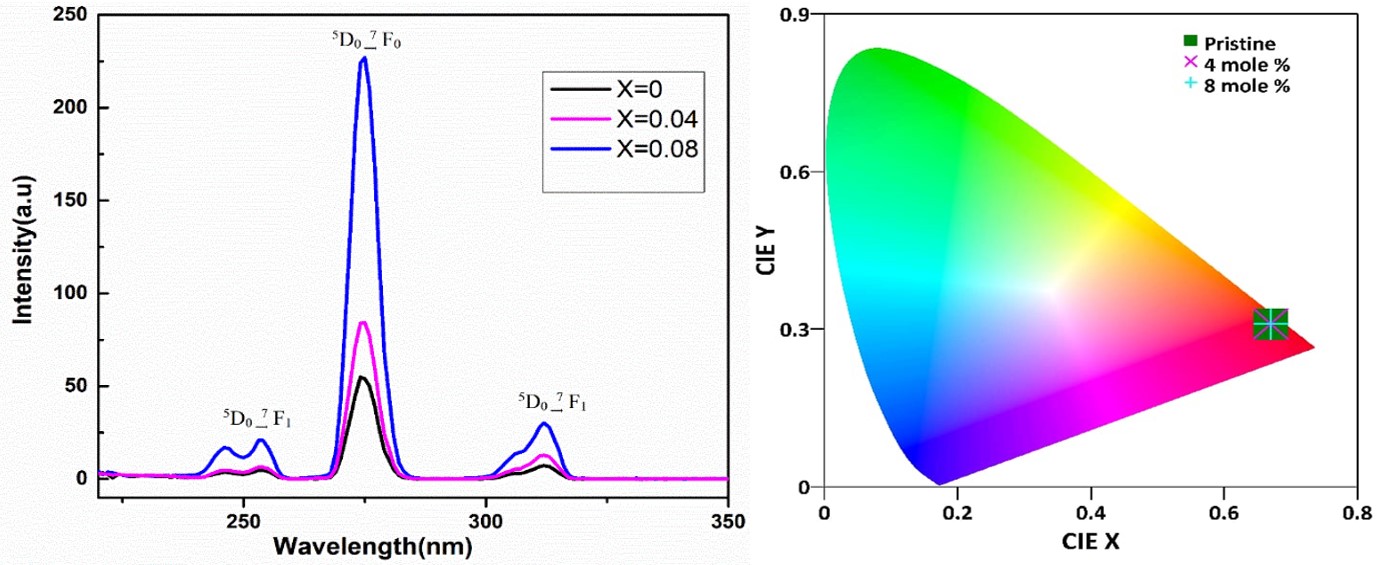
Aasim Rashid Khanday, Showket Ahmad Bhat, Faheem Ahmad Dar, Mohd. Ikram
Summary: The research examines Gd3+ doping in LiBaPO4, synthesized via the solid-state reaction method. Rietveld refinement confirms trigonal phase crystallization, while FESEM analysis reveals increased grain size with higher doping levels. Optical band gap analysis shows a decreasing trend, correlating with increased dopant concentration. The strong red luminescence of the doped phosphors suggests their applicability in red luminescent optical devices.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 105-115 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0105Magnetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Thermotherapy: A Mathematical Approach to Optimal Treatment Design
F. A. Zargar, Hilal A. Bhat, Mohd. A. Zargar, S. A. Malik
Summary: The research investigates magnetic particle hyperthermia (MPH) for cancer treatment by modeling temperature profiles in a spherical hepatic tumor using Pennes’ Bio-heat Equation. Analytical methods and numerical illustrations with magnetite nanoparticles assess the impact of varying magnetic field intensities. The findings aid in designing optimal treatment protocols, maintaining healthy tissue temperatures below 315 K (42°C) while effectively targeting tumor cells.
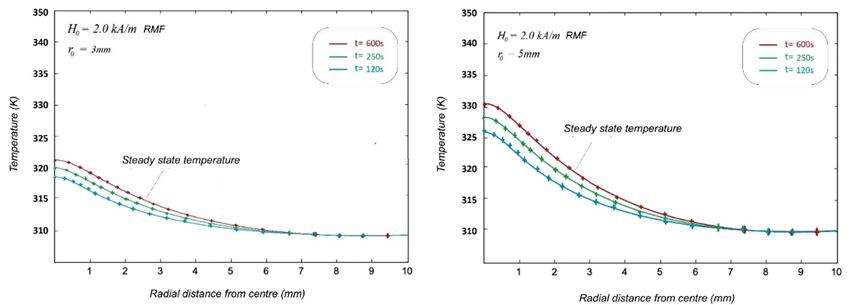
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 June 2024
MatSci Express 1(2), 116-124 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0116Volume 1, Issue 1 (March 2024)
Editorial
Welcome to the MatSci Express
Sotirios Baskoutas, Ahmad Umar
Editorial | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 1-2 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0001Review
Lanthanide Oxide Nanoparticles for Environmental Remediation: A Review
Sushil Kumar, Ganga Ram Chaudhary, Savita Chaudhary, Ahmad Umar
Summary: The article reviews the use of lanthanide oxide nanoparticles in detecting and removing environmental pollutants. It highlights their enhanced properties, cost-effectiveness, and novel methodologies for efficient remediation of pollutants in water, air, and soil.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 3-20 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0003Research Articles
Acoustic Whispering Gallery Modes in a Split Ring Resonator
Nikos Aravantinos-Zafiris, and Mihail M. Sigalas
Summary: This study employs the Finite Element Method to analyze the resonant frequencies of acoustic Whispering Gallery Modes in a split ring resonator with a defect. By examining how the resonant frequencies are affected by the defect, the study reveals a degeneration in the modes of the ring. Additionally, high Acoustic Quality factors indicate a significant enhancement of the field, with intense localization observed within the defect. These findings suggest that the proposed structure holds promise for applications involving acoustic signals, such as sensors and filters.
