

SciEngg Advances is a pioneering multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal dedicated to advancing the boundaries of scientific and engineering knowledge through the swift dissemination of revolutionary research. Our mission is to provide a dynamic platform for scientists, engineers, and scholars to showcase their groundbreaking discoveries and innovations. As a beacon of interdisciplinary collaboration, SciEngg Advances serves as a conduit for bridging various domains within science and engineering. We pride ourselves on publishing original research articles, comprehensive reviews, and insightful communications, fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange across diverse fields. Our journal unites the expertise of scientists and engineers from a range of disciplines, including chemistry, physics, biology, materials science, environmental science, computational science, engineering, and technology. By bringing together these varied perspectives, we aim to catalyze innovation and drive progress in scientific and engineering realms. With a focus on both fundamental principles and practical applications, SciEngg Advances explores the latest frontiers of scientific and engineering research, addressing pressing global challenges and propelling technological advancements. From pioneering synthetic methodologies to sustainable engineering solutions, from cutting-edge materials science to transformative bioengineering, our journal covers a wide spectrum of topics, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of modern scientific and engineering inquiry. SciEngg Advances is committed to serving as a vital resource for scientists, engineers, and researchers worldwide, providing a platform for the dissemination of impactful discoveries and the exchange of ideas that will shape the future of science and engineering.
Volume 2, Issue 2 (June 2025)
Research Articles
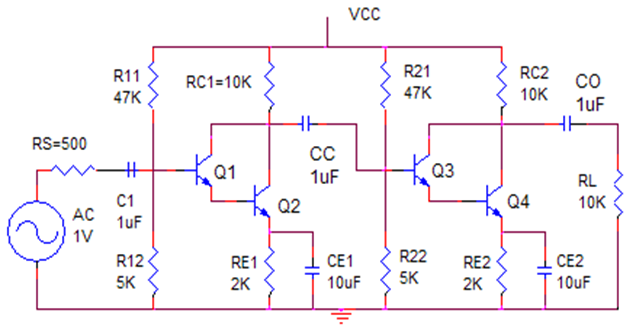
Performance Analysis and Simulation of Darlington Pair and Coupled Darlington Amplifiers: Gain, Bandwidth, and Waveform Characteristics
Satyendra Nath Tiwari, Mrityunjay Mishra, Om Prakash Yadav
Summary: This research simulates Darlington pair and coupled Darlington amplifiers, comparing gain, bandwidth, and power dissipation. The two-stage design achieves a 200.58 voltage gain (1081% higher than single-stage) but reduces bandwidth to 68.08 kHz. Current gain exceeds theoretical values, suggesting a voltage-current trade-off. Biasing analysis reveals saturation in gain at higher resistances. Both amplifiers maintain signal integrity with 14.3 mW power dissipation in the two-stage model. The study aids in optimizing high-gain amplifiers for communication systems despite bandwidth limitations.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 09 January 2025
SciEngg Advances 2(2), 50-58 (2025)
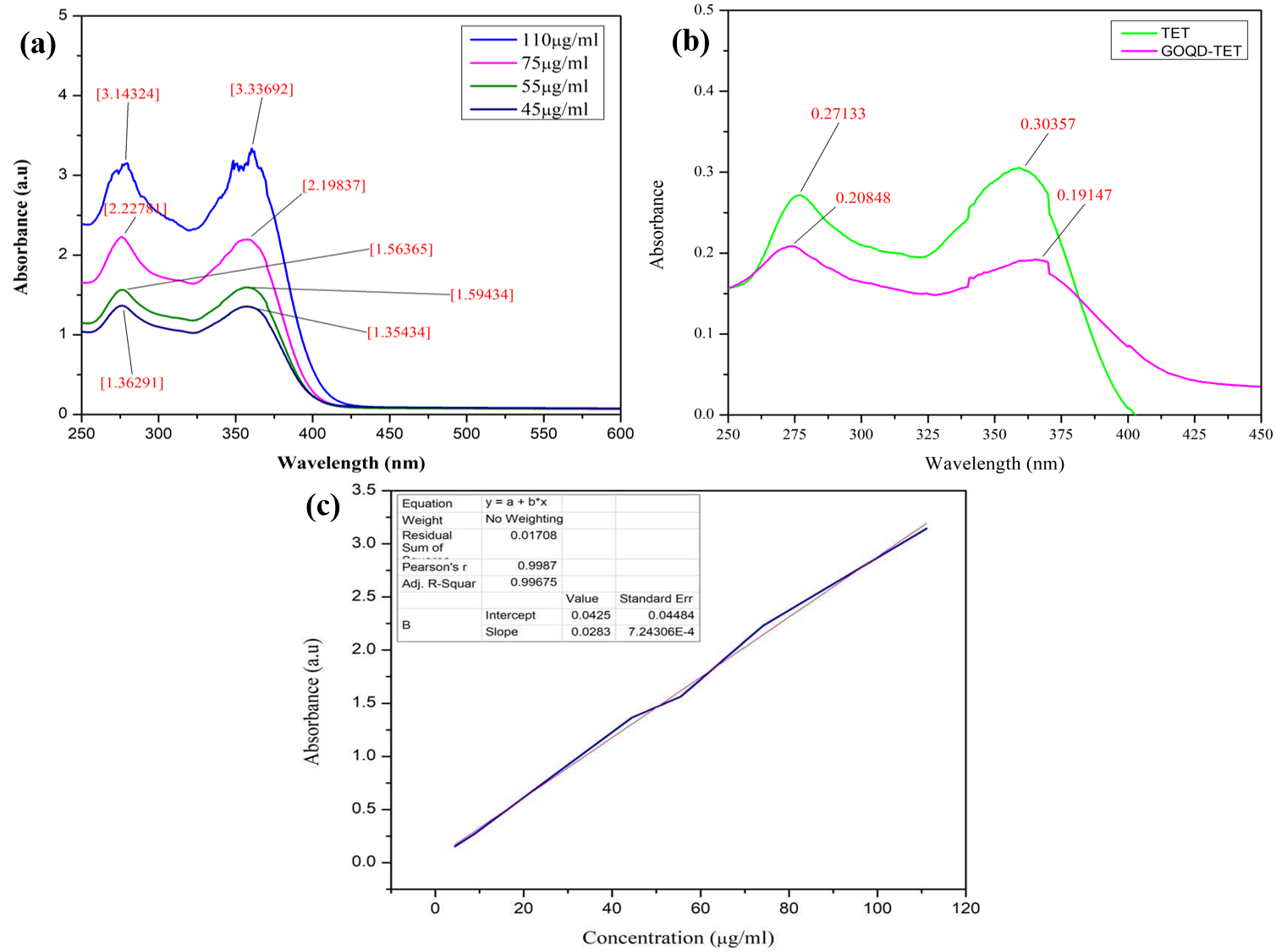
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0050Synthesis, Characterization, and Multifunctional Applications of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Environmental Remediation and Biomedical Drug Delivery
M. Beaula Ruby Kamalam, K. J. Sam Daniel, K. Hariramakrishnan, L. Ganesh, S. S. R. Inbanathan
Summary: This study synthesized graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) via hydrothermal treatment, confirming their structural and optical properties through UV-Vis, FTIR, XRD, and PL analysis. GOQDs exhibited 94.51% photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue, proving effective for environmental cleanup. In biomedicine, PEGylated GOQDs showed low toxicity and high tetracycline loading (95.8% efficiency), indicating potential for drug delivery. The findings demonstrate GOQDs’ versatility in both pollution control and nanomedicine, paving the way for future industrial and therapeutic optimizations.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 26 January 2025
SciEngg Advances 2(2), 59-70 (2025)
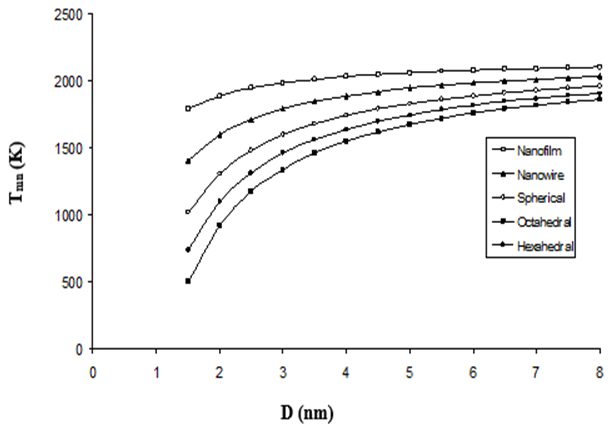
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0059Influence of Shape, Size, and Surface Effects on the Melting Temperature of Rutile (TiO2) Nanoparticles: A Cohesive Energy Model Approach
Devesh, M. P. Singh
Summary: This study employs a cohesive energy model to analyze how size (2–12 nm) and shape (spherical, nanowire, octahedral, etc.) affect rutile TiO₂ nanoparticles’ melting temperature. Results show a sharp decline in melting points below 6 nm, with non-spherical structures (e.g., hexahedral) experiencing the fastest reduction due to higher surface energy. The model agrees well with MD simulations for larger nanoparticles (>6 nm) but highlights edge/corner effects in smaller ones, aiding nanomaterial design for thermal stability in industrial applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 13 February 2025
SciEngg Advances 2(2), 71-77 (2025)
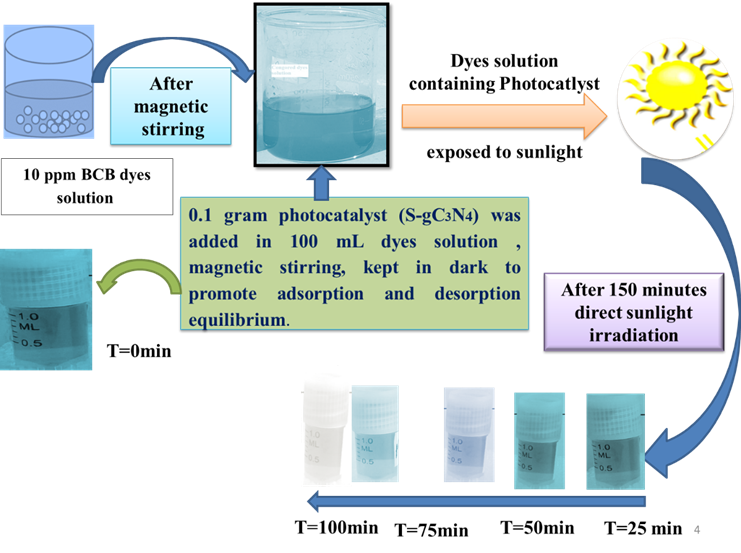
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0071Solar Light–Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Brilliant Cresyl Blue and Malachite Green Dyes Using Sulfur–Doped Graphitic Carbon Nitride (S-g-C₃N₄)
Suneel, Neda Tabassum, Devendra Pratap Mishra, Moonish Aftab
Summary: S-g-C₃N₄ was synthesized via thermal polymerization of thiourea and characterized using FTIR and XRD. The photocatalyst exhibited 64.86% and 81.28% degradation of Brilliant Cresyl Blue and Malachite Green, respectively, under solar irradiation, following pseudo-first-order kinetics. Enhanced activity was attributed to sulfur doping, which improved charge separation and light absorption. The study presents a promising, eco-friendly approach for dye wastewater remediation, emphasizing the potential of S-g-C₃N₄ for large-scale environmental applications under natural sunlight.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 March 2025
SciEngg Advances 2(2), 78-85 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0078Volume 2, Issue 1 (March 2025)
Review
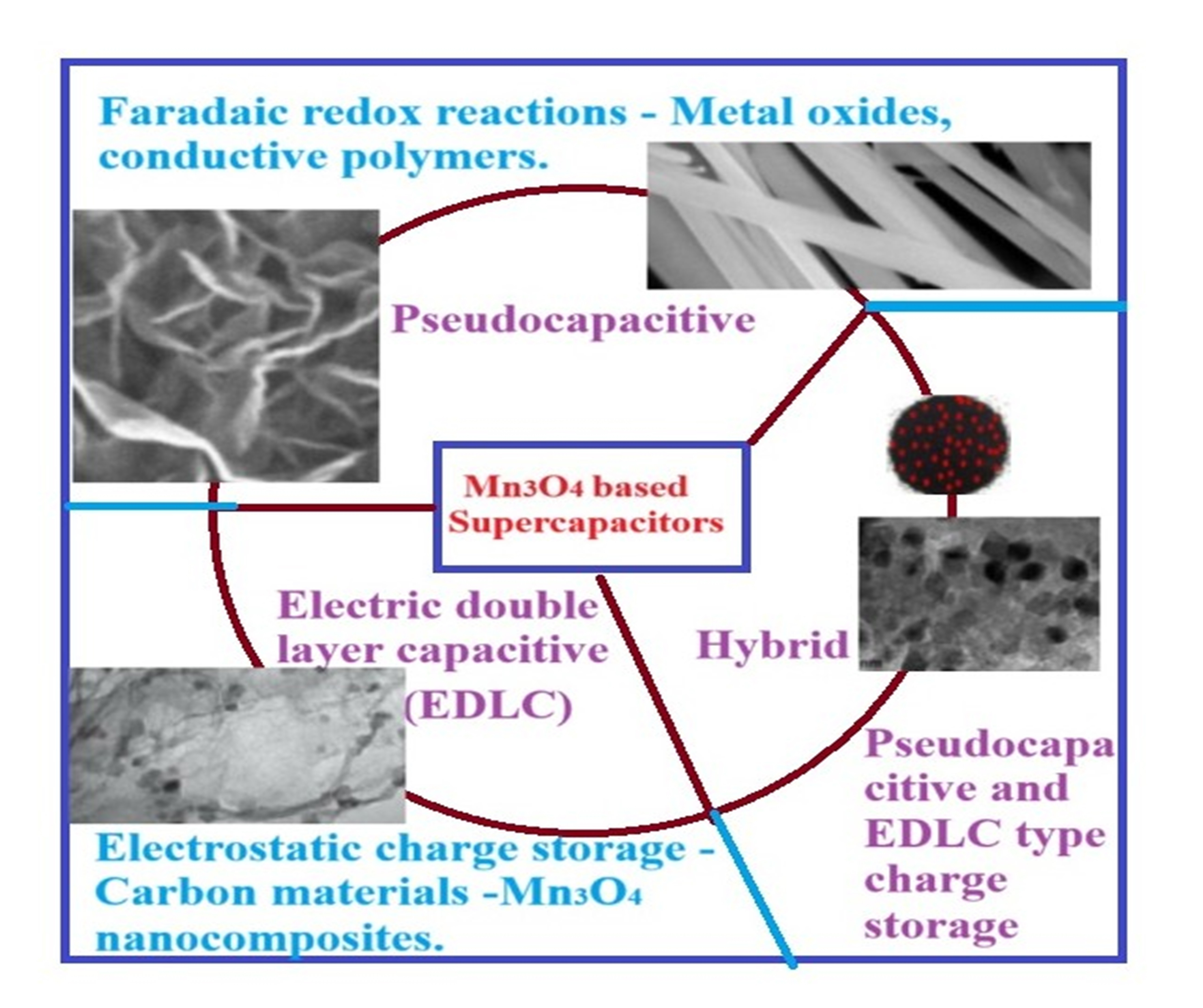
Mn3O4 Nanomaterials in Supercapacitor Applications: A Review
Tanaji S. Patil, Raviraj S. Kamble, Satish A. Gangawane
Summary: This review explores Mn₃O₄ nanomaterials as electrode materials for supercapacitors, emphasizing their pseudocapacitive behavior and structural advantages. Despite their high theoretical capacitance, low electrical conductivity limits their performance. Strategies such as doping with transition metals, forming composites with graphene, and intercalating alkali metal ions have been examined to enhance charge storage efficiency. The study underscores the potential of Mn₃O₄-based supercapacitors in next-generation energy storage, while highlighting the need for further research to optimize their electrochemical performance and long-term stability.
Review | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 03 December 2024
SciEngg Advances 2(1), 01-15 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0001Research Articles
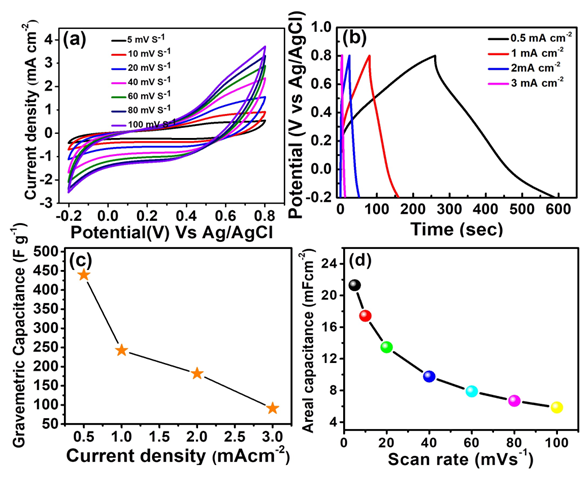
Electrodeposited MnO2 Thin Film as High–Performance Electrode for Supercapacitor Application
J. L. Patil, R. A. Chavan, A. S. Sutar, S. S. Kulkarni, R. K. Dhanvade, P. B. Patil, S. R. Shingte, S. J. Pawar
Summary: MnO₂ thin films were successfully electrodeposited onto stainless steel substrates, forming binder-free nanostructured electrodes for supercapacitor applications. Structural characterization confirmed the formation of amorphous birnessite δ-MnO₂, with XRD, FTIR, and XPS analyses validating its composition and bonding states. The electrochemical performance, evaluated through CV and GCD, revealed a high specific capacitance of 439 F g⁻¹, along with excellent energy and power densities. The study underscores the advantages of electrodeposited MnO₂, including its uniform morphology, efficient charge storage, and environmental sustainability. Future research should focus on optimizing deposition conditions, incorporating MnO₂ composites, and assessing long-term cycling stability to further enhance its supercapacitor performance.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 08 December 2024
SciEngg Advances 2(1), 16-25 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0016Impact of Ni Doping on the Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited via Chemical Bath Deposition
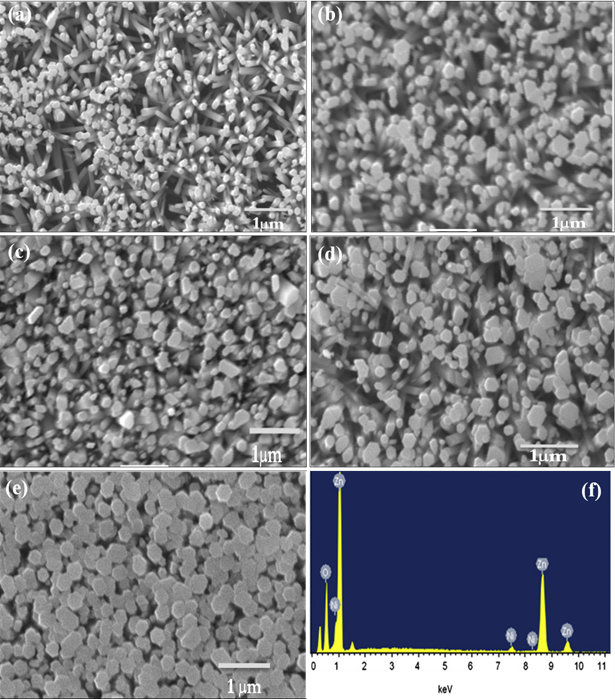
Gauri R. Patil, N. J. Kamble, B. P. Jamdade, Sikandar H. Tamboli
Summary: Nickel-doped ZnO thin films were synthesized via chemical bath deposition and analyzed for their structural, optical, and magnetic properties. XRD confirmed a wurtzite structure with no secondary phases, while SEM revealed morphological evolution with Ni doping. UV-Vis spectroscopy showed band gap narrowing, and VSM confirmed room-temperature ferromagnetism due to Ni-ion interactions with ZnO defects. The optimized 2% Ni-doped ZnO exhibited superior properties, making it a strong candidate for applications in optoelectronics and spintronics.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 09 December 2024
SciEngg Advances 2(1), 26-34 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0026Synthesis of Zinc–Doped Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Using Cissus Quadrangularis : Characterizations and Photocatalytic Applications
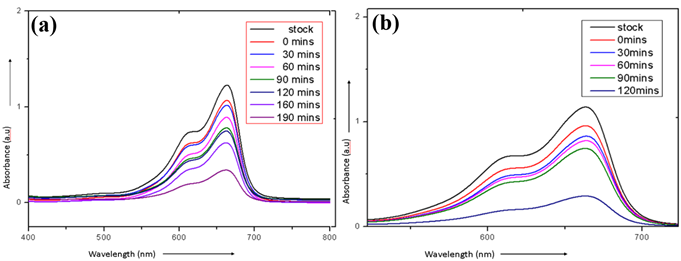
T. Pavithra, A. Muhamed Althaf, L. Ganesh, M. Beaula Ruby Kamalam, D. Rani Roshlin, S. S. R. Inbanathan
Summary: Zinc-doped iron oxide (Zn@Fe₂O₃) nanocomposites were synthesized via a green route using Cissus quadrangularis stem extract. Structural and morphological analyses confirmed the crystalline nature, elemental composition, and stabilization by plant-derived biomolecules. Optical characterization revealed bandgap narrowing, enhancing photocatalytic efficiency. Zn@Fe₂O₃ exhibited superior methylene blue degradation under visible light compared to pure Fe₂O₃. This eco-friendly approach offers a sustainable method for fabricating nanomaterials with potential applications in environmental remediation and industrial catalysis.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 15 December 2024
SciEngg Advances 2(1), 35-43 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0035Synthesis and Characterization of Al–Doped Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles
C. Palanisamy, S. Rubila, A. Kingson Solomon Jeevaraj
Summary: Al–doped MnO₂ nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized using XRD, SEM, TEM, EDX, and UV-Vis spectroscopy. Structural analysis confirmed a tetragonal MnO₂ phase, with crystallite sizes between 49.75 nm and 92.71 nm. Morphological studies revealed uniformly distributed nanoparticles with sizes ranging from 13.34 nm to 22.23 nm. EDX analysis validated the successful incorporation of aluminum, while optical characterization indicated a direct bandgap of 3.79 eV, suggesting potential optoelectronic applications. The enhanced conductivity and catalytic activity of Al-doped MnO₂ highlight its promising applications in supercapacitors, energy storage, and photocatalysis.