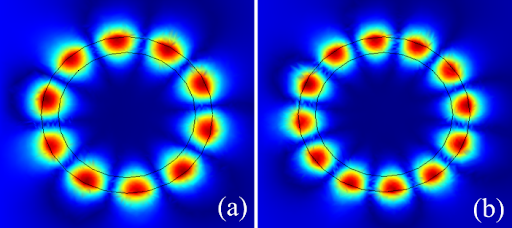
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 21-27 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0021Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants Using Iron Lanthanum Oxide Nanoparticles
Sajid Ali Ansari, and Nazish Parveen
Summary: The study synthesizes and characterizes iron lanthanum oxide nanoparticles (FeLO NPs) via a co-precipitation method. Characterization confirms their crystalline structure and surface topology. Photocatalytic tests show FeLO NPs degrade up to 90% of methylene blue under UV and visible light, indicating their effectiveness in pollutant breakdown.
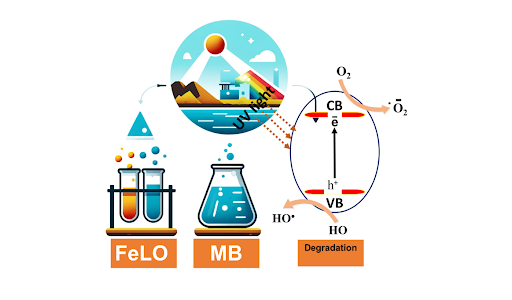
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 28-32 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0028Self-Assembled Organic Aerogel and Sponges for Rapid and Effective Absorption of Oil from Oil- Contaminated Soil Samples
Yajvinder Saharan and Joginder Singh
Summary: The study presents self-assembled sponges and organic aerogels modified with HMDS and DTMS for hydrophobicity. Characterization shows features enhancing oil adsorption. These materials achieve 100% oil removal efficiency from contaminated soil after seven cycles, offering a promising solution for oil spill cleanup.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 33-42 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0033A CrO₂ and Out-of-Plane Silicene based Sub-10nm MTJ with perfect spin filtering efficiency and high tunnel magnetoresistance
Gul Faroz Ahmad Malik, Mubashir Ahmad, Farooq Ahmad Khanday, Feroz Ahmad Najar, Sparsh Mittal, and M.Tariq Banday
Summary: This study explores a sub-10nm magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) using CrO2 electrodes and out-of-plane silicene. The device achieves perfect spin filtering efficiency and 100% tunnel magnetoresistance due to silicene’s effective barrier properties. It offers high performance for memory applications like MRAMs and integrates well with existing silicon technology.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 March 2024
MatSci Express 1(1), 43-48 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/mse.2024.0043Aims and Scope
MatSci Express
ISSN: 2997-8440
Welcome to MatSci Express (MSE), a distinguished multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal committed to the prompt dissemination of top-tier research within the materials science domain.
We aim to establish a dynamic forum where scientists, scholars, and researchers can present their pioneering findings and breakthroughs. At MSE, we recognize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in pushing the boundaries of materials science. As such, our journal serves as a nexus for research endeavors spanning across the realms of science, engineering, and medicine, offering a comprehensive reference outlet for the global scientific community. Our publication unites the expertise of materials scientists, metallurgists, engineers, physicists, chemists, ceramicists, biologists, theoreticians, and technocrats, fostering a diverse and collaborative environment. With a focus on both fundamental and applied research, MSE is dedicated to exploring the latest frontiers of advanced materials. We strive to disseminate research that not only enhances our understanding of materials at a fundamental level but also contributes to practical applications and technological advancements. We welcome researchers and scholars worldwide to participate in MatSci Express, offering their expertise and discoveries to propel the field of materials science forward.
MatSci Express is committed to advancing the frontiers of knowledge in the field of materials science through the rapid dissemination of high-quality research. Our primary aim is to provide a dynamic platform for scientists, scholars, and researchers to share their latest findings and innovations, fostering collaboration and driving progress in materials science.
Aims:
- To facilitate the swift dissemination of cutting-edge research within the materials science domain.
- To offer researchers a stage to exhibit their breakthroughs and progress in the realm of materials science.
- To nurture cross-disciplinary cooperation and facilitate the sharing of knowledge among scientists, engineers, and researchers.
- To contribute to the advancement of materials science and its applications in various fields.
Scope:
MSE covers a wide range of topics within the field of materials science, including but not limited to:
- Advanced materials characterization techniques and methodologies.
- Novel materials synthesis and processing methods.
- Functional materials for electronics, photonics, energy storage, and conversion.
- Biomaterials and their applications in medicine, healthcare, and biotechnology.
- Nanomaterials, nanotechnology, and their implications in various industries.
- Materials for sustainable development and environmental applications.
- Computational materials science, modeling, and simulation.
- Materials engineering, design, and optimization.
- Additive manufacturing, 3D printing, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
- Emerging trends, interdisciplinary research, and cross-cutting applications in materials science.
Objectives:
Facilitate Interdisciplinary Collaboration: MSE serves as a nexus for research endeavors spanning across the realms of science, engineering, and medicine, fostering a collaborative environment among materials scientists, metallurgists, engineers, physicists, chemists, ceramicists, biologists, theoreticians, and technocrats.
Disseminate Cutting-Edge Research: MSE aims to rapidly disseminate high-quality research that contributes to significant scientific and technological breakthroughs in materials science. We welcome contributions that advance our understanding of materials at both fundamental and applied levels.
Promote Practical Applications: MSE is dedicated to exploring the latest frontiers of advanced materials, with a focus on research that not only enhances fundamental understanding but also contributes to practical applications and technological advancements.
Provide a Comprehensive Reference Outlet: MSE offers a comprehensive reference outlet for the global scientific community, providing researchers and scholars with access to a diverse range of research articles, reviews, and communications in the field of materials science.
As an interdisciplinary, peer-reviewed journal, MSE welcomes original research articles, reviews, communications, Perspective Articles, Editorials, and Letters to the Editor, pertinent to significant scientific and technological breakthroughs in materials science. We encourage contributions from researchers across diverse disciplines, including materials science, engineering, physics, chemistry, mathematics, biology, and related fields.
Join us in our mission to push the boundaries of materials science and contribute to the global scientific community through MatSci Express.
Subject Covered(but not limited to):
MatSci Express encompasses a broad spectrum of topics within the domain of materials science, including:
Metallurgy and Ceramics: Investigation into the properties and behavior of metallic and ceramic materials at various scales.
Alloy Systems: Exploration of complex alloy systems, including high-entropy and shape memory alloys, with a focus on their structural and functional properties.
Non-crystalline Materials and Glass Science: Study of non-crystalline materials and glasses, delving into their atomic arrangements, properties, and applications.
Composite Materials: Analysis of composite materials comprising multiple phases, exploring their mechanical, thermal, and electrical characteristics.
Biomaterials and Dental Materials: Research on materials designed for biomedical and dental applications, focusing on biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and clinical performance.
Medical Materials: Investigation into materials utilized in medical devices, implants, and prosthetics, emphasizing biocompatibility, durability, and functionality.
Extreme Conditions Materials: Study of materials under extreme environments, such as high pressure, temperature, or radiation, to understand their behavior and stability.
Photovoltaic Materials and Devices: Research on materials used in solar cells, including perovskite, organic, and silicon-based materials, with a focus on efficiency and stability.
Artificial Photosynthesis: Exploration of materials and devices for artificial photosynthesis, aiming to harness solar energy for sustainable fuel production.
Energy Harvesting Technologies: Investigation into materials and devices for energy harvesting, including nanogenerators, piezoelectric materials, and thermoelectric devices.
Battery and Supercapacitor Materials: Research on materials for batteries and supercapacitors, focusing on energy storage capacity, cycling stability, and electrochemical performance.
Flow Batteries: Study of materials utilized in flow batteries, including electrode and electrolyte materials, for grid-scale energy storage applications.
Fuel Cell Technology: Research on materials for fuel cells, exploring catalysts, membranes, and electrode materials for efficient energy generation and conversion.
Catalytic Materials: Investigation into materials and processes for catalysis in energy-related applications, such as hydrogen production, carbon capture, and chemical synthesis.
Nanocomposites: Analysis of nanocomposite materials, incorporating nanoparticles or nanofillers into matrices for tailored properties and functionalities.
Two-dimensional (2D) Materials: Exploration of 2D materials and coatings, including graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, and MXene, for various applications.
Applications of Nanomaterials: Investigation into the practical uses of nanomaterials and nanodevices across diverse domains including electronics, healthcare, environmental restoration, and sensor technology.
Bioactive Materials: Investigation into materials designed for biomedical applications, focusing on biocompatibility, bioactivity, and interaction with biological systems.
Correlated Electron Materials: Study of exotic correlated electron materials, such as superconductors and topological insulators, exploring their unique electronic properties and potential applications.
Photonics Materials: Research on materials for photonics and electromechanical devices, including photonic crystals, waveguides, and optoelectronic materials.
Quantum Materials: Exploration of quantum materials and devices, focusing on their quantum mechanical properties and potential applications in quantum information processing.
Information Device Physics: Investigation into the physics and engineering of information devices, including transistors, memory devices, and sensors, for computing and communication applications.