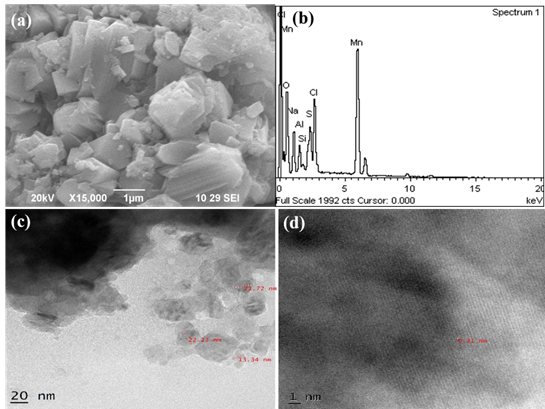
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 23 December 2024
SciEngg Advances 2(1), 44-49 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0044Volume 1, Issue 4 (December 2024)
Research Articles
Fabrication and Characterization of Silicon Quantum Dots Thin Films for Optoelectronic Applications
Aditya Srivastava, Shamshad A. Khan, Archana Srivastava
Summary: Silicon quantum dots (Si-QDs) were synthesized on quartz substrates using a physical vapor deposition method under varying substrate temperatures. Structural, optical, and electrical properties were characterized through various techniques. The results confirmed the amorphous nature of Si-QDs with sizes between 3-7 nm and tunable bandgap energy. Temperature-dependent DC conductivity revealed semiconducting behavior, enhancing potential applications in optoelectronics, especially for solar cells, due to their favorable light absorption and conductivity properties.
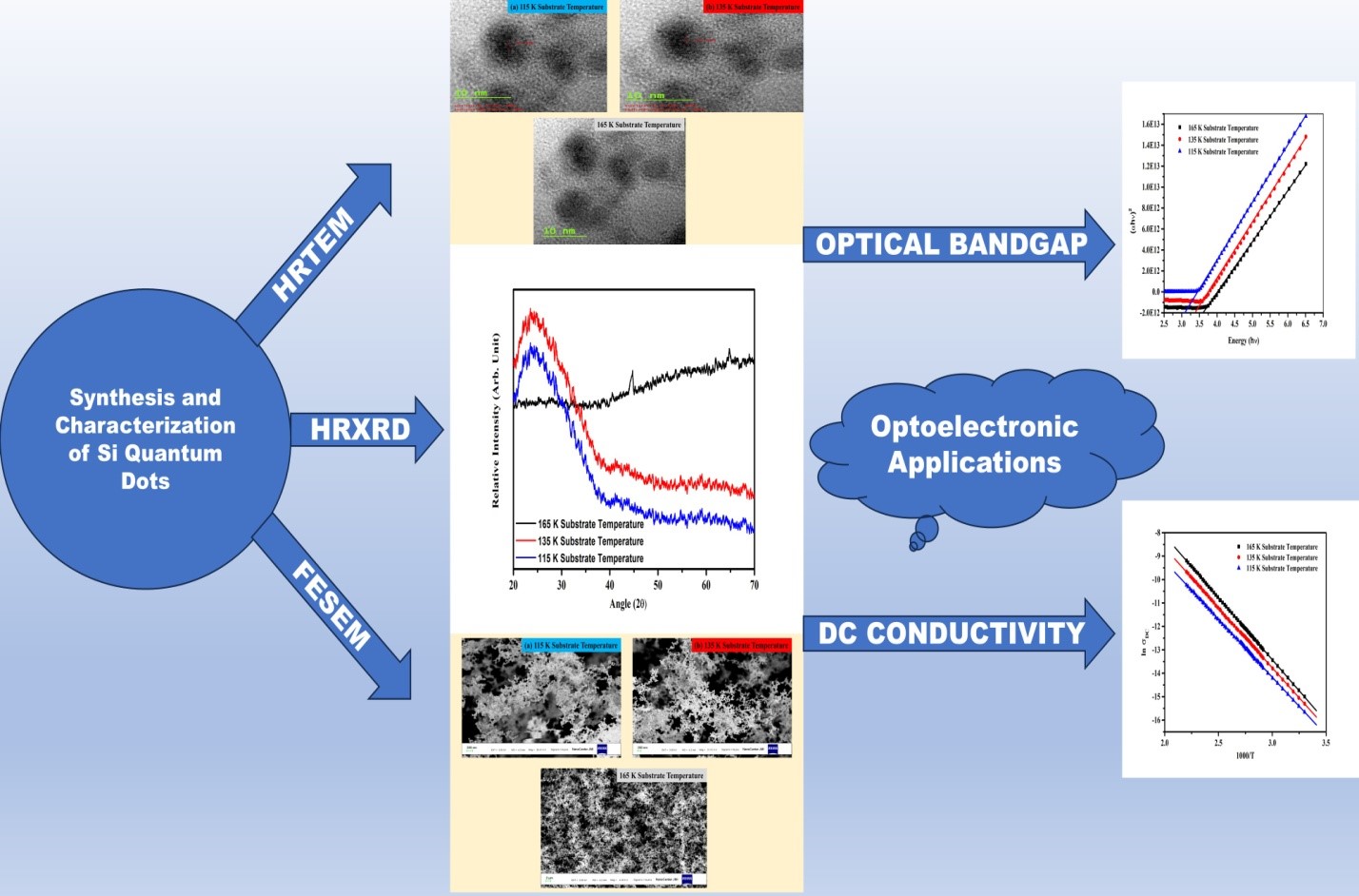
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 29 August 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(4), 124-133 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0124Preparation and Characterization of Beryllium Oxide–Diethylene Glycol Nanofluids for Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
P. Prakash, J. Catherine Grace John, T. Merita Anto Britto, B. Rohini, A. Kingson Solomon Jeevaraj
Summary: Beryllium oxide (BeO) nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized using XRD and SEM, showing a crystallite size of 22.72 nm. Nanofluids were prepared by dispersing BeO nanoparticles in diethylene glycol, and thermal conductivity, viscosity, and ultrasonic velocity were measured across varying concentrations. The 0.001 wt% concentration demonstrated optimal thermal conductivity, making the nanofluid suitable for heat transfer applications. The study offers valuable insights for developing nanofluids with enhanced thermal properties.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 September 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(4), 134-143 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0134Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles for Visible-light photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue
M. Beaula Ruby Kamalam, Sherila Adlin. J
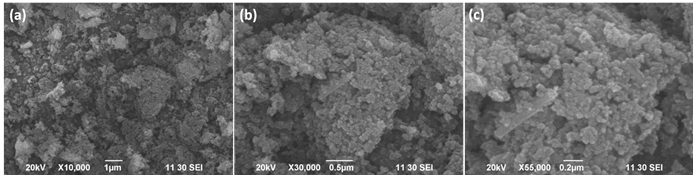
Summary: Cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄) nanoparticles were synthesized via the hydrothermal method and characterized for their structural and optical properties. XRD confirmed a cubic spinel structure with an average crystallite size of 64.86 nm. FTIR and UV-Vis spectroscopy validated the chemical bonding and light absorption capabilities. Photocatalytic tests revealed a reasonable degradation efficiency of methylene blue dye under visible light, highlighting the nanoparticles’ environmental application potential in wastewater treatment. These findings present Co₃O₄ nanoparticles as promising materials for photocatalysis.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 07 September 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(4), 144-151 (2024)
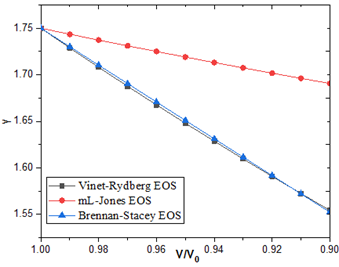
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0144Comparative Analysis of Grüneisen Parameters for Selected Geophysical Minerals Using Advanced Equations of State
Shivam Srivastava, Prachi Singh, Anjani K. Pandey, Chandra K. Dixit
Summary: This theoretical study investigates the Grüneisen parameter of MgO, Al2O3, and Mg2SiO4 using Vinet-Rydberg, modified Lenard-Jones, and Brennan-Stacey EOS. Results show a consistent decrease in the Grüneisen parameter with increasing compression, with the modified Lenard-Jones EOS displaying the least sensitivity and the Brennan-Stacey EOS showing the highest. This analysis highlights the critical role of EOS models in predicting thermodynamic properties and informs future research on high-pressure material behavior.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 09 October 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(4), 152-157 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0152Tribological Evaluation of Engine Oil Blended with Sesame, Mustard, and Olive Oils as Additives
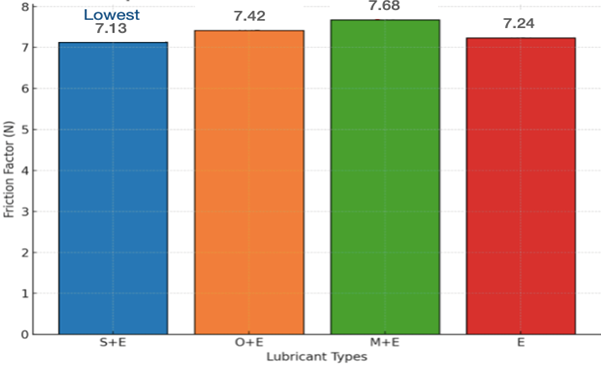
Md. Sharique Azmi, Sabah Khan, Ali Saleh Hussein Alqushaibi
Summary: The study evaluated the tribological properties of 5W-40 engine oil blended with 10% sesame, mustard, and olive oils using a Linear Reciprocating Tribometer. Sesame oil emerged as the most effective additive, reducing the coefficient of friction to 0.35 and the friction factor to 7.13. Olive oil showed moderate performance, while mustard oil was the least effective. These findings underline the potential of sesame oil as a sustainable lubricant additive, enhancing engine efficiency and reducing wear.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 19 October 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(4), 158-165 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0158Volume 1, Issue 3 (September 2024)
Research Articles
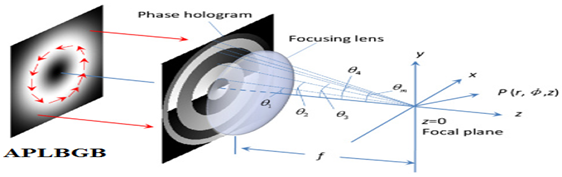
Generating Sub–Wavelength Longitudinal Magnetization Chains using High NA Lens System
M. Udhayakumar, P. Raju, S. Aswanth, K.B. Rajesh
Summary: The research demonstrates that adjusting the ring radii of a multi-belt complex phase filter allows the formation of novel sub-wavelength magnetization patterns using focused Laguerre-Bessel-Gaussian beams. These patterns include chains of magnetization spots, suitable for applications like magnetic particle transport, multilayer data storage, and optomagnetic devices. The study employs vector diffraction theory and the inverse Faraday Effect, revealing the potential for precise manipulation of magnetization fields.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 13 June 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(3), 87-93 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0087Post Synthesis Functionalization of Graphene Oxide for the Production of Cobalt Nanocomposites in Energy Storage Applications
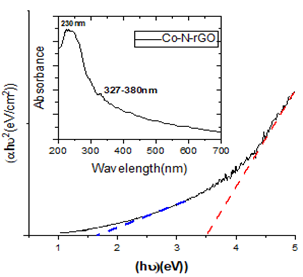
Jaiby Joseph, Mercy Mathews, Arpitha Prabhakaran
Summary: The study synthesized N-rGO and Co-N-GO using hydrothermal methods, confirmed through XRD, FTIR, UV-Vis, and Raman spectroscopy. Nitrogen doping and cobalt incorporation resulted in improved structural, optical, and electrical properties, with reduced crystallite size and bandgap. These advancements make the materials highly suitable for energy storage and catalytic applications, providing a scalable solution for future energy technologies.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 18 June 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(3), 94-101 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0094Copper Slag as a Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Aggregates in Moisture – Resistant Asphalt Pavement for Hilly Terrain
Suraj Kumar, Arun K. Mishra, Satyam Singh
Summary: The study explores copper slag (CS) as a sustainable substitute for conventional aggregates (CA) in asphalt mixes for hilly terrains. The results show that CS improves moisture resistance and forms stronger bonds with asphalt compared to CA, reducing pavement degradation. The research highlights CS’s potential to enhance road durability, offering an environmentally friendly and resource-efficient solution for road construction.