Smart Sensing Devices: Research on materials and devices for smart sensing applications, including sensors, actuators, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Materials Theory and Design: Theoretical studies and computational modeling of materials, including prediction, design, and optimization of materials properties and performance.
Utilization of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Implementations of AI and ML methodologies in materials science, encompassing data-driven exploration of materials, prediction of properties, and optimization strategies.
Materials Simulation Techniques: Computational techniques for simulating materials behavior, including molecular dynamics, Monte Carlo simulations, and density functional theory calculations.
Thermodynamic and Phase Diagram Calculations: Thermodynamic modeling and phase diagram calculations to predict phase stability, phase transitions, and material properties.
Interatomic Potentials and Force Fields: Development and application of interatomic potentials and force fields for simulating materials behavior and properties at the atomic scale.
Readership
MatSci Express appeals to a broad and diverse readership spanning across multiple disciplines and sectors. Our audience includes professionals and researchers from a wide array of fields, including materials science, chemistry, engineering, information science, electronics, physics, biology, energy science, environmental science, medicine, and pharmaceutical science. Our readership encompasses individuals from both academic institutions and industry, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of materials science and its widespread applications in various sectors. Whether from academia or industry, our readers are keen to stay abreast of the latest advancements and discoveries in materials science, making MatSci Express their go-to resource for cutting-edge research and insights.
Editorial Board
Editorial Manager
Prof. Ahmad Umar
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Ohio State University, Columbus, 43210 OH, USA
Email: umar.20@osu.edu
Editor-in-Chief
Prof. Sotirios Baskoutas
Department of Materials Science
University of Patras
Greece
Email: eicmatsci@upatras.gr
Editors
Prof. P. Davide Cozzoli
University of Salento
Department of Mathematics and Physics “E. De Giorgi”, Lecce, Italy
Prof. Zhongchang WANG
School of Chemistry, Beihang University,
Beijing 100191, China
Prof. Yao Wang
South China Academy of Advanced Optoelectronics
South China Normal University
Guangzhou-510006, China
Prof. Michael Sigalas
Department of Materials Science, University of Patras, Greece
Prof. Susmita Naskar
School of Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences
Boldrewood Innovation Campus, University of Southampton
United Kingdom
Prof. Wen Zeng
College of Materials Science and Engineering
Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400044, China
Dr. Savita Chaudhary
Department of Chemistry,
Panjab University, Panjab
India
Dr. Atresh Kumar Singh
Department of Chemistry, Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gorakhpur University,
Gorakhpur, India
Dr. Dhammanand Jagdeo Shirale
Department of Electronics, School of Physical Sciences,
Kavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University,
Jalgaon – 425001 (MS) India
Prof. Shahid Hussain
Department of Materials Science
Jiangsu University, China
Editorial Board Members
Prof. Zaiping Zeng
School of Materials Science and Engineering
Henan University, China
Prof. Nikolaos Bouropoulos
Department of Materials Science
University of Patras
Greece
Prof. David Hayrapetyan
Department of General Physics and Quantum Nanostructures
Russian-Armenian University, Armenia
Prof. Wolfram Schommers
Institute of Nanotechnology,
Karlsruhe, Germany
Prof. M. S. Akhtar
School of Computing, Department of Engineering
La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia
Prof. Bon Heun Koo
School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Changwon National University, Changwon, South Korea
Dr. Suresh Sagadevan
Nanotechnology & Catalysis Research Centre
University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur,
Malaysia.
Prof. Wenjuan Guo
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Jinan,
Jinan 250022, China
Prof. Hilal Tayara
School of International Engineering and Science
Jeonbuk National University, Republic of Korea
Dr. Muhammad Shahid Nadeem
Institute of Physics,
The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Pakistan
Prof. Georgios Psarras
Department of Materials Science
University of Patras
Greece
Dr. Sajid Ali Ansari
Department of Physics, College of Science
King Faisal University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Prof. Dilip Kumar Dwivedi
Department of Physics and Material Science,
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology,
Gorakhpur-273010, India
Dr. Sarish Rehman
McGill University, Department of Chemistry
Montreal, Canada
Dr. Abdullah Aljaafari
Department of Physics, College of Science
King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Prof. Sadia Ameen
Advanced Materials and Devices Laboratory, Department of Bio-Convergence Science,
Jeongeup Campus, Jeonbuk National University, 56212, Republic of Korea
Dr. Nazish Parveen
Department of Chemistry, College of Science
King Faisal University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Prof. Rajesh Kumar Yadav
Department of Chemistry and Environmental Science,
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology,
Gorakhpur 273010, India.
Dr. Faheem Ahmed
Department of Applied Sciences and Humanities
Faculty of Engineering and Technology,
Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi-110025, India
Dr. Firoz Alam
Nanotechnology Laboratory,
University College London (UCL), London
Prof. Wenjuan Guo
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,
University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, China.