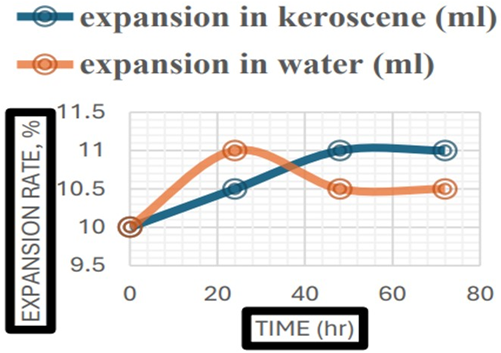
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 27 June 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(3), 102-107 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0102Performance Analysis of Fluidized Bed Gasifier Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Impact of Particle Size and Air Preheating on Gas Composition
S. Ganesan, Sravanth Chandaka, Neethusri Velangi, Jayaprasad, C. Shanthi, Satyaprasad
Summary: This study investigates the performance of a Fluidized Bed Gasifier (FBG) using sawdust as fuel through Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling. The analysis explores the effects of particle size (0.5 mm and 1 mm) and air preheating temperatures (400 K and 600 K) on the gas composition. Results show that larger particles (1 mm) at 400 K lead to improved gas production, especially of CO and H₂, with the gasifier’s performance increasing by 75%. However, at 600 K, higher combustion levels reduce fuel gas yield.
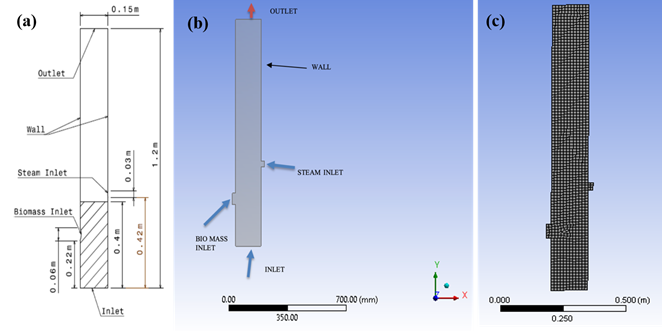
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 01 July 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(3), 108-115 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0108Spectroscopic Estimation of Thermodynamic Properties of Copper Monohalides (CuF, CuCl, CuBr, and CuI)
Shipra Tripathi, Anjani K. Pandey, Kailash Narayan Uttam, C. K. Dixit
Summary: The paper investigates the thermodynamic properties of copper monohalides (CuF, CuCl, CuBr, CuI) using spectroscopic data and partition function theory. Thermodynamic quantities, including Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, entropy, and specific heat capacity, are calculated across a temperature range of 100 K to 3000 K. The study accounts for anharmonicity and nonrigidity effects, providing a deeper understanding of molecular motion. These results are essential for developing copper-based materials with optimized thermodynamic properties for use in nanotechnology and industrial processes.
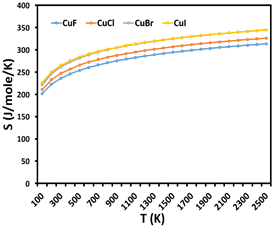
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 August 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(3), 116-123 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0116Volume 1, Issue 2 (June 2024)
Research Articles
Eco-Friendly Synthesis and Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ocimum tenuiflorum Leaf Extract
Ravi Kumar, Naveen Thakur, Saurabh Sharma, Kuldeep Kumar
Summary: The research demonstrates the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract. Characterization techniques, including UV-visible spectroscopy, SEM, TEM, and XRD, confirmed the crystalline nature and spherical morphology of the nanoparticles. The synthesized ZnO NPs showed effective photocatalytic activity in degrading methyl orange dye, highlighting their environmental applications. This eco-friendly method offers a sustainable approach for producing ZnO NPs with controlled properties suitable for various advanced applications.
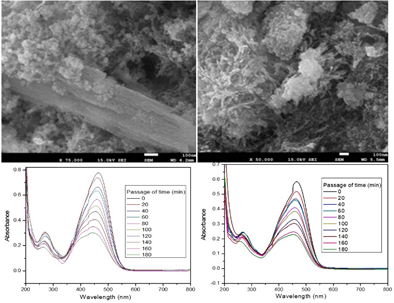
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 May 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(2), 48-55 (2024)
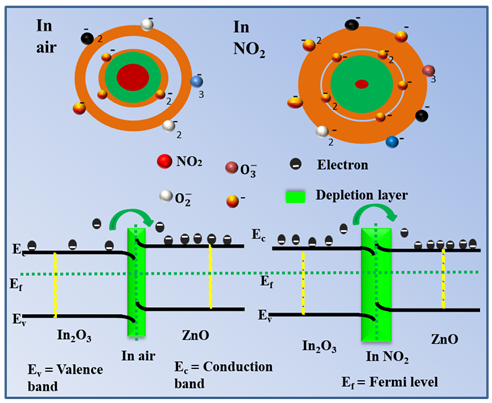
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0048In2O3 Doped ZnO Nanosheets for Ultra-Trace Detection of NO2
Adil Shafi Ganie, Shahid Hussain, Sufaid Shah, Muhammad Javed Liaqat, Amensisa Negasa Begi, Zhenyu Miao, Yuanyuan Han
Summary: In2O3-doped ZnO nanosheets were synthesized using the hydrothermal method and characterized by XRD, UV-DRS, and microscopy techniques. The gas sensor, optimized to operate at 300°C, exhibited a significantly higher response to NO2 (Rg/Ra = 41.9) compared to pure ZnO (Rg/Ra = 14.04) at 100 ppm NO2. The sensor demonstrated excellent sensitivity, selectivity, stability, and repeatability with a rapid response time of 32 seconds and effective detection of varying NO2 concentrations. The study underscores the potential of In2O3-doped ZnO nanosheets for advanced environmental monitoring applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 23 May 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(2), 56-65 (2024)
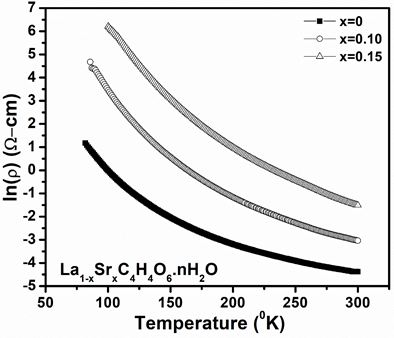
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0056Influence of Strontium Doping on the Electrical Resistivity and Microhardness of Gel Grown Lanthanum Tartrate Crystals
A. Firdous, S. Irfan, A. H. Pandith, I. Nazir, N. Ali, S. Showket, M. Q. Lone, G. N. Dar
Summary: This research investigates the effects of strontium doping on the electrical resistivity and microhardness of gel-grown lanthanum tartrate crystals. Strontium doping reduced resistivity and enhanced electrical conductivity, as confirmed by Mott’s variable range hopping model. Additionally, microhardness testing revealed increased mechanical strength with strontium incorporation. The study demonstrates that strontium-doped lanthanum tartrate crystals possess improved electrical and mechanical properties, suggesting their suitability for advanced material applications.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 24 May 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(2), 66-73 (2024)
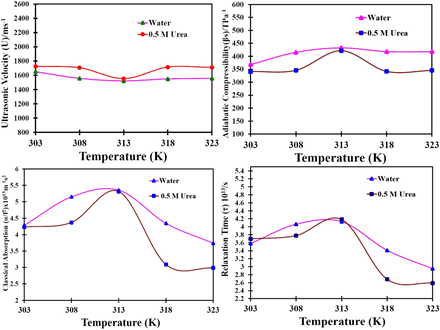
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0066Ultrasonic and Thermodynamic Analysis of Molecular Interaction in Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Urea-Water Ternary Mixtures at Various Temperatures
Narendra Prasad Tripathi, Brijesh K. Pandey, Abhay P. Srivastava
Summary: The study uses ultrasonic velocimetry to investigate the SDDS-urea-water ternary mixture at temperatures from 303 K to 323 K. Key parameters like ultrasonic velocity, density, and viscosity were measured to compute acoustic properties, indicating urea’s hydrophilic behavior at lower temperatures and hydrophobic behavior at higher temperatures. Temperature coefficients of ultrasonic velocity and adiabatic compressibility confirmed the temperature-dependent interaction behavior. Relaxation time analysis showed varying interaction dynamics across temperatures, with significant implications for solution chemistry, biochemistry, and surfactant chemistry.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 26 May 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(2), 74-80 (2024)
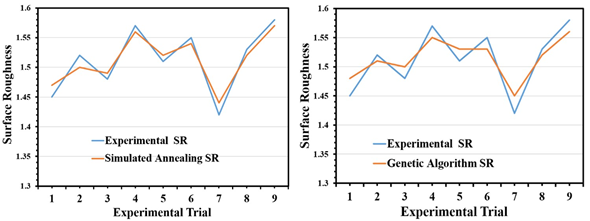
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0074Prediction of Surface Roughness in Turning of Monel K-500 Super Alloy Using Simulated Annealing and Genetic Algorithm: A Comparative Experimental Analysis
V. Dilli Ganesh, T. J. Nandhini
Summary: This study demonstrates the effectiveness of simulated annealing and genetic algorithms in predicting surface roughness during the turning of Monel K-500 super alloy. Both methods closely aligned with experimental measurements, with average deviations of ±0.02 μm and ±0.03 μm, respectively. These techniques can optimize cutting parameters, improve surface finish, and enhance component quality, proving valuable for high-precision machining of challenging materials like Monel K-500.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 27 May 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(2), 81-86 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0081Volume 1, Issue 1 (March 2024)
Editorial
Introducing SciEngg Advances: Advancing Science and Engineering
D. K. Dwivedi
Editorial | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 1-2 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0001Research Articles
Newly Designed Cutting-Edge GCN@Cd Nanocomposite Catalyst Drives Ultra-Selective Organic Transformations under Solar Light
Shivam K. Jaiswal, Rajesh K. Yadav, Satyam Singh, Rehana Shahin, Kanchan Sharma, Aditya-Nath Yadav, Indra Kumari, Jin-OoK Baeg, Kamini Singh, Maneesha Pandey, Suman Yadav, Navneet Kumar Gupta
Summary: This study presents the synthesis and development of a novel visible light active nanocomposite photocatalyst, GCN@Cd, based on graphitic carbon nitride. The GCN@Cd nanocomposite effectively drives ultra-selective organic transformations, specifically reducing nitroarene to azo compounds under solar light. Characterization confirms its superior performance, achieving a high yield of ~95.15% at ambient conditions, demonstrating its potential for environmental remediation and organic synthesis.