Prof. Shalendra Kumar
University of Petroleum Energy Studies,
Dehradun, India
Dr. Mohd. Zahid Ansari
Chemical Engineering Program,
Texas A&M University at Qatar, Doha,
23874 Qatar
Dr. S. Stephen Rajkumar Inbanathan
Post graduate and Research Department of Physics
The American College, Madurai-625002, India
Prof. Igor Paprotny
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
University of Illinois, Chicago, USA
Prof. Hayk A. Sarkisyan
Department of General Physics and Quantum Nanostructures
Russian-Armenian University, Armenia
Prof. Fatih Ungan
Faculty of Science, Department of Physics,
Sivas Cumhuriyet University, Sivas, Turkey
Prof. Ioannis Lelidis
Department of Physics,
National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece
Dr. Esam Bashir Yahya
Bioprocess Technology Division, School of Industrial Technology,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
Dr Paytsar A Mantashyan,
Department of General Physics and Quantum Nanostructures
Russian-Armenian University, Armenia
Dr. Rasool Shah
Department of Computer Science and Mathematics,
Lebanese American University,
Beirut Lebanon
Prof. Hong Seok Kang
Department of Nano & Advanced Materials,
Jeonju University, SOUTH KOREA
Prof. Maria Antoniadou
Department of Chemical Engineering
University of Western Macedonia, Greece
Prof. Yongfeng Shen
School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Northeastern University, P.R. China
Prof. Lijun Shang
School of Human Sciences,
London Metropolitan University, London, United Kingdom
Prof. Raffaele Barretta
Coordinator of the AIMETA Group of Multiscale Mechanics and Nanostructures (GAMeN)
Department of Structures for Engineering and Architecture
University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
Prof. Vassilios Mardiris
Department of Management Science and Technology,
Democritus University of Thrace, Greece
Prof. Yang Luo
North China Electric Power University,
Beijing, China
Dr. Wang Yinglin
School of Aerospace Science and Technology,
Xidian University, China
Dr. Lalla Btissam DRISSI
LPHE-Modeling and Simulations, Department of Physics,
Faculty of Science, and Centre of Physics and Mathematics,
Mohammed V University in Rabat, Morocco
Dr. Halit ÇAVUŞOĞLU
Selçuk Üniversitesi, Fen Fakültesi Fizik Bölümü
Alaeddin Keykubat Kampüsü, Konya, TÜRKİYE
Dr. Limin Ma
Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics,
Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Dr. Sanjay Kumar Swami
Department of Physics, School of Engineering,
Dayananda Sagar University, India
Dr. Krishna Chaitanya Pitike
Nuclear Sciences Division,
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, USA
Dr. Joginder Singh
Maharishi Markandeshwar, Mullana, Haryana
India
Dr. Heah Cheng Yong
Mechanical Engineering and Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia
Dr. Konstantinos Zekentes
Institute of Electronic Structure & Laser (IESL)
Foundation for Research & Technology Hellas (FORTH)
Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Dr. Avtar Singh
Research and Development, Molekule Inc, Tampa, Florida, USA
Prof. Stefania Pagliara
Interdisciplinary Laboratories for Advanced Materials Physics (i-Lamp)
Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica,
Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuor, Brescia, Italy
Dr. Rajeev Kumar
Department of Environment Studies,
Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
Dr. Sofia Evangelou
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Technical University of Crete, Greece
Guide for Reviewers and Editors
Guide to Reviewers: MatSci Express
Welcome to the Instructions for Reviewers for MatSci Express. As a valued reviewer, your expertise and insights play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and integrity of the journal’s publications. Your thorough evaluation and constructive feedback are instrumental in shaping the direction of scientific discourse in the field of materials science. Below are guidelines to assist you in conducting a comprehensive review of manuscripts submitted to MatSci Express.
Confidentiality: As a reviewer for MatSci Express, it’s crucial to maintain the confidentiality of the manuscripts you’re assigned to review. This means refraining from discussing the content of the manuscripts with anyone other than the editorial office. By upholding confidentiality, you contribute to the integrity of the peer review process.
Timeliness: Time is of the essence in the peer review process. Reviewers are expected to evaluate manuscripts promptly and submit their reports within the specified deadline. If circumstances arise that prevent you from meeting the deadline, it’s important to communicate with the editorial office and request an extension in advance.
Constructive Feedback: Reviewers play a pivotal role in providing constructive feedback to authors. When assessing manuscripts, focus on identifying both strengths and weaknesses. Your comments should be specific, objective, and aimed at helping authors improve their work. Point out areas where the manuscript excels and areas where it could be enhanced.
Originality and Ethical Standards: Evaluate the originality of the research presented in the manuscript and ensure that it meets ethical standards. Verify that proper citations are provided for previously published work and assess whether the research has been conducted in accordance with ethical guidelines and regulations.
Content Evaluation: Dive deep into the content of the manuscript and evaluate its significance, novelty, and scientific rigor. Scrutinize the methodology used, the interpretation of results, and the contribution the research makes to the field. Your evaluation should be thorough and objective, focusing on the scientific merit of the work.
Clarity and Presentation: Assess the clarity and organization of the manuscript. Consider factors such as the writing style, structure, and coherence of the presentation. Provide feedback on how the manuscript could be improved to enhance clarity and readability for readers.