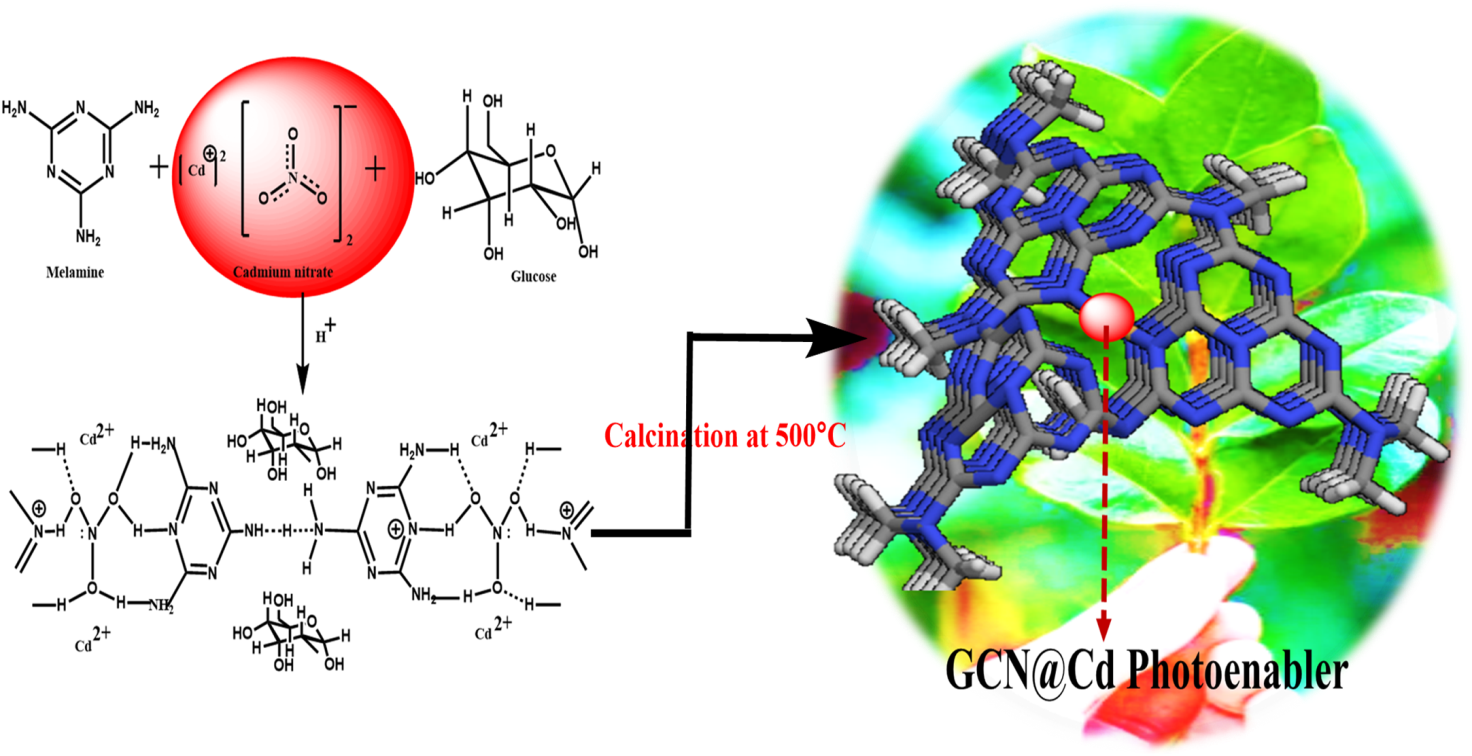
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 3-12 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0003Ambient Air Ageing Effect on Vapour-Chopped Polyaniline Thin Film Optical Waveguide for Integrated Optics
Jyotiprakash. B. Yadav, R. K. Puri, Vijaya Puri
Summary: This study investigates the ambient air ageing effects on polyaniline (PANI) thin films, synthesized via oxidation polymerization and deposited on glass substrates through vacuum evaporation. The vapour chopping technique was employed to enhance film properties. After 30 days of air ageing, vapour-chopped films showed reduced optical transmission loss, refractive index, and intrinsic stress compared to as-deposited films, demonstrating improved stability and performance for optical waveguide applications.
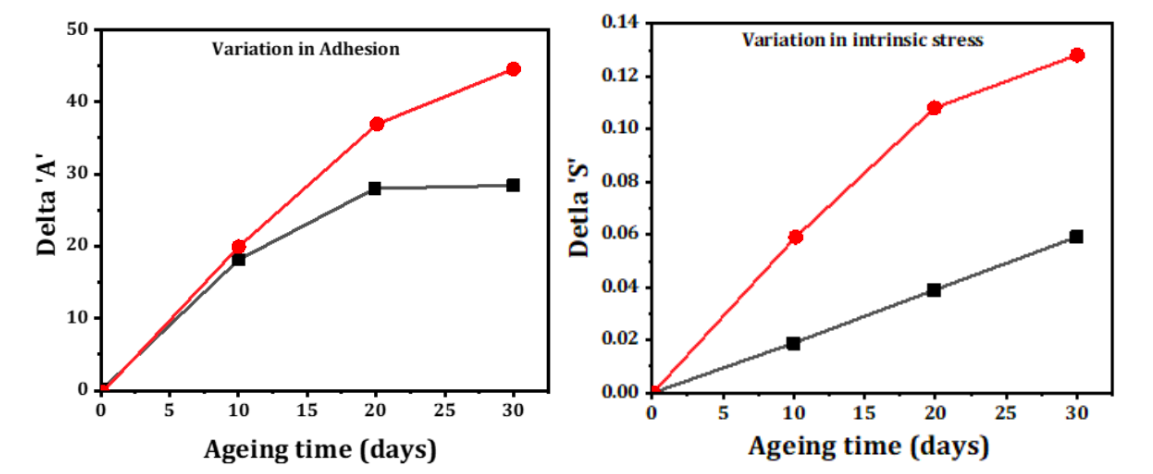
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 13-19 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0013Design and Evaluation of a Twin-Core Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensor for Human Blood Biomolecules
Vikash Mourya, Sapana Yadav, D. K. Dwivedi, Pooja Lohia
Summary: This study presents the design and evaluation of a twin-core photonic crystal fiber (TC-PCF) sensor with a rectangular analyte channel for detecting blood biomolecules. Using silica as the substrate and rectangular air-holes in the cladding, the sensor operates in the 2 µm to 3 µm wavelength range. Simulations results show high sensitivity, achieving 1641.2 nm/RIU for white blood cells and 2732.638 nm/RIU for red blood cells. This cost-effective and easy-to-fabricate sensor offers a compact solution for blood biomolecule detection.
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 20-29 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0020Investigating the Optical, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of La₂NiMnO₆ via Sr-Eu Co-Doping
Salman Firdous, Gul Faroz A. Malik, Farooq A. Khanday, Inder K. Pandey
Summary: This study examines the effects of Sr-Eu co-doping on the optical, magnetic, and mechanical properties of La₂NiMnO₆ (LNMO) using Density Functional Theory (DFT) with Local Density Approximation (LDA) and Hubbard’s Correction (LDA+U). The co-doping significantly enhances LNMO’s dielectric properties, optical conductivity, and magnetic characteristics, making it suitable for applications in spintronics, optoelectronics, and energy storage devices. The mechanical resilience of the doped material further supports its durability in technological applications.
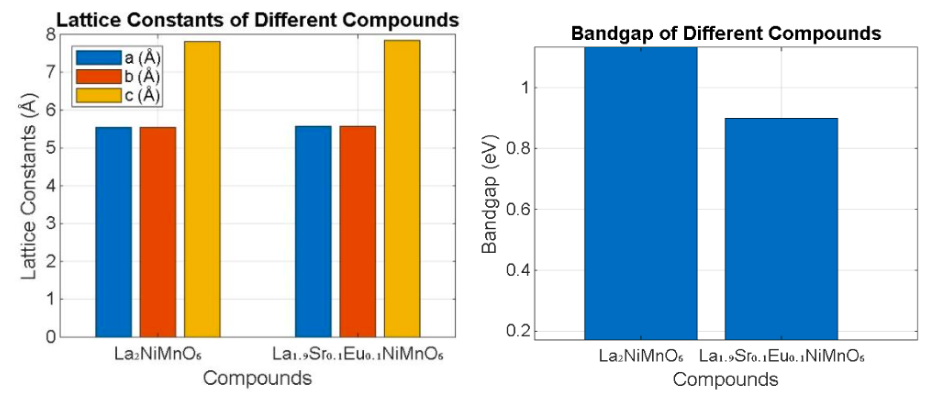
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 30-38 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0030Dissipative Dynamics of an Interacting Spin System with Collective Damping
Irfan A. Dar, Faisal Farooq, Junaid Majeed Bhat, Mehboob Rashid Bhat, G. N. Dar, Sheikh Irfan, Muzaffar Qadir Lone
Summary: This study explores the dissipative dynamics in an infinite-range Heisenberg model coupled to a non-Markovian bath and subjected to Lindblad dynamics due to site-specific spin flipping. Using Holstein-Primakoff transformations and Schwinger-Keldysh technique, the system’s mean field solution shows z₂-symmetry breaking at the transition point. An effective temperature linearly dependent on system-bath coupling is derived, and fluctuations over the mean field are found to modify the dissipative spectrum with O(1/N) corrections.
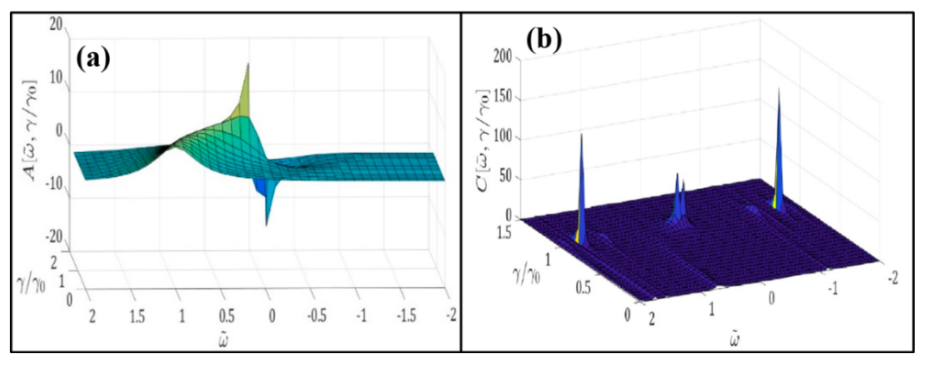
Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 21 March 2024
SciEngg Advances 1(1), 39-47 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2024.0039Aims and Scope
SciEngg Advances
Welcome to SciEngg Advances, a prestigious multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal published by Ariston Publications, devoted to pushing the frontiers of scientific and engineering knowledge through the swift dissemination of cutting-edge research. Our mission is to provide a dynamic platform where scientists, engineers, and scholars can present their pioneering discoveries and innovations, fostering progress and collaboration within the scientific and engineering communities.
SciEngg Advances acknowledges the crucial role of interdisciplinary collaboration in driving the forefront of scientific and engineering endeavors. As such, our journal serves as a central hub for research ventures spanning various disciplines within science and engineering. We welcome contributions from scientists and engineers across diverse fields, including chemistry, physics, biology, materials science, environmental science, computational science, engineering, technology, and beyond. By embracing diverse perspectives and expertise, we aim to catalyze innovation and foster interdisciplinary collaboration.
With a steadfast focus on both fundamental principles and practical applications, SciEngg Advances delves into the latest frontiers of scientific and engineering research, tackling pressing global challenges and propelling technological advancements. From pioneering synthetic methodologies to sustainable engineering solutions, from cutting-edge materials science to transformative bioengineering, our journal encompasses a broad spectrum of topics, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of modern scientific inquiry.
Our dedication to excellence extends to our rigorous editorial standards and peer-review process, ensuring that only the highest quality research is disseminated. Through our commitment to open access, we strive to promote inclusivity, collaboration, and the democratization of knowledge, facilitating global engagement and impact within the scientific and engineering communities.
We invite researchers, engineers, and scholars from around the globe to join us in advancing the frontiers of scientific and engineering knowledge by contributing their expertise and discoveries to SciEngg Advances.
Aims:
Dissemination of Cutting-Edge Research: SciEngg Advances aims to be a primary platform for the rapid dissemination of cutting-edge research in scientific and engineering disciplines. By providing a swift and efficient avenue for the publication of groundbreaking discoveries, SciEngg Advances aims to accelerate the pace of scientific advancement and facilitate the translation of research findings into practical applications.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: SciEngg Advances recognizes the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing complex scientific and engineering challenges. One of its primary aims is to foster collaboration among scientists, engineers, and scholars from diverse disciplines. By serving as a nexus for interdisciplinary research endeavors, SciEngg Advances aims to facilitate the cross-pollination of ideas and expertise, leading to novel insights and innovative solutions to multifaceted problems.
Promotion of Excellence: SciEngg Advances is committed to upholding the highest standards of excellence in scientific and engineering research. Through rigorous editorial processes and stringent peer review, SciEngg Advances aims to ensure the publication of research of the highest quality and integrity. By promoting excellence in research, SciEngg Advances seeks to elevate the standards of scientific and engineering practice and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Scope:
SciEngg Advances covers a broad spectrum of topics within the scientific and engineering domains, including but not limited to:
Chemistry:
- Synthesis and characterization of novel compounds
- Catalysis and reaction mechanisms
- Computational chemistry and molecular modeling
Physics:
- Quantum mechanics and quantum phenomena
- Condensed matter physics and materials science
- Particle physics and cosmology
- Quantum phenomena, the properties of advanced materials, and the development of nanoscale devices.
Biology:
- Genetics and genomics
- Cell biology and molecular biology
- Ecology and evolutionary biology
- Biotechnology, bioinformatics, genetics
- Development of therapeutic agents
- Application of computational methods to biological problems.
Environmental Science:
- Climate change and global warming
- Environmental pollution and remediation
- Sustainable development and conservation biology
- Mitigation of environmental pollution
- Development of sustainable technologies
Assessment of the impacts of human activities on the environment.
Earth Sciences:
- Geology and geochemistry
- Seismology and earthquake engineering
- Atmospheric sciences and meteorology
Mathematics:
- Mathematical modeling and simulation
- Optimization and operations research
- Statistical analysis and data science
Computational Science:
- Research in modeling, simulation, data analysis, and machine learning
- Development of computational models
- Simulation of complex systems
- Application of data-driven approaches to scientific and engineering problems
Materials Science:
- Research in nanomaterials, polymers, composites, and biomaterials.
- Synthesis and characterization of novel materials.
- Study of materials properties and applications.
- Development of advanced materials for various technological purposes.
Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials:
- Nanoscale fabrication techniques
- Nanomaterial synthesis and characterization
- Applications of nanotechnology in electronics, medicine, and energy
Advanced Materials and Metallurgy:
- Development of high-performance materials
- Alloy design and optimization
- Advanced processing techniques (e.g., additive manufacturing, thin film deposition)
Renewable Energy Technologies:
- Solar photovoltaics and solar thermal systems
- Wind energy harvesting and turbine design
- Biomass and biofuel production technologies
Smart Technologies and Internet of Things (IoT):
- Development of smart sensors and actuators
- IoT applications in healthcare, agriculture, and transportation
- Data analytics and machine learning for IoT systems
Sustainable Infrastructure and Urban Development:
- Green building materials and construction techniques
- Urban planning for sustainability and resilience
- Waste management and recycling technologies
Biomedical Engineering and Healthcare Technologies:
- Medical device design and innovation
- Biomedical imaging and diagnostics
- Biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
Robotics and Automation:
- Autonomous systems and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Industrial robotics and automation in manufacturing
- Human-robot interaction and collaborative robotics
Transportation and Mobility Solutions:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicle technologies
- Intelligent transportation systems (ITS)
- Alternative fuels and propulsion systems
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Engineering:
- Big data analytics for engineering applications
- Predictive maintenance and asset management
- AI-driven optimization and decision-making tools
Environmental Engineering and Sustainability:
- Pollution control and remediation technologies
- Water and wastewater treatment processes
- Sustainable design and life cycle assessment methodologies
Objectives:
SciEngg Advances aims to be a catalyst for scientific and engineering innovation and collaboration. By disseminating cutting-edge and interdisciplinary research, SciEngg Advances seeks to contribute to the advancement of knowledge and the development of solutions to pressing societal problems. In pursuit of our overarching aims, SciEngg Advances sets forth the following objectives:
Facilitate Knowledge Exchange: SciEngg Advances aims to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and ideas among scientists, engineers, and scholars worldwide. By providing a platform for the publication and dissemination of research findings, SciEngg Advances seeks to promote dialogue and collaboration within scientific and engineering communities.
Drive Technological Advancements: SciEngg Advances aims to drive technological advancements by showcasing research that has the potential to lead to practical applications and innovations with societal impact. By highlighting cutting-edge developments in scientific and engineering fields, SciEngg Advances seeks to inspire the translation of research findings into technologies that benefit society.
Address Global Challenges: SciEngg Advances is committed to addressing pressing global challenges, such as climate change, healthcare, energy sustainability, and resource conservation. By supporting research that offers sustainable solutions to these challenges, SciEngg Advances aims to contribute to the development of a more resilient and sustainable world.
Promote Open Access: SciEngg Advances promotes open access to scientific and engineering research, ensuring that knowledge is accessible to all. By providing free and unrestricted access to research articles, SciEngg Advances seeks to democratize access to knowledge and facilitate global engagement and impact within scientific and engineering communities.
Subject Covered(but not limited to):
SciEngg Advances covers a broad spectrum of subjects within the field of science and engineering, including but not limited to:
Chemistry:
- Synthesis and characterization of novel compounds
- Catalysis and reaction mechanisms
- Computational chemistry and molecular modeling
Physics:
- Quantum mechanics and quantum phenomena
- Condensed matter physics and materials science
- Particle physics and cosmology
- Quantum phenomena, the properties of advanced materials, and the development of nanoscale devices.
Biology:
- Genetics and genomics
- Cell biology and molecular biology
- Ecology and evolutionary biology
- Biotechnology, bioinformatics, genetics
- Development of therapeutic agents
- Application of computational methods to biological problems.
Environmental Science:
- Climate change and global warming
- Environmental pollution and remediation
- Sustainable development and conservation biology
- Climate change, environmental remediation, and renewable energy
- Development of sustainable technologies
- The mitigation of environmental pollution, and the assessment of the impacts of human activities on the environment.
Earth Sciences:
- Geology and geochemistry
- Seismology and earthquake engineering
- Atmospheric sciences and meteorology
Mathematics:
- Mathematical modeling and simulation
- Optimization and operations research
- Statistical analysis and data science
Computational Science:
- Modeling, simulation, data analysis, and machine learning.
- Development of computational models.
- Simulation of complex systems.
- Application of data-driven approaches to scientific and engineering problems.
Materials Science:
- Nanomaterials, polymers, composites, and biomaterials.