Recommendation: Based on your evaluation, make a recommendation regarding the manuscript’s fate—whether it should be accepted, revised, or rejected. Justify your recommendation with specific comments and suggestions for improvement. Your recommendation will be instrumental in guiding the editorial decision-making process.
Conflicts of Interest: Be transparent about any potential conflicts of interest that may influence your review. If you have personal or professional connections to the authors or their research, disclose them to the editorial office. If you feel that a conflict of interest may compromise your impartiality, notify the editorial office immediately.
Respectful Communication: Maintain professionalism and respect in all communications related to the peer review process. Avoid personal or derogatory remarks and focus solely on the scientific content of the manuscript. Your goal is to provide feedback that is helpful and constructive, regardless of your recommendation.
Final Decision: Your review will be considered alongside those of other reviewers by the editorial team to make a final decision on the manuscript. Your feedback is invaluable in ensuring the quality and integrity of the research published in MatSci Express. Thank you for your dedication to the peer review process.
Guide to Editors: MatSci Express
Welcome to the comprehensive Guide to Editors for MatSci Express. As an editor for our esteemed journal, your pivotal role revolves around ensuring the quality, integrity, and timely dissemination of groundbreaking research within the realm of materials science. This detailed guide is designed to equip you with the necessary instructions and best practices to navigate the editorial process with proficiency and efficacy. Your dedication and commitment as an editor are invaluable to the success and reputation of MatSci Express.
Editorial Workflow:
- Your initial task involves the meticulous assignment of suitable reviewers, drawing upon their expertise and availability to ensure thorough and insightful assessments.
- Efficiently manage the peer review process by overseeing the timely completion of reviews and judiciously evaluating reviewer comments to make informed editorial decisions.
- Maintain proactive communication with authors throughout the review process, providing updates, guidance, and constructive feedback as required.
- Thoughtfully evaluate the feedback provided by reviewers and exercise sound judgment in determining manuscript acceptance, revision, or rejection, upholding the journal’s standards of excellence.
Manuscript Handling:
- Uphold the journal’s submission guidelines rigorously, ensuring that submitted manuscripts adhere to formatting requirements and ethical standards.
- Conduct a comprehensive initial assessment of manuscripts to ascertain their suitability for peer review, considering factors such as novelty, relevance, and scientific rigor.
- Effectively manage revisions and resubmissions, facilitating productive interactions between authors and reviewers to address queries, concerns, or suggestions for improvement.
- Strive for consistency and rigor in the editorial process, upholding the journal’s reputation for scholarly excellence and integrity.
Ethical Considerations:
- Familiarize yourself thoroughly with the journal’s policies on plagiarism, authorship, conflicts of interest, and ethical conduct, ensuring strict adherence to established guidelines.
- Promptly address any instances of ethical misconduct or concerns, conducting impartial investigations and implementing appropriate measures in accordance with established procedures.
- Maintain the utmost confidentiality throughout the editorial process, safeguarding the anonymity of reviewers and respecting the privacy of authors to uphold the integrity of the peer review process.
Collaboration and Communication:
- Foster a collaborative and supportive environment conducive to constructive dialogue and scholarly exchange among authors, reviewers, and editorial board members.
- Encourage open communication and facilitate constructive feedback to foster continuous improvement in manuscript quality and scientific rigor.
- Serve as a liaison between authors and reviewers, facilitating effective communication and resolution of any conflicts or misunderstandings that may arise during the editorial process.
Continuous Improvement:
- Stay abreast of the latest developments and advancements in the field of materials science and scholarly publishing, adapting editorial practices to reflect evolving standards and expectations.
- Solicit feedback from authors, reviewers, and colleagues to identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of the editorial process.
- Strive for continuous improvement in all aspects of editorial management, contributing to the enhancement of the journal’s reputation and impact within the scientific community.
Publication Ethics
At MatSci Express, published by Ariston Publications, we uphold the highest ethical standards in scientific publishing to ensure the integrity, credibility, and trustworthiness of the research we disseminate. Our commitment to ethical practices extends across all stages of the publication process, from manuscript submission to post-publication dissemination. Our publication ethics policies are designed to guide authors, reviewers, editors, and all stakeholders involved in the publishing process. Adherence to these ethical principles is paramount to maintain transparency, fairness, and trust in scholarly communication.
1. Authorship and Author Responsibilities:
Authors are expected to adhere to the following ethical principles:
Authorship Criteria:
- Authorship eligibility hinges upon significant contributions to conceiving, designing, executing, or interpreting the research study.
- All contributors with substantial involvement in the work merit authorship recognition, while those offering support or assistance without meeting authorship criteria should be acknowledged accordingly.
- Authors are required to reveal any potential conflicts of interest that could impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
Originality and Plagiarism:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the originality of their work and confirming that it has not been previously published or is under consideration elsewhere for publication.
- Any form of plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, is unacceptable and will lead to immediate rejection or retraction.
- Any form of plagiarism, whether it involves directly copying text, ideas, or data without appropriate acknowledgment, is strictly forbidden.