- Synthesis and characterization of novel materials.
- Study of materials properties and applications.
- Development of advanced materials for various technological purposes.
Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials:
- Nanoscale fabrication techniques
- Nanomaterial synthesis and characterization
- Applications of nanotechnology in electronics, medicine, and energy
Advanced Materials and Metallurgy:
- Development of high-performance materials
- Alloy design and optimization
- Advanced processing techniques (e.g., additive manufacturing, thin film deposition)
Renewable Energy Technologies:
- Solar photovoltaics and solar thermal systems
- Wind energy harvesting and turbine design
- Biomass and biofuel production technologies
Smart Technologies and Internet of Things (IoT):
- Development of smart sensors and actuators
- IoT applications in healthcare, agriculture, and transportation
- Data analytics and machine learning for IoT systems
Sustainable Infrastructure and Urban Development:
- Green building materials and construction techniques
- Urban planning for sustainability and resilience
- Waste management and recycling technologies
Biomedical Engineering and Healthcare Technologies:
- Medical device design and innovation
- Biomedical imaging and diagnostics
- Biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
Robotics and Automation:
- Autonomous systems and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Industrial robotics and automation in manufacturing
- Human-robot interaction and collaborative robotics
Transportation and Mobility Solutions:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicle technologies
- Intelligent transportation systems (ITS)
- Alternative fuels and propulsion systems
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Engineering:
- Big data analytics for engineering applications
- Predictive maintenance and asset management
- AI-driven optimization and decision-making tools
Environmental Engineering and Sustainability:
- Pollution control and remediation technologies
- Water and wastewater treatment processes
- Sustainable design and life cycle assessment methodologies
Readership
SciEngg Advances, a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal, serves as a trusted source of high-quality research and insights, providing a platform for knowledge dissemination, collaboration, and inspiration among a diverse audience of professionals, researchers, educators, and enthusiasts committed to advancing science and engineering for the betterment of humanity and the planet.
SciEngg Advances is designed to attract a discerning readership deeply interested in the frontiers of scientific and engineering knowledge. Our journal is tailored to appeal to a wide range of professionals and researchers who are passionate about advancing the boundaries of science and engineering through innovative research and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Our readership includes, but is not limited to:
Scientists and Researchers:
Individuals actively engaged in scientific inquiry and research across various disciplines of science and engineering, including chemistry, physics, biology, materials science, environmental science, and computational science.
Engineers and Technologists:
Professionals working in engineering fields such as chemical engineering, materials engineering, biomedical engineering, environmental engineering, and electrical engineering, who are interested in the latest advancements and applications of science and technology.
Academics and Educators:
Faculty members, researchers, and students from universities, colleges, and research institutions worldwide seeking to explore the latest developments and discoveries in science and engineering to enhance their teaching, learning, and research endeavors.
Industry Leaders and Innovators:
Executives, entrepreneurs, and professionals from industrial sectors such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, energy, materials, electronics, and manufacturing, interested in leveraging scientific advancements for product development, process optimization, and innovation.
Policy Makers and Regulators:
Government officials, policymakers, and regulatory authorities involved in shaping policies and regulations related to scientific research, technology development, environmental sustainability, and public health.
Science and Technology Enthusiasts:
Individuals passionate about science and technology who are eager to stay informed about the latest breakthroughs, discoveries, and innovations in scientific and engineering fields, and their potential impact on society and the world.
Editorial Board
Editorial Manager
Prof. Ahmad Umar
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Ohio State University, Columbus, 43210 OH, USA
Email: umar.20@osu.edu
Editors-in-Chief
Prof. Dr. David Hayrapetyan
Department of General Physics and Quantum Nanostructures,
Russian-Armenian University, H. Emin 123, Yerevan 0051, Armenia
Email: david.hayrapetyan@rau.am
Prof. D. K. Dwivedi
Department of Physics and Material Science
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology,
India
Email: todkdwivedi@gmail.com
Editors
Prof. Brijesh. K. Pandey
Department of Physics and Material Science
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology Gorakhpur, India
Prof. Xiang Wu
School of Materials Science and Engineering
Shenyang University of Technology, China
Prof. Bal Chandra Yadav
Department of Physics
School of Physical & Decision Sciences
Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Lucknow, India
Dr. Roaa Sait
Department of Physics
Faculty of Science, King Abdulaziz University,
Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Dr. Xin Zhang
School of Architecture and Civil Engineering
Xihua University, Chengdu, China.
Dr. Mantesh K. Yadav
Department of Chemistry
Starex University, Gurugram, Haryana, India.
Dr. Kai Song
School of Life Science
Changchun Normal University, Changchun, China
Prof. Rajesh K. Verma
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Harcourt Butler Technical University Kanpur, India
Dr. Navneet K. Gupta
Centre for Sustainable Technologies,
Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Gulmohar Marg Bengaluru, India
Prof. Chinna Bathula
Department of Chemistry/Division of Electronics & Electrical Engineering
Dongguk University, Republic of Korea
Associate Editors
Prof. Rajesh K. Yadav
Department of Chemistry and Environmental Science
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology, India
Dr. Deepshikha
School of Engineering and Materials Science
Queen Mary University of London, London, United Kingdom
Dr. Pravin K. Singh
Institute of Advanced Materials
Gammalkilsvägen 18, 59053 Ulrika, Sweden
Dr. M. Khalid Hossain
Institute of Electronics,
Atomic Energy Research Establishment, Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Dr. Raman Kumar
Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, India
Dr. Pallavi Chaturavedi
HCW Biologics Miami/Fort Lauderdale Area,
2929 N Commerce Parkway, Florida, USA.
Prof. Atul P. Singh
Department of Chemistry,
Chandigarh University, India
Dr. Hailing Ma
The University of New South Wales
Australia
Prof. Joginder Singh
Maharishi Markandeshwar University
Mullana, India
Dr. Yang Luo
Department of Physics
City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR of China
Dr. Pooja Lohia
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology, India
Editorial Board Members
Prof. Wenjuan Guo
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,
University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, China.
Prof. S. Baskoutas
Department of Materials Science
University of Patras, Greece
Dr. Indresh Yadav
School of Basic Science
Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
Dr. Sajid Ali Ansari
Department of Physics, College of Science
King Faisal University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Dr. Satyendra Kumar Mishra
Space and Resilient Communications and Systems (SRCOM)
Centre Tecnològic de Telecomunicacions de Catalunya (CTTC)
Castedefels, Barcelona, Spain
Dr. Sachin Kumar Srivastava
Department of Physics,
Indian Institute of Technology Rorakee, India
Dr. Nazish Parveen
Department of Chemistry, College of Science
King Faisal University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Dr. Chandani Singh
Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology
141 Gajeong-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, South Korea.
Prof. M. S. Akhtar
Department of Semiconductor and Chemical Engineering,
Jeonbuk National University, 56212, Republic of Korea
Dr. Yadvendra Singh
School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR-97331, USA
Dr. Neelabh Srivastava
Department of Physics, School of Physical and Material Sciences
Mahatma Gandhi Central University, Bihar, India
Dr. Mohd. Zahid Ansari
Chemical Engineering Program,
Texas A&M University at Qatar, Doha, Qatar
Dr. Gul Faroz Ahmad Malik
Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Technology
University of Kashmir, Srinagar, India
Dr. Firoz Alam
Nanotechnology Laboratory,
University College London (UCL), London.
Dr. Faheem Ahmed
Department of Applied Sciences and Humanities
Faculty of Engineering and Technology, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi-110025, India
Prof. Brijesh Kumar
Department of Information Technology
Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women, Delhi, India
Prof. Y. K. Prajapati
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
MNNIT Allahabad, India
Prof. Wen Zeng
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
Dr. Simant K.Srivastava
Department of Chemistry,
Allahabad University, Allahabad, India
Prof. Vipin Kumar
Department of Applied Sciences
KIET Group of Institutions, Ghaziabad, India
Guide for Reviewers and Editors
Guide to Reviewers: SciEngg Advances
Welcome to the Instructions for Reviewers for SciEngg Advances. As a valued reviewer, the expertise and insights of the reviewer play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and integrity of the journal’s publications. A thorough evaluation and constructive feedback of the reviewers are instrumental in shaping the direction of scientific discourse in the field of sciences, engineering, technology and related fields. Below are guidelines to assist the reviewers in conducting a comprehensive review of manuscripts submitted to SciEngg Advances.
- Confidentiality: As a reviewer for SciEngg Advances, it is crucial to maintain the confidentiality of the manuscripts the reviewer assigned to review. This means refraining from discussing the content of the manuscripts with anyone other than the editorial office. By upholding confidentiality, the reviewer contribute to the integrity of the peer review process.
- Timeliness: Time is of the essence in the peer review process. Reviewers are expected to evaluate manuscripts promptly and submit their reports within the specified deadline. If circumstances arise that prevent the reviewer from meeting the deadline, it is important to communicate with the editorial office and request an extension in advance.
- Constructive Feedback: Reviewers play a pivotal role in providing constructive feedback to authors. When assessing manuscripts, focus on identifying both strengths and weaknesses. The comments of the reviewers should be specific, objective, and aimed at helping authors improve their work. Point out areas where the manuscript excels and areas where it could be enhanced.
- Originality and Ethical Standards: Evaluate the originality of the research presented in the manuscript and ensure that it meets ethical standards. Verify that proper citations are provided for previously published work and assess whether the research has been conducted in accordance with ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Content Evaluation: Dive deep into the content of the manuscript and evaluate its significance, novelty, and scientific rigor. Scrutinize the methodology used, the interpretation of results, and the contribution the research makes to the field. The evaluation of the reviewer should be thorough and objective, focusing on the scientific merit of the work.
- Clarity and Presentation: Assess the clarity and organization of the manuscript. Consider factors such as the writing style, structure, and coherence of the presentation. Provide feedback on how the manuscript could be improved to enhance clarity and readability for readers.
- Recommendation: Based on the evaluation, reviewers should make a recommendation regarding the fate of the manuscript—whether it should be accepted, revised, or rejected. Justify the recommendation with specific comments and suggestions for improvement. Reviewer recommendation will be instrumental in guiding the editorial decision-making process.
- Conflicts of Interest: Be transparent about any potential conflicts of interest that may influence your review. If reviewers have personal or professional connections to the authors or their research, disclose them to the editorial office. If reviewer feel that a conflict of interest may compromise their impartiality, notify the editorial office immediately.
- Respectful Communication: Maintain professionalism and respect in all communications related to the peer review process. Avoid personal or derogatory remarks and focus solely on the scientific content of the manuscript. The goal of the reviewer is to provide feedback that is helpful and constructive, regardless of your recommendation.
- Final Decision: The comments of the reviewers will be considered alongside those of other reviewers by the editorial team to make a final decision on the manuscript. The feedback of the reviewer is invaluable in ensuring the quality and integrity of the research published in SciEngg Advances. Thank you for your dedication to the peer review process.
Guide to Editors: SciEngg Advances
Welcome to the comprehensive Guide to Editors for SciEngg Advances. As an editor for our esteemed journal, your pivotal role revolves around ensuring the quality, integrity, and timely dissemination of groundbreaking research within the realm of sciences, engineering, technology, and related fields. This detailed guide is designed to equip you with the necessary instructions and best practices to navigate the editorial process with proficiency and efficacy. Your dedication and commitment as an editor are invaluable to the success and reputation of SciEngg Advances.
Editorial Workflow:
- Your initial task involves the meticulous assignment of suitable reviewers, drawing upon their expertise and availability to ensure thorough and insightful assessments.
- Efficiently manage the peer review process by overseeing the timely completion of reviews and judiciously evaluating reviewer comments to make informed editorial decisions.
- Maintain proactive communication with authors throughout the review process, providing updates, guidance, and constructive feedback as required.
- Thoughtfully evaluate the feedback provided by reviewers and exercise sound judgment in determining manuscript acceptance, revision, or rejection, upholding the journal’s standards of excellence.
Manuscript Handling:
- Uphold the journal’s submission guidelines rigorously, ensuring that submitted manuscripts adhere to formatting requirements and ethical standards.
- Conduct a comprehensive initial assessment of manuscripts to ascertain their suitability for peer review, considering factors such as novelty, relevance, and scientific rigor.
- Effectively manage revisions and resubmissions, facilitating productive interactions between authors and reviewers to address queries, concerns, or suggestions for improvement.
- Strive for consistency and rigor in the editorial process, upholding the journal’s reputation for scholarly excellence and integrity.
Ethical Considerations:
- Familiarize yourself thoroughly with the journal’s policies on plagiarism, authorship, conflicts of interest, and ethical conduct, ensuring strict adherence to established guidelines.
- Promptly address any instances of ethical misconduct or concerns, conducting impartial investigations and implementing appropriate measures in accordance with established procedures.
- Maintain the utmost confidentiality throughout the editorial process, safeguarding the anonymity of reviewers and respecting the privacy of authors to uphold the integrity of the peer review process.
Collaboration and Communication:
- Foster a collaborative and supportive environment conducive to constructive dialogue and scholarly exchange among authors, reviewers, and editorial board members.
- Encourage open communication and facilitate constructive feedback to foster continuous improvement in manuscript quality and scientific rigor.
- Serve as a liaison between authors and reviewers, facilitating effective communication and resolution of any conflicts or misunderstandings that may arise during the editorial process.
Continuous Improvement:
- Stay abreast of the latest developments and advancements in the field of science, engineering, technology, and related fields and scholarly publishing, adapting editorial practices to reflect evolving standards and expectations.
- Solicit feedback from authors, reviewers, and colleagues to identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of the editorial process.
- Strive for continuous improvement in all aspects of editorial management, contributing to the enhancement of the journal’s reputation and impact within the scientific community.
Publication Ethics
At SciEngg Advances, published by Ariston Publications, we uphold the highest ethical standards in scientific publishing to ensure the integrity, credibility, and trustworthiness of the research we disseminate. Our commitment to ethical practices extends across all stages of the publication process, from manuscript submission to post-publication dissemination. Our publication ethics policies are designed to guide authors, reviewers, editors, and all stakeholders involved in the publishing process. Adherence to these ethical principles is paramount to maintain transparency, fairness, and trust in scholarly communication.
1. Authorship and Author Responsibilities:
Authors are expected to adhere to the following ethical principles:
Authorship Criteria:
- Authorship eligibility hinges upon significant contributions to conceiving, designing, executing, or interpreting the research study.
- All contributors with substantial involvement in the work merit authorship recognition, while those offering support or assistance without meeting authorship criteria should be acknowledged accordingly.
- Authors are required to reveal any potential conflicts of interest that could impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
Originality and Plagiarism:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the originality of their work and confirming that it has not been previously published or is under consideration elsewhere for publication.
- Any form of plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, is unacceptable and will lead to immediate rejection or retraction.
- Any form of plagiarism, whether it involves directly copying text, ideas, or data without appropriate acknowledgment, is strictly forbidden.
- Editors utilize plagiarism detection software to screen submitted manuscripts and address any suspected cases of plagiarism promptly.
Conflict of Interest:
- Authors must reveal any potential conflicts of interest that might impact the research process or the interpretation of the results.
- This includes financial interests, employment affiliations, consulting arrangements, or personal relationships.
Data Integrity:
- Authors bear the responsibility of verifying the accuracy and integrity of their data, presenting research findings with honesty and transparency.
- Studies involving human subjects, animals, or sensitive data must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain the requisite approvals and permissions.
- Fabrication, falsification, or manipulation of data is considered unethical and constitutes scientific misconduct.
2. Peer Review Process:
- Reviewers must uphold the confidentiality of the peer review process and refrain from sharing any details about the manuscript or their assessment with unauthorized individuals without permission from the journal.
- Peer review is conducted with fairness.
- Reviewers are expected to conduct their evaluations impartially and offer constructive feedback aimed at enhancing the manuscript’s quality.
- Reviewers should declare any potential conflicts of interest and evaluate manuscripts objectively, focusing solely on their scientific quality.
- Editors oversee the peer review process to ensure its integrity and rigor, avoiding bias or favoritism.
3. Editorial Responsibilities:
Editorial Integrity:
- Editors uphold the integrity and quality of the editorial process, maintaining objectivity and impartiality in decision-making.
- Manuscripts are evaluated based on their scientific quality, significance, originality, and methodological rigor, without discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, religion, region, or institutional affiliation.
Conflict of Interest:
Editors are responsible for managing conflicts of interest transparently and impartially, ensuring that they do not compromise the integrity of the editorial process.
Transparency:
Editors should ensure transparency in the publication process by clearly communicating the editorial policies, peer review process, and any conflicts of interest.
4. Post-Publication Concerns:
Corrections and Retractions:
- Authors, editors, and publishers are responsible for promptly addressing errors or inaccuracies in published articles, issuing corrections, clarifications, or retractions as necessary.
- Corrections are published promptly to rectify errors and maintain the integrity of the scientific record.
Ethical Concerns:
Any concerns about ethical issues, such as research misconduct or violations of publication ethics, will be thoroughly investigated by the journal and appropriate actions will be taken.
5. Compliance with Policies and Guidelines:
All stakeholders are expected to comply with the journal’s policies, guidelines, and ethical standards, as well as relevant regulatory requirements and best practices in scholarly publishing.
Indexing and Abstracting
SciEngg Advances, while currently not indexed, is actively working towards being indexed in prominent databases and directories relevant to science, engineering, and related fields. Our aim is to ensure that the valuable research published in SciEngg Advances reaches a wide audience of scholars, researchers, and practitioners in the field. We are in the process of applying for indexing in key databases and directories to enhance the visibility and discoverability of articles published in our journal. Stay tuned for updates as we progress in our efforts to expand the indexing coverage of SciEngg Advances, thereby increasing its impact and reach within the scientific community.
Article Processing Charges
At present, there are no article processing charges (APCs) associated with publishing in SciEngg Advances. As an open-access journal, all articles are published free of cost to authors. The publisher covers the expenses incurred in the publication process, allowing authors to disseminate their research without any financial burden. There are no fees for submission, processing, or publication of articles in SciEngg Advances. This approach ensures equitable access to scientific knowledge and supports the dissemination of research findings across the global scientific community.
Special Issues
SciEngg Advances welcomes proposals for special issues that align with the journal’s scope and objectives. Special issues provide an opportunity to delve into specific topics or emerging areas within science, engineering, technology, and related fields, offering a focused platform for in-depth exploration and discussion.
If you have a proposal for a special issue, please submit it to the editorial office for consideration. Your proposal should include a brief outline of the proposed topic, its significance and relevance to the field, potential contributors, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Once your proposal is received, it will undergo careful evaluation by the editorial team to assess its suitability for publication in SciEngg Advances. If approved, you will be invited to serve as a guest editor or co-editor for the special issue, working closely with the editorial team to oversee the review and publication process.
We look forward to receiving your proposals and collaborating with you to bring forth exciting and impactful special issues for our readership.
Please submit the special issue proposal at: info@aristonpubs.com
Conferences
SciEngg Advances welcomes the opportunity to collaborate with organizers of conferences, symposiums, and workshops to publish special issues or proceedings featuring research articles presented at these events.
If you are organizing a conference or similar academic gathering and wish to publish selected research papers in SciEngg Advances, we encourage you to reach out to our editorial office with your proposal. Your proposal should include details such as the theme and scope of the conference, the number of anticipated submissions, and a proposed timeline for publication.
Upon receiving your proposal, our editorial team will review it carefully to assess its alignment with the journal’s scope and objectives. If approved, we will work closely with you to facilitate the submission and review process for the conference papers, ensuring timely publication in a dedicated special issue or proceeding.
By publishing conference-related research in SciEngg Advances, authors can benefit from the journal’s wide readership and open access model, maximizing the visibility and impact of their work within the science, engineering, and technology community. We look forward to the opportunity to collaborate with you on showcasing cutting-edge research from your conference in our journal.
For any inquiries, please contact us at: info@aristonpubs.com
Article in Press
Current Issue
Solar Light–Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Brilliant Cresyl Blue and Malachite Green Dyes Using Sulfur–Doped Graphitic Carbon Nitride (S-g-C₃N₄)
Suneel, Neda Tabassum, Devendra Pratap Mishra, Moonish Aftab
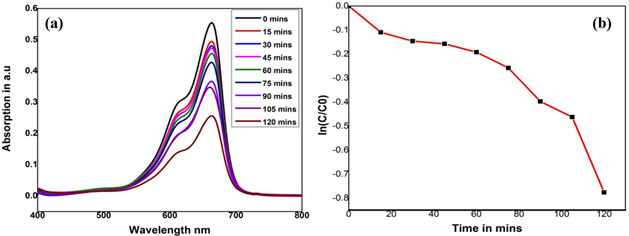
Summary: S-g-C₃N₄ was synthesized via thermal polymerization of thiourea and characterized using FTIR and XRD. The photocatalyst exhibited 64.86% and 81.28% degradation of Brilliant Cresyl Blue and Malachite Green, respectively, under solar irradiation, following pseudo-first-order kinetics. Enhanced activity was attributed to sulfur doping, which improved charge separation and light absorption. The study presents a promising, eco-friendly approach for dye wastewater remediation, emphasizing the potential of S-g-C₃N₄ for large-scale environmental applications under natural sunlight.

Research Article | PUBLISHED ONLINE: 17 March 2025
SciEngg Advances 2(2), 78-85 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.69626/sea.2025.0078