- Editors utilize plagiarism detection software to screen submitted manuscripts and address any suspected cases of plagiarism promptly.
Conflict of Interest:
- Authors must reveal any potential conflicts of interest that might impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
- This includes financial interests, employment affiliations, consulting arrangements, or personal relationships.
Data Integrity:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the accuracy and integrity of their data, presenting research findings with honesty and transparency.
- Studies involving human subjects, animals, or sensitive data must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain the requisite approvals and permissions.
- Fabrication, falsification, or manipulation of data is considered unethical and constitutes scientific misconduct.
2. Peer Review Process:
- Reviewers must uphold the confidentiality of the peer review process and refrain from sharing any details about the manuscript or their assessment with unauthorized individuals without permission from the journal.
- Peer review is conducted with fairness.
- Reviewers are expected to conduct their evaluations impartially and offer constructive feedback aimed at enhancing the manuscript’s quality.
- Reviewers should declare any potential conflicts of interest and evaluate manuscripts objectively, focusing solely on their scientific quality.
- Editors oversee the peer review process to ensure its integrity and rigor, avoiding bias or favoritism.
3. Editorial Responsibilities:
Editorial Integrity:
- Editors uphold the integrity and quality of the editorial process, maintaining objectivity and impartiality in decision-making.
- Manuscripts are evaluated based on their scientific quality, significance, originality, and methodological rigor, without discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, religion, region, or institutional affiliation.
Conflict of Interest:
Editors are responsible for managing conflicts of interest transparently and impartially, ensuring that they do not compromise the integrity of the editorial process.
Transparency:
Editors should ensure transparency in the publication process by clearly communicating the editorial policies, peer review process, and any conflicts of interest.
4. Post-Publication Concerns:
Corrections and Retractions:
- Authors, editors, and publishers are responsible for promptly addressing errors or inaccuracies in published articles, issuing corrections, clarifications, or retractions as necessary.
- Corrections are published promptly to rectify errors and maintain the integrity of the scientific record.
Ethical Concerns:
Any concerns about ethical issues, such as research misconduct or violations of publication ethics, will be thoroughly investigated by the journal and appropriate actions will be taken.
5. Compliance with Policies and Guidelines:
All stakeholders are expected to comply with the journal’s policies, guidelines, and ethical standards, as well as relevant regulatory requirements and best practices in scholarly publishing.
Indexing and Abstracting
MatSci Express, while currently not indexed, is actively working towards being indexed in prominent databases and directories relevant to materials science and related fields. Our aim is to ensure that the valuable research published in MatSci Express reaches a wide audience of scholars, researchers, and practitioners in the field. We are in the process of applying for indexing in key databases and directories to enhance the visibility and discoverability of articles published in our journal. Stay tuned for updates as we progress in our efforts to expand the indexing coverage of MatSci Express, thereby increasing its impact and reach within the scientific community.
Article Processing Charges
At present, there are no article processing charges (APCs) associated with publishing in MatSci Express. As an open-access journal, all articles are published free of cost to authors. The publisher covers the expenses incurred in the publication process, allowing authors to disseminate their research without any financial burden. There are no fees for submission, processing, or publication of articles in MatSci Express. This approach ensures equitable access to scientific knowledge and supports the dissemination of research findings across the global scientific community.
Special Issues
MatSci Express welcomes proposals for special issues that align with the journal’s scope and objectives. Special issues provide an opportunity to delve into specific topics or emerging areas within materials science and related fields, offering a focused platform for in-depth exploration and discussion.
If you have a proposal for a special issue, please submit it to the editorial office for consideration. Your proposal should include a brief outline of the proposed topic, its significance and relevance to the field, potential contributors, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Once your proposal is received, it will undergo careful evaluation by the editorial team to assess its suitability for publication in MatSci Express. If approved, you will be invited to serve as a guest editor or co-editor for the special issue, working closely with the editorial team to oversee the review and publication process.
We look forward to receiving your proposals and collaborating with you to bring forth exciting and impactful special issues for our readership.
Please submit the special issue proposal at: info@aristonpubs.com
Special Issue
On
“Advanced Catalysts, Sensors, Batteries, and Supercapacitors for Environmental Sustainability”
Scope of the Special Issue:
In an era of unprecedented technological advancement and environmental awareness, the need for sustainable innovations has never been greater. The integration of advanced catalysts, sensor technologies, next-generation batteries, and cutting-edge supercapacitors offers transformative potential for a greener and more sustainable future. Recognizing this crucial intersection, MatSci Express is proud to announce a special issue dedicated to “Advanced Catalysts, Sensors, Batteries, and Supercapacitors for Environmental Sustainability.” This special issue aims to serve as a comprehensive platform for the latest research and developments in these pivotal areas, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative solutions.
The special issue seeks to bring together groundbreaking research that explores the synergy between materials science, energy technology, and environmental sustainability. By addressing both fundamental principles and practical applications, this issue aims to showcase innovative solutions that contribute to environmental monitoring, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices. We invite contributions that push the boundaries of current knowledge and offer novel insights into the development and application of advanced materials for catalysts, sensors, batteries, and supercapacitors.
Topics of Interest:
We welcome original research articles, comprehensive reviews, and insightful communications on a wide range of topics, including but not limited to:
Catalysis for Environmental Applications:
- Catalysts for pollution control, including air and water purification.
- Photocatalysis and electrocatalysis for sustainable energy production.
- Catalysts for the degradation of hazardous substances and waste treatment.
Advanced Sensor Technologies:
- Development of high-sensitivity and selective sensors for environmental monitoring.
- Novel materials for chemical, biological, and physical sensors.
- Wearable and flexible sensors for health and environmental applications.
Battery Science and Technology:
- Innovations in battery materials and design for improved performance and safety.
- Next-generation batteries: lithium-ion, solid-state, flow batteries, and beyond.
- Recycling, sustainability, and lifecycle analysis of battery technologies.
- Applications of batteries in renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
Supercapacitors:
- Design and synthesis of advanced materials for supercapacitors.
- Hybrid systems combining batteries and supercapacitors for enhanced energy storage.
- Characterization and performance metrics of supercapacitor technologies.
- Environmental impact and recycling of supercapacitor materials.
Interdisciplinary Applications:
- Cross-disciplinary approaches integrating materials science, engineering, and environmental science.
- Innovative applications in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and smart cities.
- Future trends and challenges in sustainable energy and sensor technologies.
Why Submit to This Special Issue?
Visibility and Impact: Your research will be part of a high-visibility special issue that addresses critical advancements in materials science and environmental sustainability.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Engage with a broad audience of scientists, engineers, and environmentalists, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation.
Rapid Publication: Benefit from MatSci Express’s commitment to rapid dissemination of cutting-edge research.
Submission Guidelines:
- Manuscripts should be written in English and adhere to the journal’s submission guidelines.
- All submissions will undergo a rigorous peer-review process to ensure the highest quality of published research.
- Authors should submit their manuscripts through the MatSci Express online submission system, clearly indicating their submission is for the special issue on “Advanced Catalysts, Sensors, Batteries, and Supercapacitors for Environmental Sustainability.”
Key Dates:
Submission Deadline: 25 July, 2024
Notification of Acceptance: 30 August, 2024
Publication Date: 15 September, 2024
We look forward to your valuable contributions and are excited to see the innovative solutions and discussions this special issue will bring to the forefront of materials science and environmental sustainability.
Guest Editors:
Dr. Dhammanand Jagdeo Shirale
Department of Electronics, School of Physical Sciences,
Kavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University,
Jalgaon – 425001 (MS) India
Email: shiraledj@gmail.com, djshirale@nmu.ac.in
For further inquiries, please contact the special issue editorial team at [shiraledj@gmail.com, djshirale@nmu.ac.in].
Conferences
MatSci Express welcomes the opportunity to collaborate with organizers of conferences, symposiums, and workshops to publish special issues or proceedings featuring research articles presented at these events.
If you are organizing a conference or similar academic gathering and wish to publish selected research papers in MatSci Express, we encourage you to reach out to our editorial office with your proposal. Your proposal should include details such as the theme and scope of the conference, the number of anticipated submissions, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Upon receiving your proposal, our editorial team will review it carefully to assess its alignment with the journal’s scope and objectives. If approved, we will work closely with you to facilitate the submission and review process for the conference papers, ensuring timely publication in a dedicated special issue or proceeding.
By publishing conference-related research in MatSci Express, authors can benefit from the journal’s wide readership and open access model, maximizing the visibility and impact of their work within the materials science community. We look forward to the opportunity to collaborate with you on showcasing cutting-edge research from your conference in our journal.
For any inquiry, please contact at: info@aristonpubs.com
Article in Press
Current Issue
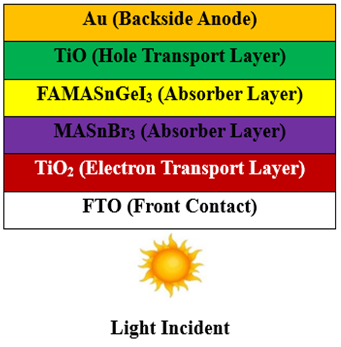
High-Efficiency Lead-Free FAMASnGeI₃/ MASnBr₃ Perovskite Solar Cells: A Comprehensive Numerical Optimization Study Using SCAPS-1D
K. C. Dubey, Anchal Srivastava, R. K. Shukla
Summary: Through SCAPS-1D simulations, this work designed an optimized FAMASnGeI₃/MASnBr₃ double-absorber PSC with 34.70% PCE, featuring 150/225 nm absorber thicknesses, minimized defect densities (10¹³-10⁹ cm⁻³), and ideal charge transport layers (10 nm TiO₂/150 nm NiO). Key achievements include exceptional Voc (1.3284 V) and FF (90.52%) through recombination suppression, with performance validated at 300 K. The study provides a complete theoretical blueprint for fabricating efficient, eco-friendly PSCs while identifying future research directions in stability and interface engineering.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 April 2025
Energy & Environment Advances 2(2), 105-119 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/eea.2025.0105